Macro-economic Thinking and the Market Economy
... the first, the neo-Ricardians, led in Cambridge (England) by Professors Joan Robinson, Piero SrafFa, and Nicholas Kaldor, and the second, the neo-classical school, represented mainly by Professors Paul Samuelson, Robert Solow and Sir John Hicks. In a recent article1 Professor James Tobin is highly c ...
... the first, the neo-Ricardians, led in Cambridge (England) by Professors Joan Robinson, Piero SrafFa, and Nicholas Kaldor, and the second, the neo-classical school, represented mainly by Professors Paul Samuelson, Robert Solow and Sir John Hicks. In a recent article1 Professor James Tobin is highly c ...
SCHOOLS OF ECONOMIC THOUGHT A BRIEF HISTORY OF
... The Neoclassicals won a complete and final victory over the Institutionalists in the 1930s. This was accomplished by the rise of econometrics, the application of new statistical tools to economic analysis. Econometrics allowed the Neoclassicals to finally test their theories against economic data. ...
... The Neoclassicals won a complete and final victory over the Institutionalists in the 1930s. This was accomplished by the rise of econometrics, the application of new statistical tools to economic analysis. Econometrics allowed the Neoclassicals to finally test their theories against economic data. ...
Measuring business profits: economists versus accountants
... Periodicity lends meaning and significance to the organism of a firm. Both economic theory and ...
... Periodicity lends meaning and significance to the organism of a firm. Both economic theory and ...
The Industrial Revolution and the Demographic Transition
... services requires two inputs. The first is labor. The total quantity of labor used by a business is measured as the number of workers times the average hours worked by each. A rise in the quantity of labor, either because there are more workers or because they work longer hours, increases the total ...
... services requires two inputs. The first is labor. The total quantity of labor used by a business is measured as the number of workers times the average hours worked by each. A rise in the quantity of labor, either because there are more workers or because they work longer hours, increases the total ...
PDF
... In terms of the question that originally brought together Russian and American authors of this paper - that is, the selection of the most appropriate U.S. textbook for use in Russia one existing text stood out in its realism, awareness of environmental and social issues, and clear presentation of bo ...
... In terms of the question that originally brought together Russian and American authors of this paper - that is, the selection of the most appropriate U.S. textbook for use in Russia one existing text stood out in its realism, awareness of environmental and social issues, and clear presentation of bo ...
The Specific-Factors Model: HO Model in the Short Run
... bundles are released with higher K/L ratio then that needed to produce good X (since X is labor-intensive). As a result, both goods are produced with higher K/L ratio, which results in higher real return to labor and lower real return to capital. The free mobility of factors ...
... bundles are released with higher K/L ratio then that needed to produce good X (since X is labor-intensive). As a result, both goods are produced with higher K/L ratio, which results in higher real return to labor and lower real return to capital. The free mobility of factors ...
Economic Costs and Consequences of War
... Note that in this case, only the warring countries are assumed to be affected. Yet generally, wars will have an impact on the international community at large. As such, the social cost of war is greater than the private cost since the war leads to what may be termed a negative externality on the wor ...
... Note that in this case, only the warring countries are assumed to be affected. Yet generally, wars will have an impact on the international community at large. As such, the social cost of war is greater than the private cost since the war leads to what may be termed a negative externality on the wor ...
Binary Economics: The Economic Theory that Gave Rise
... living expenses, Kelso proposed an approach to capital acquisition that does not require workers to use their current labor income either but rather enables them to acquire capital using the future income of the capital acquired just as wealthy people are presently able to do. Binary economists main ...
... living expenses, Kelso proposed an approach to capital acquisition that does not require workers to use their current labor income either but rather enables them to acquire capital using the future income of the capital acquired just as wealthy people are presently able to do. Binary economists main ...
lecture7_j_profit_revenu [režim kompatibility]
... determined by comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost. Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling one more unit of output. Profit is maximized at the output level where marginal revenue and marginal cost are ...
... determined by comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost. Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling one more unit of output. Profit is maximized at the output level where marginal revenue and marginal cost are ...
Firms, Resources and Production Functions
... To return for a moment to the context of economic growth in the aggregate, two broad empirical observations feature in the literature as being important in stimulating economists to reexamine the traditional categorizations (Lucas 1990, Romer 1994). The first is the lack of convergence between rich ...
... To return for a moment to the context of economic growth in the aggregate, two broad empirical observations feature in the literature as being important in stimulating economists to reexamine the traditional categorizations (Lucas 1990, Romer 1994). The first is the lack of convergence between rich ...
BASIC CONCEPTS OF ECONOMICS
... – Individuals may try to maximize utility given the constraints of income, time, prices, etc. – Firms may have objectives such as the maximization of profits, sales, market share, etc. or the minimization of costs per unit – Social objective, maximize the well being of the members of society ...
... – Individuals may try to maximize utility given the constraints of income, time, prices, etc. – Firms may have objectives such as the maximization of profits, sales, market share, etc. or the minimization of costs per unit – Social objective, maximize the well being of the members of society ...
Economic growth and human capital accumulation: a discrete
... human factor may well have a higher payoff in terms of increased output than does any other input, and find evidence supporting that higher levels of human capital contribute to reduce income inequality and improve living standards -Gunder Frank (1960), Lucas (1988), Glomm and Ravikumar (1992), Rome ...
... human factor may well have a higher payoff in terms of increased output than does any other input, and find evidence supporting that higher levels of human capital contribute to reduce income inequality and improve living standards -Gunder Frank (1960), Lucas (1988), Glomm and Ravikumar (1992), Rome ...
Profit Maximization
... and Marginal Cost • The Profit maximizing quantity of output can be determined by comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost. • Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. • Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling one more unit of output. • Profit is ...
... and Marginal Cost • The Profit maximizing quantity of output can be determined by comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost. • Marginal cost is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. • Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling one more unit of output. • Profit is ...
John Milios
... considered such cases to be ‘exceptions’ from the ‘law of value’. However, Robert Malthus commented (in 1822) that these exceptions: ‘are both theoretically and practically so considerable as entirely to destroy the position that commodities exchange with each other according to the quantity of labo ...
... considered such cases to be ‘exceptions’ from the ‘law of value’. However, Robert Malthus commented (in 1822) that these exceptions: ‘are both theoretically and practically so considerable as entirely to destroy the position that commodities exchange with each other according to the quantity of labo ...
Ecological Economics
... or a person who lives in balance with the environment; The way in which nature itself is valued, whether in monetary or biophysical terms; Judgements about the relationship between sustainable development and growth; The extent to which economics should be considered as a scientific study; Differing ...
... or a person who lives in balance with the environment; The way in which nature itself is valued, whether in monetary or biophysical terms; Judgements about the relationship between sustainable development and growth; The extent to which economics should be considered as a scientific study; Differing ...
Profit Maximization Profit Maximization Profit
... MC = ∆TC/∆Q • Comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost determines whether the firm needs to supply more or less in order to maximize profit. ...
... MC = ∆TC/∆Q • Comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost determines whether the firm needs to supply more or less in order to maximize profit. ...
The Methodology of Profit Maximization: An Austrian
... Of course, the firm to which this assumption holds is what Hirshleifer calls “an artificial entity created in response to economic incentives,” but nonetheless, it is the subject of much study and speculation. This is hardly to say the issue truly is settled, at least within some quarters of the eco ...
... Of course, the firm to which this assumption holds is what Hirshleifer calls “an artificial entity created in response to economic incentives,” but nonetheless, it is the subject of much study and speculation. This is hardly to say the issue truly is settled, at least within some quarters of the eco ...
Key
... labor and how much to increase (increase, decrease) the use of capital and materials? (Note that the price of labor is $8 per unit (hour) and the price of materials is $4 per unit and the price of capital is $16 per unit.) Total cost is the price of capital times the amount of capital used, plus the ...
... labor and how much to increase (increase, decrease) the use of capital and materials? (Note that the price of labor is $8 per unit (hour) and the price of materials is $4 per unit and the price of capital is $16 per unit.) Total cost is the price of capital times the amount of capital used, plus the ...
Chapter 10 - Pegasus @ UCF
... – Decreasing: output changes less than proportionate to the change in the inputs ...
... – Decreasing: output changes less than proportionate to the change in the inputs ...
Total costs
... • The nature of the supply decision varies with the relevant time frame. • The short-run production decision is the selection of the short-run rate of output (with existing plant and equipment). • The short run is characterized by the existence of fixed costs. ...
... • The nature of the supply decision varies with the relevant time frame. • The short-run production decision is the selection of the short-run rate of output (with existing plant and equipment). • The short run is characterized by the existence of fixed costs. ...
`Classical` vs. `Neoclassical` Theories of Value and Distribution and
... How to analyse such a highly complex system? The ingenious device of the classical authors to see through these complexities and intricacies consisted of distinguishing between market or actual values of the relevant variables, in particular the prices of commodities and the rates of remuneration o ...
... How to analyse such a highly complex system? The ingenious device of the classical authors to see through these complexities and intricacies consisted of distinguishing between market or actual values of the relevant variables, in particular the prices of commodities and the rates of remuneration o ...
Response to a Skeptic - Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis
... equilibrium response to technology shocks as predicted by the neoclassical growth model. I do not argue that disruptions in the payment and credit system would not disrupt the economy. That theory predicts one factor has a particular nature and magnitude does not imply that theory predicts all other ...
... equilibrium response to technology shocks as predicted by the neoclassical growth model. I do not argue that disruptions in the payment and credit system would not disrupt the economy. That theory predicts one factor has a particular nature and magnitude does not imply that theory predicts all other ...
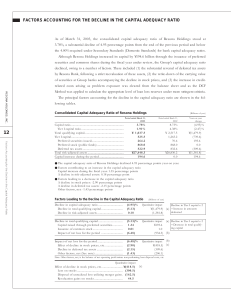
factors accounting for the decline in the capital adequacy ratio
... 3.78%, a substantial decline of 4.95 percentage points from the end of the previous period and below the 4.00% required under Secondary Standards (Domestic Standards) for bank capital adequacy ratios. Although Resona Holdings increased its capital by ¥194.6 billion through the issuance of preferred ...
... 3.78%, a substantial decline of 4.95 percentage points from the end of the previous period and below the 4.00% required under Secondary Standards (Domestic Standards) for bank capital adequacy ratios. Although Resona Holdings increased its capital by ¥194.6 billion through the issuance of preferred ...
Interest and the Marginal Product of Capital: Böhm
... writers suggested that the orthodox theory proceeded in a vicious circle, because (unlike labor) there was really no such thing as units of abstract "capital"; the only way to amalgamate heterogeneous units of physical machinery, factories, and goods in process into a single number, was to sum their ...
... writers suggested that the orthodox theory proceeded in a vicious circle, because (unlike labor) there was really no such thing as units of abstract "capital"; the only way to amalgamate heterogeneous units of physical machinery, factories, and goods in process into a single number, was to sum their ...








![lecture7_j_profit_revenu [režim kompatibility]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002692681_1-f62cf6a04f649c7064660697b3d517aa-300x300.png)