File
... Divisibility tests These are simple tricks to test what a number can be shared by . We are going to learn tricks for testing if a number can be shared by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, and multiples of 10. ...
... Divisibility tests These are simple tricks to test what a number can be shared by . We are going to learn tricks for testing if a number can be shared by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, and multiples of 10. ...
Prime, Composite, Divisibility and Square Numbers
... If one whole number is divisible by another number, then the second number is a factor of the first number. Since 18 is divisible by 9, 9 is a factor of 18. A divisibility test is a rule for determining whether one whole number is divisible by another. It is a quick way to find factors of large numb ...
... If one whole number is divisible by another number, then the second number is a factor of the first number. Since 18 is divisible by 9, 9 is a factor of 18. A divisibility test is a rule for determining whether one whole number is divisible by another. It is a quick way to find factors of large numb ...
Prime, Composite, Divisibility and Square Numbers
... If one whole number is divisible by another number, then the second number is a factor of the first number. Since 18 is divisible by 9, 9 is a factor of 18. A divisibility test is a rule for determining whether one whole number is divisible by another. It is a quick way to find factors of large numb ...
... If one whole number is divisible by another number, then the second number is a factor of the first number. Since 18 is divisible by 9, 9 is a factor of 18. A divisibility test is a rule for determining whether one whole number is divisible by another. It is a quick way to find factors of large numb ...
Positive/Negative and Odd/Even Functions
... Remarks: If any argument is nonnumeric, GCD returns the #VALUE! error value. If any argument is less than zero, GCD returns the #NUM! error value. One divides any value evenly. A prime number has only itself and one as even divisors. Examples: GCD(5, 2) equals 1 GCD(24, 36) equals 12 GCD(7, 1) equal ...
... Remarks: If any argument is nonnumeric, GCD returns the #VALUE! error value. If any argument is less than zero, GCD returns the #NUM! error value. One divides any value evenly. A prime number has only itself and one as even divisors. Examples: GCD(5, 2) equals 1 GCD(24, 36) equals 12 GCD(7, 1) equal ...
Non Calculator Arithmetic
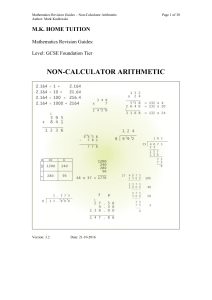
... f) If we try to move the decimal point three places to the right, we seem to ‘run out’, as multiplying 1.95 by 100 gives us 195, which is a whole number. We still have to multiply by another 10, so we must use the ‘whole number’ method and insert an extra 0 on the end, so 1.95 1000 = 1950. g) We c ...
... f) If we try to move the decimal point three places to the right, we seem to ‘run out’, as multiplying 1.95 by 100 gives us 195, which is a whole number. We still have to multiply by another 10, so we must use the ‘whole number’ method and insert an extra 0 on the end, so 1.95 1000 = 1950. g) We c ...
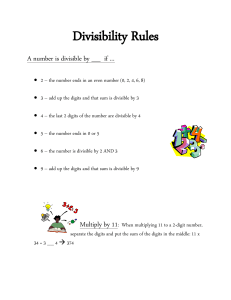
Divisibility Rules - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
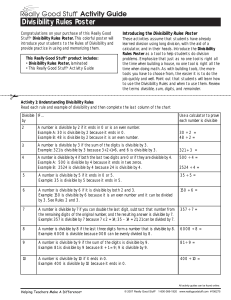
... From the divisibility rule for 5 we know the number must end in a 5 or 0. From the divisibility rule for 9 we know the sum of the digits must be divisible by 9. If we guess the last digit is 0 then the first digit or first two digits must add to 9. 90 does not work because the number must be great ...
... From the divisibility rule for 5 we know the number must end in a 5 or 0. From the divisibility rule for 9 we know the sum of the digits must be divisible by 9. If we guess the last digit is 0 then the first digit or first two digits must add to 9. 90 does not work because the number must be great ...
Parity of zero
Zero is an even number. In other words, its parity—the quality of an integer being even or odd—is even. The simplest way to prove that zero is even is to check that it fits the definition of ""even"": it is an integer multiple of 2, specifically 0 × 2. As a result, zero shares all the properties that characterize even numbers: 0 is divisible by 2, 0 is neighbored on both sides by odd numbers, 0 is the sum of an integer (0) with itself, and a set of 0 objects can be split into two equal sets.Zero also fits into the patterns formed by other even numbers. The parity rules of arithmetic, such as even − even = even, require 0 to be even. Zero is the additive identity element of the group of even integers, and it is the starting case from which other even natural numbers are recursively defined. Applications of this recursion from graph theory to computational geometry rely on zero being even. Not only is 0 divisible by 2, it is divisible by every power of 2, which is relevant to the binary numeral system used by computers. In this sense, 0 is the ""most even"" number of all.Among the general public, the parity of zero can be a source of confusion. In reaction time experiments, most people are slower to identify 0 as even than 2, 4, 6, or 8. Some students of mathematics—and some teachers—think that zero is odd, or both even and odd, or neither. Researchers in mathematics education propose that these misconceptions can become learning opportunities. Studying equalities like 0 × 2 = 0 can address students' doubts about calling 0 a number and using it in arithmetic. Class discussions can lead students to appreciate the basic principles of mathematical reasoning, such as the importance of definitions. Evaluating the parity of this exceptional number is an early example of a pervasive theme in mathematics: the abstraction of a familiar concept to an unfamiliar setting.