NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS
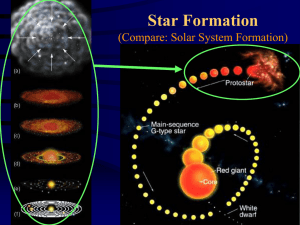
... and becomes warmer near the center. ⦿ When the center reaches about 10,000 degrees Celsius (about 18,000 degrees F) and hydrogen fusion begins, a STAR is born. ...
... and becomes warmer near the center. ⦿ When the center reaches about 10,000 degrees Celsius (about 18,000 degrees F) and hydrogen fusion begins, a STAR is born. ...
Chapter 18 The Interstellar Medium
... Light from distant stars may pass through more than one nebula; it is often possible to sort out the spectra of the star and the nebulae. ...
... Light from distant stars may pass through more than one nebula; it is often possible to sort out the spectra of the star and the nebulae. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
Document
... dust clouds in space. • Since space is full of dust, the farther away stars are, the redder they look. • Enough dust and eventually all visible light is scattered or absorbed. ...
... dust clouds in space. • Since space is full of dust, the farther away stars are, the redder they look. • Enough dust and eventually all visible light is scattered or absorbed. ...
Star Formation - University of Redlands
... dust clouds in space. • Since space is full of dust, the farther away stars are, the redder they look. • Enough dust and eventually all visible light is scattered or absorbed. ...
... dust clouds in space. • Since space is full of dust, the farther away stars are, the redder they look. • Enough dust and eventually all visible light is scattered or absorbed. ...
Star Formation - University of Redlands
... a. it is hot and things that are hot glow red. b. it is ionized hydrogen which appears red because the brightest emission line is red. c. it is cold and things that are cold appear red. d. it is full of red stars. e. dust between the observer and the region blocks the blue light, but lets the red li ...
... a. it is hot and things that are hot glow red. b. it is ionized hydrogen which appears red because the brightest emission line is red. c. it is cold and things that are cold appear red. d. it is full of red stars. e. dust between the observer and the region blocks the blue light, but lets the red li ...
Star Dust By the Rev. Tom Garrison
... There are some 59 elements in the human body that are also found on the earth’s crust. iv And scientists like Margaret Meixner say the “earth on which we stand is made almost entirely of ...
... There are some 59 elements in the human body that are also found on the earth’s crust. iv And scientists like Margaret Meixner say the “earth on which we stand is made almost entirely of ...
Superwind - The University of Sydney
... they are driven by minute dust grains, which form in the atmosphere of the star and absorb its light. The star light pushes the dust grains (silicates) away from the star. However, models show that this mechanism does not work well. The dust grains become too hot, and evaporate before they can be pu ...
... they are driven by minute dust grains, which form in the atmosphere of the star and absorb its light. The star light pushes the dust grains (silicates) away from the star. However, models show that this mechanism does not work well. The dust grains become too hot, and evaporate before they can be pu ...
Solar System
... Solar System Notes – Part 1 Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one ...
... Solar System Notes – Part 1 Universe: all of space and ________________________________________________ Galaxy: A large group of __________________________________, solar systems, and associated gas and dust in space that is bound by _____________________________ Solar System: Composed of one ...
May 2015
... As everything expanded, gases and dust that were close to each other were attracted, and clumped together by the force of gravity to form galaxies, stars and planetary systems, comets and other celestial objects. Very large stars live a relatively short time and die in massive, cataclysmic explosion ...
... As everything expanded, gases and dust that were close to each other were attracted, and clumped together by the force of gravity to form galaxies, stars and planetary systems, comets and other celestial objects. Very large stars live a relatively short time and die in massive, cataclysmic explosion ...
powerpoint version
... Measurements on HH1 and HH2 showed they were coming from a common source. In between was a T Tauri star, buried in the ISM, visible only in the infrared. PHYS1142 ...
... Measurements on HH1 and HH2 showed they were coming from a common source. In between was a T Tauri star, buried in the ISM, visible only in the infrared. PHYS1142 ...
Cosmic dust

Cosmic dust is dust which exists in space. It is for the most part a type of small dust particles which are a few molecules to 0.1 µm in size. A smaller fraction of all dust in space consists of larger refractory minerals that condensed as matter left the stars. It is called ""stardust"" and is included in a separate section below. The dust density in the local interstellar medium of the Local Bubble is approximately 10−6 × dust grain/m3 with each grain having a mass of approximately 10−17 kg.Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust (such as in the zodiacal cloud) and circumplanetary dust (such as in a planetary ring). In the Solar System, interplanetary dust causes the zodiacal light. Sources of Solar System dust include comet dust, asteroidal dust, dust from the Kuiper belt, and interstellar dust passing through the Solar System. The terminology has no specific application for describing materials found on the planet Earth except for dust that has demonstrably fallen to Earth. By one estimate, as much as 40,000 tons of cosmic dust reaches the Earth's surface every year. In October 2011, scientists reported that cosmic dust contains complex organic matter (""amorphous organic solids with a mixed aromatic–aliphatic structure"") that could be created naturally, and rapidly, by stars.On August 14, 2014, scientists announced the collection of possible interstellar dust particles from the Stardust spacecraft since returning to Earth in 2006.