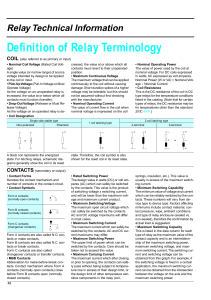
electrical machines ii - SK Engineering Academy
... The winding factor kw is defined as the ratio of phasor addition of emf induced in all the coils of each phase winding to their arithmetic addition of emf’s. 9. Why are Alternators rated in kVA and not in kW? The continuous power rating of any machine is generally defined as the power of the machine ...
... The winding factor kw is defined as the ratio of phasor addition of emf induced in all the coils of each phase winding to their arithmetic addition of emf’s. 9. Why are Alternators rated in kVA and not in kW? The continuous power rating of any machine is generally defined as the power of the machine ...
S230-55-1
... capacitor units. 5. For capacitor banks with units containing discharge resistors designed to discharge the capacitor unit from peak rated voltage to less than 50 V in five (5) minutes, wait at least five (5) minutes before re-energizing the bank after it has been disconnected from the system. For c ...
... capacitor units. 5. For capacitor banks with units containing discharge resistors designed to discharge the capacitor unit from peak rated voltage to less than 50 V in five (5) minutes, wait at least five (5) minutes before re-energizing the bank after it has been disconnected from the system. For c ...
DIY Ballast Training - Universal Lighting Technologies
... Universal’s HID product line covers more lamp types and lamp wattages than most of our competitors. It is interesting to see the “holes” in competitor’s lines where they are limited or have no offering. ...
... Universal’s HID product line covers more lamp types and lamp wattages than most of our competitors. It is interesting to see the “holes” in competitor’s lines where they are limited or have no offering. ...
BD6586MUV
... and output voltage is kept invariably. As for the inputs of the PWM comparator as the feature of the PWM current mode, one is overlapped with error components from the error amplifier, and the other is overlapped with a current sense signal that controls the inductor current into Slope waveform to p ...
... and output voltage is kept invariably. As for the inputs of the PWM comparator as the feature of the PWM current mode, one is overlapped with error components from the error amplifier, and the other is overlapped with a current sense signal that controls the inductor current into Slope waveform to p ...
Chap 2
... CD = T I/Vt = TT I/Vt diffusion cap EX IF a Diode is forward biased by a ID = 0.1mA current find the small signal ac model for a the diode the on voltage (VDQ) across the diode. Assume a Si diode with n=N=1, TT= 27.5nS, CJ0 = 8.3pFd and Is= IS= 2fA rd = nVt /I = 25mV/0.1mA = 250 ohms CD = (27.5nS) ...
... CD = T I/Vt = TT I/Vt diffusion cap EX IF a Diode is forward biased by a ID = 0.1mA current find the small signal ac model for a the diode the on voltage (VDQ) across the diode. Assume a Si diode with n=N=1, TT= 27.5nS, CJ0 = 8.3pFd and Is= IS= 2fA rd = nVt /I = 25mV/0.1mA = 250 ohms CD = (27.5nS) ...
Investigation of PWM-controlled MOSFET with inductive load
... Unclamped inductive switching is the case when for example switching a MOSFET in a circuit with an inductive load. Unclamped switching means that there is no freewheeling diode to discharge the energy through when the device is turned off. Instead all the energy is dissipated in the device, which in ...
... Unclamped inductive switching is the case when for example switching a MOSFET in a circuit with an inductive load. Unclamped switching means that there is no freewheeling diode to discharge the energy through when the device is turned off. Instead all the energy is dissipated in the device, which in ...
st_diode_10
... – Below a certain difference in potential between the two leads, the depletion layer has significant width, and the diode can be thought of as an open (non-conductive) circuit. – As the potential difference is increased, at some stage the diode will become conductive and allow charges to flow, at wh ...
... – Below a certain difference in potential between the two leads, the depletion layer has significant width, and the diode can be thought of as an open (non-conductive) circuit. – As the potential difference is increased, at some stage the diode will become conductive and allow charges to flow, at wh ...
Deney3
... output voltage and be capable of dissipating the power that results when RL is very large. This type of regulator is generally not good for output voltages less than 5 volts or so because low voltage diodes with a sharp knee at reverse breakdown are not available. The difference between VS and Vout ...
... output voltage and be capable of dissipating the power that results when RL is very large. This type of regulator is generally not good for output voltages less than 5 volts or so because low voltage diodes with a sharp knee at reverse breakdown are not available. The difference between VS and Vout ...
Three-Phase Induction Motor Operating from Single
... phase voltages at all motor speeds. It can be shown that ideally the capacitor should be varied continuously with the speed of the machine, but in practice the choice is limited to two set capacitor values, as in the case of split-phase motors, one is used for starting period to increase the startin ...
... phase voltages at all motor speeds. It can be shown that ideally the capacitor should be varied continuously with the speed of the machine, but in practice the choice is limited to two set capacitor values, as in the case of split-phase motors, one is used for starting period to increase the startin ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.