Unit I: Electrostatics -Chapter–1: Electric Charges and Fields
... 7. To estimate the charge induced on each one of the two identical styrofoam (or pith) balls suspended in a vertical plane by making use of Coulomb's law. 8. To set up a common base transistor circuit and to study its input and output characteristic and to calculate its current gain. 9. To study the ...
... 7. To estimate the charge induced on each one of the two identical styrofoam (or pith) balls suspended in a vertical plane by making use of Coulomb's law. 8. To set up a common base transistor circuit and to study its input and output characteristic and to calculate its current gain. 9. To study the ...
Announcements l Help room hours (1248 BPS) LON-CAPA #7 due Oct. 25
... l So it’s not a magnetic field that creates an electric current; it’s a changing magnetic field l And not the magnetic field per se, but the magnetic flux ◆ just think of the flux as the number of magnetic field lines going through a loop ...
... l So it’s not a magnetic field that creates an electric current; it’s a changing magnetic field l And not the magnetic field per se, but the magnetic flux ◆ just think of the flux as the number of magnetic field lines going through a loop ...
Chapter 13: Magnetically Coupled Circuit
... community a detailed model of light as an electromagnetic phenomenon, building upon the earlier hypothesis advanced by Faraday. ...
... community a detailed model of light as an electromagnetic phenomenon, building upon the earlier hypothesis advanced by Faraday. ...
Biot-Savart law
... In which the magnetic flux density (or magnetic induction) in free space is: and where the free space permeability is ...
... In which the magnetic flux density (or magnetic induction) in free space is: and where the free space permeability is ...
Magnetic field probe.indd
... being used to find the magnetic field strength of a speaker. By placing the probe in different parts of the speakers coil, the magnetic field strength of the speaker’s magnet can be found. ...
... being used to find the magnetic field strength of a speaker. By placing the probe in different parts of the speakers coil, the magnetic field strength of the speaker’s magnet can be found. ...
Physics 12 Electromagnetic Induction
... This sudden increase in magnetic field strength causes a current to be induced momentarily in the secondary coil. Once the current in the primary coil is steady and the magnetic field in the iron ring is established, the induced current no longer exists. If the switch is then opened, the iron ring b ...
... This sudden increase in magnetic field strength causes a current to be induced momentarily in the secondary coil. Once the current in the primary coil is steady and the magnetic field in the iron ring is established, the induced current no longer exists. If the switch is then opened, the iron ring b ...
BASIC ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY (ELE 101/102)
... (ii) Using Node voltage method, determine the power dissipated in 6 resistance. A 10 V battery is switched on to a series RL circuit at time t = 0. The circuit components are 50 and 10 mH. Calculate the circuit current and voltage across inductor at 0.15 milli second after switching. A magnetic circ ...
... (ii) Using Node voltage method, determine the power dissipated in 6 resistance. A 10 V battery is switched on to a series RL circuit at time t = 0. The circuit components are 50 and 10 mH. Calculate the circuit current and voltage across inductor at 0.15 milli second after switching. A magnetic circ ...
Exercise 4
... until the middle of the 19th century, physicists widely believed that EM waves could exist in a vacuum. Further, they did not connect EM waves to light, even though some of them suspected that there would be a connection. The magnetic field of a coil of current-carrying wire Equipment needed: a coil ...
... until the middle of the 19th century, physicists widely believed that EM waves could exist in a vacuum. Further, they did not connect EM waves to light, even though some of them suspected that there would be a connection. The magnetic field of a coil of current-carrying wire Equipment needed: a coil ...
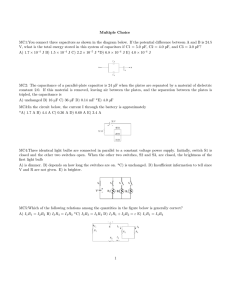
Multiple Choice MC1:You connect three capacitors as shown in the
... MC2: The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is 24 mF when the plates are separated by a material of dielectric constant 2.0. If this material is removed, leaving air between the plates, and the separation between the plates is tripled, the capacitance is A) unchanged B) 16 mF C) 36 mF D) 0.14 ...
... MC2: The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is 24 mF when the plates are separated by a material of dielectric constant 2.0. If this material is removed, leaving air between the plates, and the separation between the plates is tripled, the capacitance is A) unchanged B) 16 mF C) 36 mF D) 0.14 ...
Ch 29 Magnetic Fields due to Currents
... Key contents Biot-Savart law Ampere’s law The magnetic dipole field ...
... Key contents Biot-Savart law Ampere’s law The magnetic dipole field ...
Deflecting electron beams in a magnetic field
... gun and the coils, probably using a gimballed bar magnet to show the direction of the field. You will probably get a spread of circles, perhaps due to the field being non-uniform (a Helmholtz pair only produce an approximately uniform field in the central third of the volume they enclose), due to th ...
... gun and the coils, probably using a gimballed bar magnet to show the direction of the field. You will probably get a spread of circles, perhaps due to the field being non-uniform (a Helmholtz pair only produce an approximately uniform field in the central third of the volume they enclose), due to th ...
s040211-examII
... (ii) Hence derive an expression for the linear acceleration of the solid cylinder in terms of M, r, g and from (d)(i). (iii) Determine whether a similar hollow cylinder of the same mass M and radius r will roll down the inclined plane at a greater or smaller acceleration. Explain briefly. (7 marks ...
... (ii) Hence derive an expression for the linear acceleration of the solid cylinder in terms of M, r, g and from (d)(i). (iii) Determine whether a similar hollow cylinder of the same mass M and radius r will roll down the inclined plane at a greater or smaller acceleration. Explain briefly. (7 marks ...
IPC Final Exam Study Sheet
... 7. A toy car is traveling 12 m/s and has a mass of 50 kg. How much kinetic energy does the car have? ...
... 7. A toy car is traveling 12 m/s and has a mass of 50 kg. How much kinetic energy does the car have? ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.