L5 Magnets - Hookitup.ws
... Place the cork into a bowl of water. The cork will rotate to point towards the north. ...
... Place the cork into a bowl of water. The cork will rotate to point towards the north. ...
End of chapter exercises
... connected to the load via brushes. In an AC generator the two ends of the coil are each attached to a slip ring that makes contact with brushes as the coil turns. The direction of the current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic fi ...
... connected to the load via brushes. In an AC generator the two ends of the coil are each attached to a slip ring that makes contact with brushes as the coil turns. The direction of the current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic fi ...
Magnetism and Electricity - Bloomsburg Area School District
... • Working with your group, determine what happens when both of the poles on the magnet labeled “N” are touching, or both of the poles on the magnet labeled “S.” ...
... • Working with your group, determine what happens when both of the poles on the magnet labeled “N” are touching, or both of the poles on the magnet labeled “S.” ...
Charge-to-Mass Ratio of the Electron
... The Bainbridge apparatus will be used to measure the charge-to-mass ratio e/m of the electron. The apparatus consists of an evacuated glass chamber, containing an electron source and electrode plates for accelerating the electrons. A small amount of mercury vapor in the chamber is ionized by the pas ...
... The Bainbridge apparatus will be used to measure the charge-to-mass ratio e/m of the electron. The apparatus consists of an evacuated glass chamber, containing an electron source and electrode plates for accelerating the electrons. A small amount of mercury vapor in the chamber is ionized by the pas ...
Unit 10C Magnetism
... What orientation is angle 0o ? What is sin 0o equal to? What orientation is angle 90o ? What is sin 90o equal to? ...
... What orientation is angle 0o ? What is sin 0o equal to? What orientation is angle 90o ? What is sin 90o equal to? ...
No Slide Title
... What is an alternating current (AC)? What is an AC generator? What is an AC transformer? How to calculate a transformer’s expected step-up or step-down AC voltage? ...
... What is an alternating current (AC)? What is an AC generator? What is an AC transformer? How to calculate a transformer’s expected step-up or step-down AC voltage? ...
Using and making transformers - School
... 1. The PRIMARY coil is fed by high voltage AC from the mains. 2. This makes ALTERNATING MAGNETISM in the ‘soft’ iron cores. 3. The magnetism reaches the second half of the core. 4. An alternating VOLTAGE is INDUCED across the SECONDARY coil. 5. This voltage can then power another device with a new v ...
... 1. The PRIMARY coil is fed by high voltage AC from the mains. 2. This makes ALTERNATING MAGNETISM in the ‘soft’ iron cores. 3. The magnetism reaches the second half of the core. 4. An alternating VOLTAGE is INDUCED across the SECONDARY coil. 5. This voltage can then power another device with a new v ...
Chapter 16
... magnetic field of the electromagnet to make an electric current in a ____________ wire. Faraday realized that electric current in the _______________ wire was made only when the magnetic field was __________. The process by which an electric current is made by changing a magnetic field is called e ...
... magnetic field of the electromagnet to make an electric current in a ____________ wire. Faraday realized that electric current in the _______________ wire was made only when the magnetic field was __________. The process by which an electric current is made by changing a magnetic field is called e ...
Dilute magnetic semiconductors for spintronic applications.
... The field of dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) is currently one of intense activity. These materials are of great interest because of the novelty of their fundamental properties and also due to their potential as the basis of future semiconductor spintronic technologies which promise integration ...
... The field of dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) is currently one of intense activity. These materials are of great interest because of the novelty of their fundamental properties and also due to their potential as the basis of future semiconductor spintronic technologies which promise integration ...
Weekly Science Lesson Plans
... (light, sound, heat, electrical, and magnetic) as the ability to cause motion or create change. 4.P.1.2 Explain how electrically charged objects push or pull on other electrically charged objects and produce motion. ...
... (light, sound, heat, electrical, and magnetic) as the ability to cause motion or create change. 4.P.1.2 Explain how electrically charged objects push or pull on other electrically charged objects and produce motion. ...
notes
... The third term also is caused by a current, but not i1. This is evident by the fact that if we impress a voltage across the primary winding but leave the secondary open circuited (so that i1=(N2/N1)i2=0 because i2=0), we will still be able to measure a voltage across the ...
... The third term also is caused by a current, but not i1. This is evident by the fact that if we impress a voltage across the primary winding but leave the secondary open circuited (so that i1=(N2/N1)i2=0 because i2=0), we will still be able to measure a voltage across the ...
ir`H`/WE
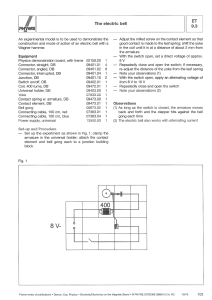
... Although the permanent load on the coil used is rated at maximally 1 A, the recommended voltage is not critical, because the current is repeatedly interrupted. Despite this, the bell should not be rung for longer than necessary, so that the area of contact of the contact screw with the leaf spring ( ...
... Although the permanent load on the coil used is rated at maximally 1 A, the recommended voltage is not critical, because the current is repeatedly interrupted. Despite this, the bell should not be rung for longer than necessary, so that the area of contact of the contact screw with the leaf spring ( ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.