Induced Voltage and Inductance
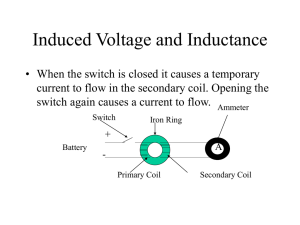
... magnetic field is produced. This in turn causes a temporary current to flow in the secondary coil. The ammeter reads only for a brief time and then returns to zero. • When the switch is opened the ammeter reads a current in the opposite direction for a brief moment, indicating a magnetic field in th ...
... magnetic field is produced. This in turn causes a temporary current to flow in the secondary coil. The ammeter reads only for a brief time and then returns to zero. • When the switch is opened the ammeter reads a current in the opposite direction for a brief moment, indicating a magnetic field in th ...
Circuit Improvements for the TL-922
... 1. The filament inrush-current is 48 peak amperes. This exceeds Eimac®'s maximum allowable rating for the 3-500Z. 2. When operated from a stiff 240vac source, the inrush-current through the on/off switch is so great that it will eventually cause switch failure. . 3. The filament-voltage is typically ...
... 1. The filament inrush-current is 48 peak amperes. This exceeds Eimac®'s maximum allowable rating for the 3-500Z. 2. When operated from a stiff 240vac source, the inrush-current through the on/off switch is so great that it will eventually cause switch failure. . 3. The filament-voltage is typically ...
Toy Transmitter Instruction Manual
... The loudspeaker (8 ohms) in this circuit works like a microphone. Microphone is a device which converts sound waves into electrical impulses (electrical currents). The microphone is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a small coil (voice coil) attached to a freely mov ...
... The loudspeaker (8 ohms) in this circuit works like a microphone. Microphone is a device which converts sound waves into electrical impulses (electrical currents). The microphone is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of a small coil (voice coil) attached to a freely mov ...
Physics 2 for Electrical Engineering Ben Gurion University of the Negev , www.bgu.ac.il/atomchip
... opposes the falling magnet, until the magnetic force exactly balances the force of gravity on the magnet, which falls with constant speed v. (b) Gravity, the only external force on this system, does work at the rate Mgv. By energy conservation, this must be the rate of heat dissipation in the tube. ...
... opposes the falling magnet, until the magnetic force exactly balances the force of gravity on the magnet, which falls with constant speed v. (b) Gravity, the only external force on this system, does work at the rate Mgv. By energy conservation, this must be the rate of heat dissipation in the tube. ...
Measurement of magnetic characteristics of transformer
... Measurement of magnetic characteristics of transformercores and coil materials Precision loss power measurement of sheet iron and ferrite cores with high signal frequency: exact, easy and in real-time! With the precision power meters ZES ZIMMER LMG95 and other LMG models it is possible to obtain the ...
... Measurement of magnetic characteristics of transformercores and coil materials Precision loss power measurement of sheet iron and ferrite cores with high signal frequency: exact, easy and in real-time! With the precision power meters ZES ZIMMER LMG95 and other LMG models it is possible to obtain the ...
Unit 4 Electrical Principles and Technologies - Topic 6
... Generators can also produce direct current (DC), or current in only one direction. A generator that produces direct current is often called a dynamo. In a dynamo, the armature (rotating loop of wire) is connected to the outside circuit by a split-ring commutator (Figure 4.38A). To visualize how the ...
... Generators can also produce direct current (DC), or current in only one direction. A generator that produces direct current is often called a dynamo. In a dynamo, the armature (rotating loop of wire) is connected to the outside circuit by a split-ring commutator (Figure 4.38A). To visualize how the ...
Unit 4 Electrical Principles and Technologies
... Generators can also produce direct current (DC), or current in only one direction. A generator that produces direct current is often called a dynamo. In a dynamo, the armature (rotating loop of wire) is connected to the outside circuit by a split-ring commutator (Figure 4.38A). To visualize how the ...
... Generators can also produce direct current (DC), or current in only one direction. A generator that produces direct current is often called a dynamo. In a dynamo, the armature (rotating loop of wire) is connected to the outside circuit by a split-ring commutator (Figure 4.38A). To visualize how the ...
The interaction of electrons with a uniform magnetic field. A... field couples to the electronic motion, and to the electron...
... Hund’s three rules determine the ground state(s) of the partially-filled ion. However, that ground state is still degenerate. Take for example, the case n = 2 in the Table. After applying Hund’s first and second rules, it has total spin S = 1 and total orbital angular momentum L = 3. This means tha ...
... Hund’s three rules determine the ground state(s) of the partially-filled ion. However, that ground state is still degenerate. Take for example, the case n = 2 in the Table. After applying Hund’s first and second rules, it has total spin S = 1 and total orbital angular momentum L = 3. This means tha ...
physics-igcse8
... • The downwards acceleration of an object is caused by gravity. This happens most when an object is in free fall (falling with nothing holding it up). Objects are slowed down by air resistance. Once air resistance is equal to the force of gravity, the object has reached terminal velocity. This means ...
... • The downwards acceleration of an object is caused by gravity. This happens most when an object is in free fall (falling with nothing holding it up). Objects are slowed down by air resistance. Once air resistance is equal to the force of gravity, the object has reached terminal velocity. This means ...
PHYSICS IGCSE 2012 EXAM REVISION NOTES
... • The downwards acceleration of an object is caused by gravity. This happens most when an object is in free fall (falling with nothing holding it up). Objects are slowed down by air resistance. Once air resistance is equal to the force of gravity, the object has reached terminal velocity. This means ...
... • The downwards acceleration of an object is caused by gravity. This happens most when an object is in free fall (falling with nothing holding it up). Objects are slowed down by air resistance. Once air resistance is equal to the force of gravity, the object has reached terminal velocity. This means ...
Magnetic Repulsion Piston Engine - International Journal of Science
... of individuals, more the requirement of automobiles to commute. Every year there are around 50 million automobiles being manufactured all over the world. This situation is very grim. With this rise in use of fossil fuels, there arises a need to switch to alternative sources of fuel, to drive our eng ...
... of individuals, more the requirement of automobiles to commute. Every year there are around 50 million automobiles being manufactured all over the world. This situation is very grim. With this rise in use of fossil fuels, there arises a need to switch to alternative sources of fuel, to drive our eng ...
Calculate Inductor AC Flux Density
... gap in the magnetic path: l = l m + μ l g where l m is the path length in the magnetic material and l g is the path length in the gap. Note that (3) looks very different from (1). If a voltage is applied across an inductor as in (1), you increase N to decrease B, but if the inductor current is fixed ...
... gap in the magnetic path: l = l m + μ l g where l m is the path length in the magnetic material and l g is the path length in the gap. Note that (3) looks very different from (1). If a voltage is applied across an inductor as in (1), you increase N to decrease B, but if the inductor current is fixed ...
PHYSICS Paper & Solution CBSE-XII-2014 EXAMINATION CAREER POINT
... (b) Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third Polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60º with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted t ...
... (b) Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity Io is incident on P1. A third Polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60º with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted t ...
III. Transverse and Radial Magnetic Field
... the light intensity emitted by the arc in points placed at 30 on the contact circumference were used 8 channels: there are 4 channels (Cxi, i=1÷4) for recording of the arc light intensity along the Ox direction and another 4 ones (Cyj, j=1÷4) for recording it along the Oy direction. The 8 signals a ...
... the light intensity emitted by the arc in points placed at 30 on the contact circumference were used 8 channels: there are 4 channels (Cxi, i=1÷4) for recording of the arc light intensity along the Ox direction and another 4 ones (Cyj, j=1÷4) for recording it along the Oy direction. The 8 signals a ...
Capacitors - Honors Physics Website (Blue 5)
... material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
... material (typically waxed paper) between them. This material is called a dielectric. ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.