StudyQuestions2
... 4. Where are intrusive (plutonic) and extrusive (volcanic) igneous rocks formed? 5 How is magma different from lava? How are magma and lava the same? 6. What are dikes and batholiths, and how are they formed? 7. How are the compositions of felsic and mafic rocks different? List three different ways ...
... 4. Where are intrusive (plutonic) and extrusive (volcanic) igneous rocks formed? 5 How is magma different from lava? How are magma and lava the same? 6. What are dikes and batholiths, and how are they formed? 7. How are the compositions of felsic and mafic rocks different? List three different ways ...
Characteristics of Igneous Rocks
... Pictured above are two pairs of igneous rocks ( Figures above and above). The first pair is two rocks that formed from a felsic magma. The rhyolite cooled rapidly, and the granite cooled slowly. The second pair is two rocks that formed from mafic magma. The basalt cooled rapidly, and the gabbro cool ...
... Pictured above are two pairs of igneous rocks ( Figures above and above). The first pair is two rocks that formed from a felsic magma. The rhyolite cooled rapidly, and the granite cooled slowly. The second pair is two rocks that formed from mafic magma. The basalt cooled rapidly, and the gabbro cool ...
Igneous Rocks
... volcano or fissure glassy holes from gas basaltic – dark color high % -iron -magnesium ...
... volcano or fissure glassy holes from gas basaltic – dark color high % -iron -magnesium ...
The Inter-relationship of Bulk Density and Porosity of
... were sampled and tested for their petrography (mineralogy, texture and microstructures), bulk density and porosity. ImageJ was used for image analysis of the photo-micrographs, the bulk density was calculated from the determined specific gravity while the porosity was determined by water saturation ...
... were sampled and tested for their petrography (mineralogy, texture and microstructures), bulk density and porosity. ImageJ was used for image analysis of the photo-micrographs, the bulk density was calculated from the determined specific gravity while the porosity was determined by water saturation ...
geology and mineral resources in the hopewell and bromide no. 2
... U-Th-REE veins, and placer gold deposits are found in the Hopewell and Bromide No. 2 mining districts in the northern Tusas Mountains in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico. The mineral deposits are found in Proterozoic rocks that can be divided into four assemblages, 1) Moppin Metavolcanic Complex, 2) Va ...
... U-Th-REE veins, and placer gold deposits are found in the Hopewell and Bromide No. 2 mining districts in the northern Tusas Mountains in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico. The mineral deposits are found in Proterozoic rocks that can be divided into four assemblages, 1) Moppin Metavolcanic Complex, 2) Va ...
`granitic` laver of the crust in the southern norwegian precambrian
... more granitic, a feature already noted by BoTT (1961). Definite evidence exists, therefore, for vertical compositional gradients that render the metamorphic rocks less dense (more granitic) with depth and the intrusive granites more dense. The effect is to decrease the density contrast between grani ...
... more granitic, a feature already noted by BoTT (1961). Definite evidence exists, therefore, for vertical compositional gradients that render the metamorphic rocks less dense (more granitic) with depth and the intrusive granites more dense. The effect is to decrease the density contrast between grani ...
UNIT 3 MINERALS, ROCKS, AND RESOURCES
... with the bottom layered being the oldest. 4. Fossils – Because of the absence of EXTREME heat and pressure, fossils will usually only be found in Sedimentary Rocks. IMPORTANT!!! The presence of fossils also provides evidence for the environment in which the rocks formed. Seashells would indicate a m ...
... with the bottom layered being the oldest. 4. Fossils – Because of the absence of EXTREME heat and pressure, fossils will usually only be found in Sedimentary Rocks. IMPORTANT!!! The presence of fossils also provides evidence for the environment in which the rocks formed. Seashells would indicate a m ...
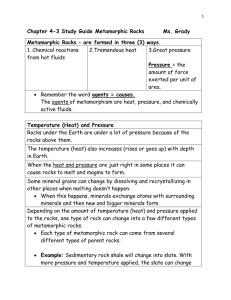
Temperature (Heat) and Pressure
... Fluids can react chemically with a rock and change its composition, especially when the fluids are HOT. Most fluids that transform (change) rocks during the metamorphic processes are HOT and mainly have water and carbon dioxide. Example: When seawater flows through hot igneous rock near the Mid-Atla ...
... Fluids can react chemically with a rock and change its composition, especially when the fluids are HOT. Most fluids that transform (change) rocks during the metamorphic processes are HOT and mainly have water and carbon dioxide. Example: When seawater flows through hot igneous rock near the Mid-Atla ...
Ch 11 rocks and minerals Practice Ques
... FRANCONIA, N.H. — Crowds of visitors were drawn to Franconia Notch on Sunday to mourn the loss of New Hampshire’s well-known symbol — the Old Man of the Mountain granite profile. The 700-ton natural formation was just a pile of rocks after breaking loose from its 1,200-foot-high mountainside pe ...
... FRANCONIA, N.H. — Crowds of visitors were drawn to Franconia Notch on Sunday to mourn the loss of New Hampshire’s well-known symbol — the Old Man of the Mountain granite profile. The 700-ton natural formation was just a pile of rocks after breaking loose from its 1,200-foot-high mountainside pe ...
Igneous Rocks Lab
... Igneous rocks are classified based on their mineral content and their texture. The rock color is a simple indicator of the mineral content. The dark colored rocks are rich in the metallic minerals that contain a high percentage of iron and magnesium. These dark colored igneous rocks are referred to ...
... Igneous rocks are classified based on their mineral content and their texture. The rock color is a simple indicator of the mineral content. The dark colored rocks are rich in the metallic minerals that contain a high percentage of iron and magnesium. These dark colored igneous rocks are referred to ...
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION The researched rocks outcrop in the
... secondary minerals form 10-15% portion of .the rock. Secondary quartz is less than 5% forming little xenomorph grains. Mafic minerals are do not occur or invisible. The laths of alkali feldspar of groundmass are only 10x70 (im long. The oriented sampling shows that the dyke material flowed from East ...
... secondary minerals form 10-15% portion of .the rock. Secondary quartz is less than 5% forming little xenomorph grains. Mafic minerals are do not occur or invisible. The laths of alkali feldspar of groundmass are only 10x70 (im long. The oriented sampling shows that the dyke material flowed from East ...
minerals of igneous rocks
... is black, shiny and often occurs in small hexagonal (6sided) books. Unfortunately, it is often confused with amphibole and pyroxene. Like muscovite, it is soft and has good cleavage. Try scratching the black grains with a nail or knife. Biotite will flake off easily. Biotite is differentiated from a ...
... is black, shiny and often occurs in small hexagonal (6sided) books. Unfortunately, it is often confused with amphibole and pyroxene. Like muscovite, it is soft and has good cleavage. Try scratching the black grains with a nail or knife. Biotite will flake off easily. Biotite is differentiated from a ...
There is a close connection between Geology and
... provided a wide variety of stone. It used to be the local availability of a particular rock type that dictated the building stone giving each area and county its own distinctive character of built heritage. The Mourne and Newry granites, the greywacke sandstone of Down and the black basalt of Antrim ...
... provided a wide variety of stone. It used to be the local availability of a particular rock type that dictated the building stone giving each area and county its own distinctive character of built heritage. The Mourne and Newry granites, the greywacke sandstone of Down and the black basalt of Antrim ...
Minerals of Igneous Rocks
... Olivine is always some shade of green. Lighter green indicates greater Mg content (and lower density), darker color more Fe (and higher density). Large crystals uncommon, almost always occurring as dominant or sole mineral in a rock, as small granular crystals. No cleavage – conchoidal fracture (lik ...
... Olivine is always some shade of green. Lighter green indicates greater Mg content (and lower density), darker color more Fe (and higher density). Large crystals uncommon, almost always occurring as dominant or sole mineral in a rock, as small granular crystals. No cleavage – conchoidal fracture (lik ...
Origin and metamorphic evolution of magnesite
... rarely observed relics and pseudomorphs of mica after andalusite and cordierite (Dianiška 1983; Faryad 1992), high-T minerals are not present in phyllitic rocks at the granite contact. The scarcity of these minerals is probably due to: 1) small size of granite bodies that could have produced only na ...
... rarely observed relics and pseudomorphs of mica after andalusite and cordierite (Dianiška 1983; Faryad 1992), high-T minerals are not present in phyllitic rocks at the granite contact. The scarcity of these minerals is probably due to: 1) small size of granite bodies that could have produced only na ...
What are Igneous Rocks
... Broad classification = Intrusive / Extrusive Further classification would include Chemical Composition and Texture ...
... Broad classification = Intrusive / Extrusive Further classification would include Chemical Composition and Texture ...
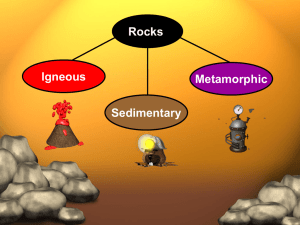
Rocks
... Compared to felsic magma, mafic magma is much hotter, thinner and faster moving. Mafic magma contains large amounts of iron and magnesium and very small amounts of silica. Rocks formed from mafic magma are much darker in color due to large amounts of dark silicate minerals such as biotite, augite, ...
... Compared to felsic magma, mafic magma is much hotter, thinner and faster moving. Mafic magma contains large amounts of iron and magnesium and very small amounts of silica. Rocks formed from mafic magma are much darker in color due to large amounts of dark silicate minerals such as biotite, augite, ...
Introduction to Petrology
... To determine the proportion of the elements in the Sun, we make use of the energy levels between the electron orbitals of the atoms of the different elements. The electromagnetic spectra of the Sun were noted to contain dark lines in 1802 by Wollaston and later studied by Fraunhofer (early 1800's), ...
... To determine the proportion of the elements in the Sun, we make use of the energy levels between the electron orbitals of the atoms of the different elements. The electromagnetic spectra of the Sun were noted to contain dark lines in 1802 by Wollaston and later studied by Fraunhofer (early 1800's), ...
How do you Interpret Clues in Rocks?
... rubbing a mineral gently but firmly on a streak plate. You can often see a streak that’s the same color as the mineral surface. However, pyrite is a yellow mineral. When you rub it on a streak plate, you see a thin trail of black powder. ...
... rubbing a mineral gently but firmly on a streak plate. You can often see a streak that’s the same color as the mineral surface. However, pyrite is a yellow mineral. When you rub it on a streak plate, you see a thin trail of black powder. ...
Deep-Seated Geology and Fracture System of the EGS Soultz
... 2.1 Petrographic characterization Because of the granite basement does not outcrop, its petrographic characterization has been determined only by well information, such as cores, cutting samples and welllogs. The upper part of the massif is well known because one well has been fully cored to 2200m d ...
... 2.1 Petrographic characterization Because of the granite basement does not outcrop, its petrographic characterization has been determined only by well information, such as cores, cutting samples and welllogs. The upper part of the massif is well known because one well has been fully cored to 2200m d ...
Rocks, Weathering and Erosion
... define and provide examples of weathering and erosion describe the three classes of rocks ...
... define and provide examples of weathering and erosion describe the three classes of rocks ...
diverse intrusive and volcanic rocks in the axis of the abandoned
... A fine- to medium-grained granite appears to cut the rhyolite and is in sharp intrusive contact with a medium- to coarse-grained gabbro, represented by both a typical and cumulate form. The combined thickness of the granite and both gabbros is 15m. The difference between the typical and cumulate gab ...
... A fine- to medium-grained granite appears to cut the rhyolite and is in sharp intrusive contact with a medium- to coarse-grained gabbro, represented by both a typical and cumulate form. The combined thickness of the granite and both gabbros is 15m. The difference between the typical and cumulate gab ...
the archean granites of mumias–kakamega
... magmas formed by partial melting of protoliths with short prior residence time in the crust thus the granitic crust underlying Tanzania and parts of Uganda and Kenya (with reference to western granites) formed about 2.8 Ga and 2.4 Ga. Huddlestone et al. (1959), states that the Archean Maragoli grani ...
... magmas formed by partial melting of protoliths with short prior residence time in the crust thus the granitic crust underlying Tanzania and parts of Uganda and Kenya (with reference to western granites) formed about 2.8 Ga and 2.4 Ga. Huddlestone et al. (1959), states that the Archean Maragoli grani ...
Section 3.2 Igneous Rocks
... composed primarily of quartz and feldspar have a granitic true composition. Rocks that contain dark silicate minerals and plagioclase feldspar have a(n) basaltic composition . Circle the letters of the minerals that are found in andesitic rocks. a. amphibole b. pyroxene c. biotite d. plagioclase fel ...
... composed primarily of quartz and feldspar have a granitic true composition. Rocks that contain dark silicate minerals and plagioclase feldspar have a(n) basaltic composition . Circle the letters of the minerals that are found in andesitic rocks. a. amphibole b. pyroxene c. biotite d. plagioclase fel ...
Igneous Rocks - cloudfront.net
... composed primarily of quartz and feldspar have a granitic composition. Rocks that contain dark silicate minerals and plagioclase feldspar have a(n) ...
... composed primarily of quartz and feldspar have a granitic composition. Rocks that contain dark silicate minerals and plagioclase feldspar have a(n) ...
Granite
Granite /ˈɡrænɨt/ is a common type of felsic intrusive igneous rock that is granular and phaneritic in texture. Granites can be predominantly white, pink, or gray in color, depending on their mineralogy. The word ""granite"" comes from the Latin granum, a grain, in reference to the coarse-grained structure of such a holocrystalline rock. By definition, granite is an igneous rock with at least 20% quartz and up to 65% alkali feldspar by volume.The term ""granitic"" means granite-like and is applied to granite and a group of intrusive igneous rocks with similar textures and slight variations on composition and origin. These rocks mainly consist of feldspar, quartz, mica, and amphibole minerals, which form interlocking, somewhat equigranular matrix of feldspar and quartz with scattered darker biotite mica and amphibole (often hornblende) peppering the lighter color minerals. Occasionally some individual crystals (phenocrysts) are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic texture is known as a granite porphyry. Granitoid is a general, descriptive field term for lighter-colored, coarse-grained igneous rocks. Petrographic examination is required for identification of specific types of granitoids.Granite differs from granodiorite in that at least 35% of the feldspar in granite is alkali feldspar as opposed to plagioclase; it is the potassium feldspar that gives many granites a distinctive pink color. The extrusive igneous rock equivalent of granite is rhyolite.Granite is nearly always massive (lacking any internal structures), hard and tough, and therefore it has gained widespread use throughout human history, and more recently as a construction stone. The average density of granite is between 2.65 and 2.75 g/cm3, its compressive strength usually lies above 200 MPa, and its viscosity near STP is 3–6 • 1019 Pa·s.Melting temperature of dry granite at ambient pressure is or 1215–1260 °C (2219–2300 °F); it is strongly reduced in the presence of water, down to 650 °C at a few kBar pressure.Granite has poor primary permeability, but strong secondary permeability.The rock known as ""black granite"" is usually gabbro.