Slide 1
... Oracle In-Memory Database Cache Accelerator for Oracle Database Applications • Reduced response time and increased throughput for Oracle Database applications • Oracle Database tables cached in the application-tier – Groups of related tables – All or subset of rows and columns ...
... Oracle In-Memory Database Cache Accelerator for Oracle Database Applications • Reduced response time and increased throughput for Oracle Database applications • Oracle Database tables cached in the application-tier – Groups of related tables – All or subset of rows and columns ...
SQL Server Replication
... Although brief overviews are given of both replication and database mirroring, it is easier to understand this white paper if you have some experience with one or both of these technologies, and have at least a rudimentary knowledge of database concepts such as transactions. The information about ar ...
... Although brief overviews are given of both replication and database mirroring, it is easier to understand this white paper if you have some experience with one or both of these technologies, and have at least a rudimentary knowledge of database concepts such as transactions. The information about ar ...
download
... If a database must be recovered to a point in the past, Oracle's recovery facilities enable database administrators at other sites to return their databases to the earlier point in time also. This ensures that the global database remains consistent. ...
... If a database must be recovered to a point in the past, Oracle's recovery facilities enable database administrators at other sites to return their databases to the earlier point in time also. This ensures that the global database remains consistent. ...
LABELVIEW 10 Database Manager Guide
... 1 Go to File > Create new database. 2 Select dBase or Access database from the submenu. A Save as dialog box will open, allowing you to specify a name and location for the database file, and then click Save. The new database connection will be displayed in the Database Connections window. ...
... 1 Go to File > Create new database. 2 Select dBase or Access database from the submenu. A Save as dialog box will open, allowing you to specify a name and location for the database file, and then click Save. The new database connection will be displayed in the Database Connections window. ...
CODESOFT 10 Database Manager
... Remove a filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Modify a filter in SQL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Choose an existing query in a database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Remove a filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Modify a filter in SQL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Choose an existing query in a database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Chapter 7: Relational Database Design
... add the resulting functional dependencies to F+ for each pair of functional dependencies f1and f2 in F+ if f1 and f2 can be combined using transitivity then add the resulting functional dependency to F+ until F+ does not change any further NOTE: We will see an alternative procedure for this task lat ...
... add the resulting functional dependencies to F+ for each pair of functional dependencies f1and f2 in F+ if f1 and f2 can be combined using transitivity then add the resulting functional dependency to F+ until F+ does not change any further NOTE: We will see an alternative procedure for this task lat ...
Database Lifecycle Management
... Section 5 considers the applicability of the practices and methods described in Section 2 to the broader "data ecosystem", to the ETL process that supply the data, BI systems that must analyze it, as well as to the design, development, delivery, and maintenance of non-relational databases and other ...
... Section 5 considers the applicability of the practices and methods described in Section 2 to the broader "data ecosystem", to the ETL process that supply the data, BI systems that must analyze it, as well as to the design, development, delivery, and maintenance of non-relational databases and other ...
Chapter 19: Distributed Databases
... The three-phase commit (3PC) protocol is more complicated and more ...
... The three-phase commit (3PC) protocol is more complicated and more ...
Chapter 21:Application Development and Administration
... » The search criteria of the update/delete must be evaluated again if the transaction commits – update/delete includes updating the header information of the old tuple as well as creating a new tuple ...
... » The search criteria of the update/delete must be evaluated again if the transaction commits – update/delete includes updating the header information of the old tuple as well as creating a new tuple ...
With Oracle Database 12c, there is all the more reason to use
... Edition-based redefinition enhancements Edition-based redefinition, hereinafter EBR, was introduced in Oracle Database 11g Release 2, hereinafter 11.2. In that release, it had some properties that made its adoption, in general, possible only after making changes to the disposition of the application ...
... Edition-based redefinition enhancements Edition-based redefinition, hereinafter EBR, was introduced in Oracle Database 11g Release 2, hereinafter 11.2. In that release, it had some properties that made its adoption, in general, possible only after making changes to the disposition of the application ...
title
... It requires ASYNC redo transport, the LGWR process never waits for acknowledgment from the Standby database. ▶ Maximum Availability – Keyword: P1 = Availability: Zero data loss protect as a very close P2. It requires SYNC redo transport, thus Primary database performance may be impacted by the amoun ...
... It requires ASYNC redo transport, the LGWR process never waits for acknowledgment from the Standby database. ▶ Maximum Availability – Keyword: P1 = Availability: Zero data loss protect as a very close P2. It requires SYNC redo transport, thus Primary database performance may be impacted by the amoun ...
Cloud.2013.pdf
... that provide effective resource sharing among tenants while ensuring good performance, low latency transaction processing, and low overhead live database migration. The key observation driving the design of ElasTraS is that even though classical RDBMSs and key-value stores form two different classes ...
... that provide effective resource sharing among tenants while ensuring good performance, low latency transaction processing, and low overhead live database migration. The key observation driving the design of ElasTraS is that even though classical RDBMSs and key-value stores form two different classes ...
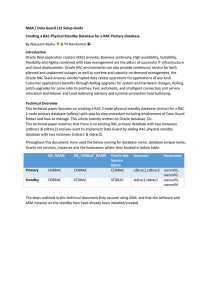
MAA / Data Guard 12c Setup Guide Creating a RAC Physical
... 5. We are performing Active duplicate of 11g feature, hence no need to take backup or copy to the standby server. 6. Create standby redo logs on the RAC primary database to support the standby role. The recommended number of standby redo logs is: (maximum # of logfiles +1) * maximum # of threads Th ...
... 5. We are performing Active duplicate of 11g feature, hence no need to take backup or copy to the standby server. 6. Create standby redo logs on the RAC primary database to support the standby role. The recommended number of standby redo logs is: (maximum # of logfiles +1) * maximum # of threads Th ...
Chapter B: Hierarchical Model
... type> within the designated subtree to resume search. Use currency pointer to determine where to resume search. DB-status is set to a nonzero value if no such record exists in the ...
... type> within the designated subtree to resume search. Use currency pointer to determine where to resume search. DB-status is set to a nonzero value if no such record exists in the ...
Security and Backups
... • Create new user account – General information about user account – System privileges user has in database – User’s tablespace quota on database server ...
... • Create new user account – General information about user account – System privileges user has in database – User’s tablespace quota on database server ...
Database Configuration - L-Soft
... The administrator must determine the maximum key length value used internally by his Oracle database installation and must take care to enter the correct value in the Oracle database settings on the Administration Hub page described above. If the value entered exceeds the actual maximum key length ...
... The administrator must determine the maximum key length value used internally by his Oracle database installation and must take care to enter the correct value in the Oracle database settings on the Administration Hub page described above. If the value entered exceeds the actual maximum key length ...
slides
... during that transaction are undone. That may not be what you want! – Suppose you want to add an audit record every time someone tries to make some specific kind of change. – You want to add that audit record even if the ...
... during that transaction are undone. That may not be what you want! – Suppose you want to add an audit record every time someone tries to make some specific kind of change. – You want to add that audit record even if the ...
Document
... – Automatically handles setting certain system parameters that can otherwise cause problems during upgrade (E.g. set job_queue_processes = 0) DBMS_REGISTRY package and system table are used to record and manage information about all the component upgrades – E.g. ...
... – Automatically handles setting certain system parameters that can otherwise cause problems during upgrade (E.g. set job_queue_processes = 0) DBMS_REGISTRY package and system table are used to record and manage information about all the component upgrades – E.g. ...
Oracle Database Appliance Sales Jarosław Skibiński
... The Oracle Database Appliance is an engineered solution, using the very best of breed of products, AND it comes fully integrated so you don’t need to spend the time and money on alternative approaches, or assume the risk of not designing it correctly. The exclusive Oracle Appliance Manager software ...
... The Oracle Database Appliance is an engineered solution, using the very best of breed of products, AND it comes fully integrated so you don’t need to spend the time and money on alternative approaches, or assume the risk of not designing it correctly. The exclusive Oracle Appliance Manager software ...
Scalable Query Result Caching for Web Applications
... the same name parameter is used. Template U1 also affects any instantiation of Template Q4 for which the entry date was in the past, and instantiations of Template Q5 whose quantity parameter was greater than that of the newly inserted item. Template U2 affects instantiations of Template Q3 whose na ...
... the same name parameter is used. Template U1 also affects any instantiation of Template Q4 for which the entry date was in the past, and instantiations of Template Q5 whose quantity parameter was greater than that of the newly inserted item. Template U2 affects instantiations of Template Q3 whose na ...
Expression and Enforcement of Dynamic Integrity Constraints
... necessary to centralize the specification of constraints. Consequently, the consistency constraints that hold in a particular application area have to be specified in the conceptual schema that describes the semantics of the application area. System software will then enforce these constraints auto ...
... necessary to centralize the specification of constraints. Consequently, the consistency constraints that hold in a particular application area have to be specified in the conceptual schema that describes the semantics of the application area. System software will then enforce these constraints auto ...
Continuous Database Integration
... discuss which database files are committed to a version control repository. Automating a database integration build process solves only part of the problem, so we go one step further by rebuilding the database and data at every software change—making the verification process continuous. If a team is ...
... discuss which database files are committed to a version control repository. Automating a database integration build process solves only part of the problem, so we go one step further by rebuilding the database and data at every software change—making the verification process continuous. If a team is ...
Low-Overhead Asynchronous Checkpointing in Main
... Recent work by Cao et al. [2] presented some promising results for taking low overhead complete checkpoints of database state without requiring a database log. This work focused on applications that have frequent points of consistency, such as massive multiplayer online games that have distinct step ...
... Recent work by Cao et al. [2] presented some promising results for taking low overhead complete checkpoints of database state without requiring a database log. This work focused on applications that have frequent points of consistency, such as massive multiplayer online games that have distinct step ...