Wine Faults - fnbservicenotes
... oxygen and a catalyst are the only requirements for the process to occur. It is also known as maderized wine, from Madeira wine, which is intentionally oxidized. Oxidation can occur throughout the winemaking process, and even after the wine has been bottled. Anthocyanins, catechins, epicatechins and ...
... oxygen and a catalyst are the only requirements for the process to occur. It is also known as maderized wine, from Madeira wine, which is intentionally oxidized. Oxidation can occur throughout the winemaking process, and even after the wine has been bottled. Anthocyanins, catechins, epicatechins and ...
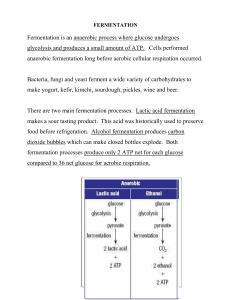
FERMENTATION
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
Lactic Acid Fermentation vs. Alcoholic Fermentation
... ○ C3H4O3 + C21H27N7O14P2 + → Alcohol + C21H27N7O14P2 ○ Pyruvic acid + NADH → Alcohol + Carbon Dioxide + NAD+ ...
... ○ C3H4O3 + C21H27N7O14P2 + → Alcohol + C21H27N7O14P2 ○ Pyruvic acid + NADH → Alcohol + Carbon Dioxide + NAD+ ...
Impact of Malolactic Fermentation Strain on Wine Composition
... Production of yeast inhibitors such as acetic acid ...
... Production of yeast inhibitors such as acetic acid ...
Phenolic Compounds and Tannins in Wine
... Directly from the grape From non-volatile grape precursors - (many grape aroma compounds occur in a ‘bound’ form – not able to be smelled until they are converted to a ‘free’ form) Yeast and bacterial metabolism Oak wood extraction Chemical reactions during wine ageing Distribution within the grape ...
... Directly from the grape From non-volatile grape precursors - (many grape aroma compounds occur in a ‘bound’ form – not able to be smelled until they are converted to a ‘free’ form) Yeast and bacterial metabolism Oak wood extraction Chemical reactions during wine ageing Distribution within the grape ...
Chapter 17-Alcoholic Beverages
... Wine is fermented fruit juice, but usually refers to fermented juicenof grapes, Vitis vinifera. Estimates of wine-making with grapes vary from 8000-3000 B.C. Wine may be the oldest fermented beverage made by humans, but some authors think beer or mead was produced earlier. Mead is a fermented soluti ...
... Wine is fermented fruit juice, but usually refers to fermented juicenof grapes, Vitis vinifera. Estimates of wine-making with grapes vary from 8000-3000 B.C. Wine may be the oldest fermented beverage made by humans, but some authors think beer or mead was produced earlier. Mead is a fermented soluti ...
Fermentation Due: April 19th by 5:00 PM Please submit your
... 5. Investigate and describe the difference in red wine vinegar as compared to balsamic vinegar – make sure to note the difference in the production process. Both vinegars are made from red wine using acetobacter. Red wine vinegar takes 1-2 years to make (and very little control is needed to make thi ...
... 5. Investigate and describe the difference in red wine vinegar as compared to balsamic vinegar – make sure to note the difference in the production process. Both vinegars are made from red wine using acetobacter. Red wine vinegar takes 1-2 years to make (and very little control is needed to make thi ...
Flavonoids
... Introduction to Oxidation in Wine Andrew L. Waterhouse Department of Viticulture & Enology University of California, Davis ...
... Introduction to Oxidation in Wine Andrew L. Waterhouse Department of Viticulture & Enology University of California, Davis ...
Cell Respiration Basics
... • After glycolysis, if there is not enough oxygen present, an anaerobic pathway is used to breakdown pyruvic acid called fermentation. ...
... • After glycolysis, if there is not enough oxygen present, an anaerobic pathway is used to breakdown pyruvic acid called fermentation. ...
Secondary Fermentation: Malolactic Fermentation
... • Ethanol Bacteria are inhibited at around 14% EtOH ...
... • Ethanol Bacteria are inhibited at around 14% EtOH ...
Common Defects in Wine
... can out-compete yeast and stop a fermentation. Acetic Acid Bacteria can utilize sugars and oxidize ethanol to make VA. They are more common after fermentation. ...
... can out-compete yeast and stop a fermentation. Acetic Acid Bacteria can utilize sugars and oxidize ethanol to make VA. They are more common after fermentation. ...
Winemaking

Winemaking or vinification, is the production of wine, starting with selection of the grapes or other produce and ending with bottling the finished wine. Although most wine is made from grapes, it may also be made from other fruits or plants. Mead is a wine that is made with honey being the primary ingredient after water.Winemaking can be divided into two general categories: still wine production (without carbonation) and sparkling wine production (with carbonation — natural or injected).The science of wine and winemaking is known as oenology. A person who makes wine is traditionally called a winemaker or vintner.