Observation of quasiparticles with one
... the existence of these quasiparticles in the FQH regime. Shot noise, resulting from the granular nature of the particles, is proportional to the charge of the current carriers, in this case quasiparticles4,5. In these experiments a quantum point contact (QPC) embedded in a two-dimensional electron g ...
... the existence of these quasiparticles in the FQH regime. Shot noise, resulting from the granular nature of the particles, is proportional to the charge of the current carriers, in this case quasiparticles4,5. In these experiments a quantum point contact (QPC) embedded in a two-dimensional electron g ...
Coherent manipulations of charge-number states in a Cooper-pair box Y. Nakamura,
... all the charge(-number) states are degenerate and, thus, form a one-dimensional tight-binding array in the charge space (Fig. 1(b)). As a result, the phase difference θ between the two superconductors, a conjugate variable to the charge number n, becomes a good quantum number, and we obtain a single ...
... all the charge(-number) states are degenerate and, thus, form a one-dimensional tight-binding array in the charge space (Fig. 1(b)). As a result, the phase difference θ between the two superconductors, a conjugate variable to the charge number n, becomes a good quantum number, and we obtain a single ...
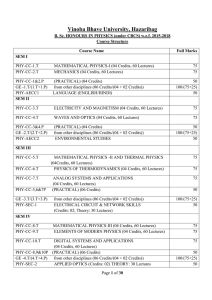
Revised B. Sc. Honours in Physics (under CBCS) w.e.f. 2015-2018
... (04 Credits, 60 Lectures) Wave Motion: Plane and Spherical Waves. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves.Plane Progressive (Travelling) Waves. Wave Equation. Particle and Wave Velocities. Differential Equation. Pressure of a Longitudinal Wave. Energy Transport. Intensity of Wave. (6 Lectures) Velocity of ...
... (04 Credits, 60 Lectures) Wave Motion: Plane and Spherical Waves. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves.Plane Progressive (Travelling) Waves. Wave Equation. Particle and Wave Velocities. Differential Equation. Pressure of a Longitudinal Wave. Energy Transport. Intensity of Wave. (6 Lectures) Velocity of ...
Signatures of Majorana zero-modes in nanowires, quantum spin
... Majorana zero-modes, also referred to as Majorana bound states or Majorinos, are states in the middle of the excitation gap of a superconductor (so at zero excitation energy), bound to a magnetic vortex or other defect. The name goes back to a concept introduced by the Italian physicist Ettore Major ...
... Majorana zero-modes, also referred to as Majorana bound states or Majorinos, are states in the middle of the excitation gap of a superconductor (so at zero excitation energy), bound to a magnetic vortex or other defect. The name goes back to a concept introduced by the Italian physicist Ettore Major ...
Quantum Transport in Finite Disordered Electron Systems
... conductance oscillations are absent and applicability of the resistor model (multilayer resistance understood as the sum of resistances of individual layers and interfaces) is analyzed. ...
... conductance oscillations are absent and applicability of the resistor model (multilayer resistance understood as the sum of resistances of individual layers and interfaces) is analyzed. ...
Nonequilibrium effects in transport through quantum dots - ICMM-CSIC
... Quantum dots are paradigms with which to study the transition from macroscopic to microscopic physics. At present, the role of single-electron charging is well understood.1 Processes which otherwise are found in solids at the single-atom level, such as the Kondo effect, are being currently investiga ...
... Quantum dots are paradigms with which to study the transition from macroscopic to microscopic physics. At present, the role of single-electron charging is well understood.1 Processes which otherwise are found in solids at the single-atom level, such as the Kondo effect, are being currently investiga ...
Lossless Quantum Data Compression and Secure Direct
... protocols rely on the existence of a shared secret key. How can this key be established without having an unauthorized person potentially eavesdropping it? The BB84 protocol now offers a method to distribute a random key between two parties which is secure against eavesdropping. Based on the fact th ...
... protocols rely on the existence of a shared secret key. How can this key be established without having an unauthorized person potentially eavesdropping it? The BB84 protocol now offers a method to distribute a random key between two parties which is secure against eavesdropping. Based on the fact th ...
Near-Optimal Dynamical Decoupling of a Qubit
... processing requires the faithful manipulation and preservation of quantum states. In the course of a quantum evolution, uncontrolled coupling between a quantum system and its environment (or bath) may cause the system state to decohere and deviate from its desired evolution. Here we present a dynami ...
... processing requires the faithful manipulation and preservation of quantum states. In the course of a quantum evolution, uncontrolled coupling between a quantum system and its environment (or bath) may cause the system state to decohere and deviate from its desired evolution. Here we present a dynami ...
Equilibrium concentration of point defects in crystalline
... give helium enough zero-point quantum motion to prevent solidification; the large quantum effects have many other consequences for the liquid, including superfluidity and its associated striking phenomena. Quantum effects are also responsible for the possibility that an equilibrium helium crystal ca ...
... give helium enough zero-point quantum motion to prevent solidification; the large quantum effects have many other consequences for the liquid, including superfluidity and its associated striking phenomena. Quantum effects are also responsible for the possibility that an equilibrium helium crystal ca ...
Conclusive exclusion of quantum states
... suppose that χ does not give a complete description of the system. We assume that such a description exists, although it may always be unknown to us, and we denote it by λ. As χ is an incomplete description of the system, it will be compatible with many different complete states. We denote these sta ...
... suppose that χ does not give a complete description of the system. We assume that such a description exists, although it may always be unknown to us, and we denote it by λ. As χ is an incomplete description of the system, it will be compatible with many different complete states. We denote these sta ...
Duality of Strong Interaction - Indiana University Bloomington
... classical Einstein-Hilbert functional has to be taken under the divergence-free constraint. Namely, the variational element must be energy-momentum conserved. With PID at our disposal, we derive in [14, 15] a unified field model. This model leads not only to consistent results with the standard mode ...
... classical Einstein-Hilbert functional has to be taken under the divergence-free constraint. Namely, the variational element must be energy-momentum conserved. With PID at our disposal, we derive in [14, 15] a unified field model. This model leads not only to consistent results with the standard mode ...
Download: PDF
... The world is a strange place, but it wasn’t until 1900, when Max Planck was studying the thermal spectrum of light (black body radiation) that we began to understand just how strange it was. Although this represented the formal start of modern quantum mechanics, it is easier to start in 1877, with H ...
... The world is a strange place, but it wasn’t until 1900, when Max Planck was studying the thermal spectrum of light (black body radiation) that we began to understand just how strange it was. Although this represented the formal start of modern quantum mechanics, it is easier to start in 1877, with H ...
Physics 137B
... energy Ea ), and ψb (with energy Eb ). They are orthogonal, normalized, and non-degenerate (assume Ea is the smaller of the two energies). Now turn on a pertubation H ! , with the following matrix elements: #ψa |H ! |ψa " = #ψb |H ! |ψb " = 0 #ψa |H ! |ψb " = #ψb |H ! |ψa " = h where h is some speci ...
... energy Ea ), and ψb (with energy Eb ). They are orthogonal, normalized, and non-degenerate (assume Ea is the smaller of the two energies). Now turn on a pertubation H ! , with the following matrix elements: #ψa |H ! |ψa " = #ψb |H ! |ψb " = 0 #ψa |H ! |ψb " = #ψb |H ! |ψa " = h where h is some speci ...
Atomic Quantum Metrology with Narrowband Entangled and Squeezed States of Light DISSERTATION
... in the same mode and can form a NOON state with N =2, a so-called 2-NOON state [13]. In the past, high efforts were made to increase the size of NOON states and ‘NOON-like’ states by superposing a 2-NOON state with a coherent beam [14, 15] or by using double-pair emission of an SPDC crystal [16]. Th ...
... in the same mode and can form a NOON state with N =2, a so-called 2-NOON state [13]. In the past, high efforts were made to increase the size of NOON states and ‘NOON-like’ states by superposing a 2-NOON state with a coherent beam [14, 15] or by using double-pair emission of an SPDC crystal [16]. Th ...
The Violation of Bell Inequalities in the Macroworld
... (Bell, 1964). The fact that Bell took the EPR result literally is evident from the abstract of his 1964 paper: ``The paradox of Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen was advanced as an argument that quantum theory could not be a complete theory but should be supplemented by additional variables. These additi ...
... (Bell, 1964). The fact that Bell took the EPR result literally is evident from the abstract of his 1964 paper: ``The paradox of Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen was advanced as an argument that quantum theory could not be a complete theory but should be supplemented by additional variables. These additi ...
3.3 The time-dependent Schrödinger equation
... as long as we always multiply it by a factor exp iEt / If r is a solution of the time-independent Schrödinger equation, with eigenenergy E then r, t r exp iEt / is a solution of both the time-independent and the time-dependent Schrödinger equations making these two ...
... as long as we always multiply it by a factor exp iEt / If r is a solution of the time-independent Schrödinger equation, with eigenenergy E then r, t r exp iEt / is a solution of both the time-independent and the time-dependent Schrödinger equations making these two ...
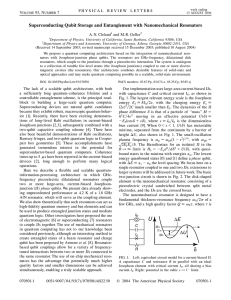
Superconducting Qubit Storage and Entanglement with Nanomechanical Resonators A. N. Cleland
... apart from expected phase factors. The JJ state has actually been swapped with that of the resonator. The cavity-QED analog of this operation has been demonstrated in Ref. [15]. To assess the limitations of the RWA and examine the feasibility of future experiments, we also solve Eq. (2) numerically, ...
... apart from expected phase factors. The JJ state has actually been swapped with that of the resonator. The cavity-QED analog of this operation has been demonstrated in Ref. [15]. To assess the limitations of the RWA and examine the feasibility of future experiments, we also solve Eq. (2) numerically, ...
Differentiation of vectors
... This is read as del or nabla and is not to be confused with ∆, the capital Greek letter delta. One can form “products” of this vector with other vectors and scalars, but because it is an operator, it always has to be ...
... This is read as del or nabla and is not to be confused with ∆, the capital Greek letter delta. One can form “products” of this vector with other vectors and scalars, but because it is an operator, it always has to be ...