Historical overview of the developments of quantum mechanics
... and potential energies. For an atom in a crystalline solid, there are three degrees of freedom (associated with the three directions they can wiggle about their equilibrium positions), and thus they have kinetic energy K = 3/2kB T , and potential energy U = 3/2kB T , giving total thermal energy stor ...
... and potential energies. For an atom in a crystalline solid, there are three degrees of freedom (associated with the three directions they can wiggle about their equilibrium positions), and thus they have kinetic energy K = 3/2kB T , and potential energy U = 3/2kB T , giving total thermal energy stor ...
Solar Winds
... is a special product, the cross (or vector) product. The result of this calculation depends on the angle between the two, as is the case in the less formal notation. For a single charged particle equation 4.1 changes into: F = qv × B ...
... is a special product, the cross (or vector) product. The result of this calculation depends on the angle between the two, as is the case in the less formal notation. For a single charged particle equation 4.1 changes into: F = qv × B ...
Path Integrals in Quantum Field Theory
... the configuration space that describes the state of the system at any given time. For quantum field theory, the configuration space is a Fock space where each vector represents the number of each type of particle with momentum k. The key to the whole thing, though, is that each path that the system ...
... the configuration space that describes the state of the system at any given time. For quantum field theory, the configuration space is a Fock space where each vector represents the number of each type of particle with momentum k. The key to the whole thing, though, is that each path that the system ...
Quantum Computation with Neutral Atoms
... 1. A scalable physical system with well characterized qubits Optical lattices: loading of one atom per site may be achieved using Mott insulator transition. Scalability: the properties of optical lattice system do not change in the principal way when the size of the system is increased. Designer lat ...
... 1. A scalable physical system with well characterized qubits Optical lattices: loading of one atom per site may be achieved using Mott insulator transition. Scalability: the properties of optical lattice system do not change in the principal way when the size of the system is increased. Designer lat ...
Random non-local games
... We studied random XOR games with n questions to Alice and Bob. For both quantum and classical strategies, the best winning probability ½. ...
... We studied random XOR games with n questions to Alice and Bob. For both quantum and classical strategies, the best winning probability ½. ...
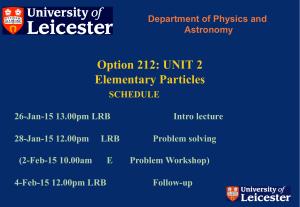
Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles - X
... • (c) The six flavors of quark are up, down, charmed, strange, left and right • (d) Neutrons have no charm (a) False: leptons are fundamental particles e.g e(b) True (c) False: there is no left and right quark, but there are top and bottom quarks (d) True: neutrons are made of udd quarks ...
... • (c) The six flavors of quark are up, down, charmed, strange, left and right • (d) Neutrons have no charm (a) False: leptons are fundamental particles e.g e(b) True (c) False: there is no left and right quark, but there are top and bottom quarks (d) True: neutrons are made of udd quarks ...
Philosophy of Mind and the Problem of Free Will
... quantum theory, in his analysis of free will. However, the opening words of Bohr’s 1934 book Atomic Theory and the Description of Nature5 are: “The task of science is both to extend the range of our experience and reduce it to order.” This idea is restated many times in many ways, for example as: “I ...
... quantum theory, in his analysis of free will. However, the opening words of Bohr’s 1934 book Atomic Theory and the Description of Nature5 are: “The task of science is both to extend the range of our experience and reduce it to order.” This idea is restated many times in many ways, for example as: “I ...
Document
... • Balakrishnan, S. and R. Sankaranarayanan, Entangling characterization of (SWAP)1/m and controlled unitary gates, Phys. Rev. A 78, 052305 (2008). • Balakrishnan, S. and R. Sankaranarayanan, Characterizing the geometrical edges of nonlocal two-qubit gates, Phys. Rev. A 79, 052339 (2009). • Balakrish ...
... • Balakrishnan, S. and R. Sankaranarayanan, Entangling characterization of (SWAP)1/m and controlled unitary gates, Phys. Rev. A 78, 052305 (2008). • Balakrishnan, S. and R. Sankaranarayanan, Characterizing the geometrical edges of nonlocal two-qubit gates, Phys. Rev. A 79, 052339 (2009). • Balakrish ...
AQA GCE Mark Scheme January 2005 - School
... to lose one mark. The candidate’s incorrect value should be carried through all subsequent calculations for the question and, if there are no subsequent errors, the candidate can score all remaining marks (indicated by ticks). These subsequent ticks should be marked CE (consequential error). ...
... to lose one mark. The candidate’s incorrect value should be carried through all subsequent calculations for the question and, if there are no subsequent errors, the candidate can score all remaining marks (indicated by ticks). These subsequent ticks should be marked CE (consequential error). ...
two electron energy sprectrum in concentrical quantum ribbons
... the importance of this study [5], we consider also interesting to analyze the case of two particles constrained to move into the two dimensional cylindrical ribbons, since allows us to study the electron-electron correlation and the influence on the energy spectrum in two dimensional spaces. We are ...
... the importance of this study [5], we consider also interesting to analyze the case of two particles constrained to move into the two dimensional cylindrical ribbons, since allows us to study the electron-electron correlation and the influence on the energy spectrum in two dimensional spaces. We are ...
Quantum Hall Plateau Transitions in Disordered Superconductors
... states at isolated energies in an otherwise localized spectrum. Physically, such systems have more than one distinct insulating phase, each characterized by its number of edge states and separated from other phases by delocalization transitions. Second, it may happen that the Hamiltonian has an addi ...
... states at isolated energies in an otherwise localized spectrum. Physically, such systems have more than one distinct insulating phase, each characterized by its number of edge states and separated from other phases by delocalization transitions. Second, it may happen that the Hamiltonian has an addi ...
THE MANY CLASSICAL FACES OF QUANTUM STRUCTURES 1
... Definition 2.1. For a unital C*-algebra A, write C(A) for its family of commutative unital C*-subalgebras C (with the same unit as A). We can think of it either as a partially ordered set under inclusion, or as a diagram that remembers that the points of the partially ordered set are C*-algebras C. ...
... Definition 2.1. For a unital C*-algebra A, write C(A) for its family of commutative unital C*-subalgebras C (with the same unit as A). We can think of it either as a partially ordered set under inclusion, or as a diagram that remembers that the points of the partially ordered set are C*-algebras C. ...
Even-denominator fractional quantum Hall effect in bilayer graphene
... Do momentum relaxation and charge inhomogeneity originate from the same or from different microscopic processes? If the same microscopic mechanisms cause elastic scattering and charge inhomogeneity m and n* measured in different devices should show a correlation ...
... Do momentum relaxation and charge inhomogeneity originate from the same or from different microscopic processes? If the same microscopic mechanisms cause elastic scattering and charge inhomogeneity m and n* measured in different devices should show a correlation ...
QUANTUM DYNAMICS OF A MASSLESS RELATIVISTIC
... The string can then be quantized by making x(o, t) quantum mechanical operators and subjecting the physical states to the subsidiary conditions. This procedure clear ly uses a positive definite Hilbert space so there is no problem with negative norm states. However, manifest Lorentz covariance is lo ...
... The string can then be quantized by making x(o, t) quantum mechanical operators and subjecting the physical states to the subsidiary conditions. This procedure clear ly uses a positive definite Hilbert space so there is no problem with negative norm states. However, manifest Lorentz covariance is lo ...
COMMUNICATION SCIENCES ENGINEERING AND
... tion is easily determined, the documentary information is stored only once in a file, the file organization allows the use of various matching functions and thresholds, and the dimensionality of the transform is easily expanded to accommodate data bases of various ...
... tion is easily determined, the documentary information is stored only once in a file, the file organization allows the use of various matching functions and thresholds, and the dimensionality of the transform is easily expanded to accommodate data bases of various ...
Theoretische und Mathematische Grundlagen der Physik
... part of my talk I will give an overview over the results obtained so far for this manifold with the help of what M. Blau and G. Thompson call “torus gauge fixing”. In the last part of my talk I will sketch what remains to be done in order to complete Steps 1 and 2 for the latter manifold and I will ...
... part of my talk I will give an overview over the results obtained so far for this manifold with the help of what M. Blau and G. Thompson call “torus gauge fixing”. In the last part of my talk I will sketch what remains to be done in order to complete Steps 1 and 2 for the latter manifold and I will ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... states of atomic objects, but of macroscopic objects also. This point was best illustrated by Schrödinger in his famous 'cat paradox'. A single photon in a state of superposition is connected to a detector, which is wired up to release poison gas inside a box in which a living cat has been placed. I ...
... states of atomic objects, but of macroscopic objects also. This point was best illustrated by Schrödinger in his famous 'cat paradox'. A single photon in a state of superposition is connected to a detector, which is wired up to release poison gas inside a box in which a living cat has been placed. I ...
The Analytical Study of Electronic and Optical Properties of Pyramid
... work one considers the particles with characteristic dimensions about 10 nm. Because of doped semiconductor characterized by electron concentration about 1016 –1018 sm−3 , one can suppose that there is not more than one electron per the particle. This means, that electron–electron interaction can be ...
... work one considers the particles with characteristic dimensions about 10 nm. Because of doped semiconductor characterized by electron concentration about 1016 –1018 sm−3 , one can suppose that there is not more than one electron per the particle. This means, that electron–electron interaction can be ...
Solution #3 - Temple University Department of Physics
... total angular momentum of the atom is F = J + I, where I is the nuclear spin. The eigenvalues of J 2 and F 2 are J(J + 1)~2 and F (F + 1)~2 respectively. a. What are the possible values of the quantum number J and F for a deuterium atom in the 1s ground state? In the 1s ground state of the deuterium ...
... total angular momentum of the atom is F = J + I, where I is the nuclear spin. The eigenvalues of J 2 and F 2 are J(J + 1)~2 and F (F + 1)~2 respectively. a. What are the possible values of the quantum number J and F for a deuterium atom in the 1s ground state? In the 1s ground state of the deuterium ...