the lab manual here
... 7. A computer printout of the graph is preferred though not mandatory. 8. If more than one measurement has been made at a value either show all the points on the graph or plot the mean and the standard error . . . or plot both if they do not clutter the graph too much. Error bars should be shown eve ...
... 7. A computer printout of the graph is preferred though not mandatory. 8. If more than one measurement has been made at a value either show all the points on the graph or plot the mean and the standard error . . . or plot both if they do not clutter the graph too much. Error bars should be shown eve ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrint?assignmentI... ...
... http://session.masteringphysics.com/myct/assignmentPrint?assignmentI... ...
JECT TO LORENTZ FORCE IAA-AAS-DyCoSS2-04-11
... equilibrium positions and the shaded regions are the regions where the equilibrium positions will be stable. Figure (8, left) and figure (8, right) are given for . The locations of the stable re‐ gions are nearly unaffected by the changing values of the charge to mass ratios but the loca‐ tions and ...
... equilibrium positions and the shaded regions are the regions where the equilibrium positions will be stable. Figure (8, left) and figure (8, right) are given for . The locations of the stable re‐ gions are nearly unaffected by the changing values of the charge to mass ratios but the loca‐ tions and ...
Potential - Chabot College
... – Move with the field direction, KE increases – Move against the field direction, U increases – Overall, total energy U + KE is constant. ...
... – Move with the field direction, KE increases – Move against the field direction, U increases – Overall, total energy U + KE is constant. ...
Forces between charges Forces on charges
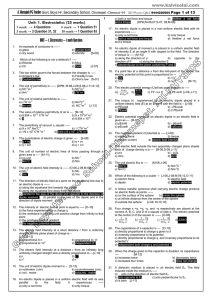
... (c) Suppose a charge Q exerts a force F on a test charge q that is brought near to it. By how much would the force exerted by Q increase if the test charge increased by a factor of a, where a can be any constant (i.e. a = 17 or 5 or 7.812, etc.)? By how much would the ratio of the force on the test ...
... (c) Suppose a charge Q exerts a force F on a test charge q that is brought near to it. By how much would the force exerted by Q increase if the test charge increased by a factor of a, where a can be any constant (i.e. a = 17 or 5 or 7.812, etc.)? By how much would the ratio of the force on the test ...
Course Competency Learning Outcomes
... Distinguish between linear and angular momentum. State the rotational energy of a body and apply tye workenergy theorem to a rotating rigid body. ...
... Distinguish between linear and angular momentum. State the rotational energy of a body and apply tye workenergy theorem to a rotating rigid body. ...