Word Doc - Bodge It and Scarper Ltd
... information content of the vacuum needs balancing so to raise the flywheel, which requires more information, we must destroy information somewhere else and that somewhere else is in our arms. Complex sugars etc have high information content but our cells break these down forming heat (dis-informati ...
... information content of the vacuum needs balancing so to raise the flywheel, which requires more information, we must destroy information somewhere else and that somewhere else is in our arms. Complex sugars etc have high information content but our cells break these down forming heat (dis-informati ...
1. Which of the following statements is always true
... Depends how fast it is going 4. When you kick a ball, it moves away from you but you stay where you are. This is because: ...
... Depends how fast it is going 4. When you kick a ball, it moves away from you but you stay where you are. This is because: ...
AP Physics 2
... of the net force exerted on object X by objects W, Y, and Z? Explain your answer. (AP sample test) ...
... of the net force exerted on object X by objects W, Y, and Z? Explain your answer. (AP sample test) ...
Document
... • Is quantized • elementary charge, e, is charge on 1 electron or 1 proton • e = 1.602 10-19 Coulombs ...
... • Is quantized • elementary charge, e, is charge on 1 electron or 1 proton • e = 1.602 10-19 Coulombs ...
03_E2_ws2_key
... 3. Calculate the gravitational potential difference between: a) point A and the base of the hill GP = gh = (10N/kg)-100m = -1000J/kg b) point B and the base of the hill GP = gh = (10N/kg)-200m = -2000J/kg c) point C and point A GP = gh = (10N/kg) 0m = 0 d) point C and point E GP = gh = (10N/kg)2 ...
... 3. Calculate the gravitational potential difference between: a) point A and the base of the hill GP = gh = (10N/kg)-100m = -1000J/kg b) point B and the base of the hill GP = gh = (10N/kg)-200m = -2000J/kg c) point C and point A GP = gh = (10N/kg) 0m = 0 d) point C and point E GP = gh = (10N/kg)2 ...
Grade 11 Physics – Course Review Part 2
... 1.50 cm. Find the electric force on an oil drop floating between the plates and carrying a charge of + 50e. 7. If the drop in the above problem has a mass of 1.6 x 10 – 13 kg, what will be its acceleration as it falls between the two plates? Assume the field points upwards. 8. What sort of field or ...
... 1.50 cm. Find the electric force on an oil drop floating between the plates and carrying a charge of + 50e. 7. If the drop in the above problem has a mass of 1.6 x 10 – 13 kg, what will be its acceleration as it falls between the two plates? Assume the field points upwards. 8. What sort of field or ...
URL - StealthSkater
... The astronauts will not experience any “g-force” because their bodies are subjected to the same acceleration field as the spacecraft is (in like manner to a spacecraft in orbit around the Earth since Earth’s gravity field accelerates both the spacecraft and the astronauts equally). A “g-force” only ...
... The astronauts will not experience any “g-force” because their bodies are subjected to the same acceleration field as the spacecraft is (in like manner to a spacecraft in orbit around the Earth since Earth’s gravity field accelerates both the spacecraft and the astronauts equally). A “g-force” only ...
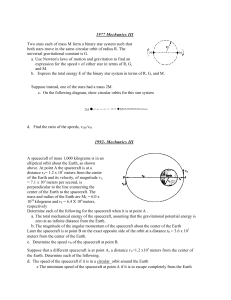
Space #3
... velocity of about 30 000 km/h o This velocity boost is maximised if a rocket is launched from the equator, as radius and hence tangential velocity are greatest here o First, the rocket is launched vertically to penetrate dense lower portion of the atmosphere by shortest possible route, then its traj ...
... velocity of about 30 000 km/h o This velocity boost is maximised if a rocket is launched from the equator, as radius and hence tangential velocity are greatest here o First, the rocket is launched vertically to penetrate dense lower portion of the atmosphere by shortest possible route, then its traj ...
revision lecture.
... developed by any source of electrical energy such as a battery or dynamo. It is generally defined as the electrical potential for a source in a circuit. The word ”force” in this case is not used to mean mechanical force, measured in newtons, N, but a potential, or energy per unit of charge, measured ...
... developed by any source of electrical energy such as a battery or dynamo. It is generally defined as the electrical potential for a source in a circuit. The word ”force” in this case is not used to mean mechanical force, measured in newtons, N, but a potential, or energy per unit of charge, measured ...
L47-Midterm-EST-Study Guide Enriched 2015
... w = Fg = mg, where w is the weight, Fg is the gravitational force, and m is the mass in kg. Mechanical Energy: These problems are based upon the Law of Conservation of Energy, that the energy in a closed system remains constant. Mechanical energy is the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy ...
... w = Fg = mg, where w is the weight, Fg is the gravitational force, and m is the mass in kg. Mechanical Energy: These problems are based upon the Law of Conservation of Energy, that the energy in a closed system remains constant. Mechanical energy is the sum of the potential energy and kinetic energy ...