Physics 103-02 Exam IV 4 Dec
... A force F = 100 N presses a brake pad against the edge of a spinning disk. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a mo ...
... A force F = 100 N presses a brake pad against the edge of a spinning disk. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a mo ...
Objects that are changing their speed or their direction are said to be
... (such as roller coasters) are characterized by rapid changes in speed and or direction. These rides have large accelerations. Rides such as the carousel result in small accelerations; the speed and direction of the riders change gradually. balanced and unbalanced forces A balanced force results when ...
... (such as roller coasters) are characterized by rapid changes in speed and or direction. These rides have large accelerations. Rides such as the carousel result in small accelerations; the speed and direction of the riders change gradually. balanced and unbalanced forces A balanced force results when ...
revised newton pres
... Newton’s First Law • Law I: Every body persists in the state of rest or moving uniformly straight, except when it is compelled to change its state by the force impressed upon it. This is called Inertia. • Galileo actually discovered inertia, but Newton rephrased it. DUDE YOU THIEF! ...
... Newton’s First Law • Law I: Every body persists in the state of rest or moving uniformly straight, except when it is compelled to change its state by the force impressed upon it. This is called Inertia. • Galileo actually discovered inertia, but Newton rephrased it. DUDE YOU THIEF! ...
VI. Newton`s Third Law
... on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first. ...
... on a second object, the second object exerts an equal but opposite force on the first. ...
EART 160: Planetary Sciences
... • Compare orbital velocity to period • I’ll show this for a circular orbit • Works for elliptical orbit as well, but the derivation is unpleasant and not very informative. • Should recover Kepler’s version if we stick in the Sun’s Mass, keep times in years, and distances in AU. ...
... • Compare orbital velocity to period • I’ll show this for a circular orbit • Works for elliptical orbit as well, but the derivation is unpleasant and not very informative. • Should recover Kepler’s version if we stick in the Sun’s Mass, keep times in years, and distances in AU. ...
Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
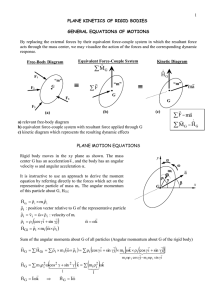
... PLANE KINETICS OF RIGID BODIES GENERAL EQUATIONS OF MOTIONS By replacing the external forces by their equivalent force-couple system in which the resultant force acts through the mass center, we may visualize the action of the forces and the corresponding dynamic ...
... PLANE KINETICS OF RIGID BODIES GENERAL EQUATIONS OF MOTIONS By replacing the external forces by their equivalent force-couple system in which the resultant force acts through the mass center, we may visualize the action of the forces and the corresponding dynamic ...
Science Benchmark 3 Review
... A runner speeds up at the end of a race A car slows down because they ran out of gas It takes more force to stop a bus than a ...
... A runner speeds up at the end of a race A car slows down because they ran out of gas It takes more force to stop a bus than a ...
ppt
... • In the absence of air resistance, all objects accelerate towards Earth at the same rate. • We call this “free-fall” acceleration- meaning gravity is the only force acting on an object. • Because we use this value so often we’ll give it a name- g • What do you think g depends on? ...
... • In the absence of air resistance, all objects accelerate towards Earth at the same rate. • We call this “free-fall” acceleration- meaning gravity is the only force acting on an object. • Because we use this value so often we’ll give it a name- g • What do you think g depends on? ...
Ch 5 & 6 Powerpoint - Taylor County Schools
... work put into a machine is changed into useful output work. Calculated using the following formula: ...
... work put into a machine is changed into useful output work. Calculated using the following formula: ...
19.2 Gravity and the Moon
... where F is the gravitational force (in newtons) M, m are the masses of the attracting bodies (in kilograms) r is the distance between the (centers) of the bodies G is a proportionality constant that depends on units ...
... where F is the gravitational force (in newtons) M, m are the masses of the attracting bodies (in kilograms) r is the distance between the (centers) of the bodies G is a proportionality constant that depends on units ...