File - PhysicsLovers
... potential energy is (g = 10 m/s2) (a) 0.25 J (b) 0.5 J (c) 0.75J (d) 1.0 J A bullet, moving with a speed of 150 m/s, strikes a wooden plank. After passing through the plank, its speed becomes 125 m/s. Another bullet of the same mass and size strikes the plank with a speed of 90 m/s. Its speed after ...
... potential energy is (g = 10 m/s2) (a) 0.25 J (b) 0.5 J (c) 0.75J (d) 1.0 J A bullet, moving with a speed of 150 m/s, strikes a wooden plank. After passing through the plank, its speed becomes 125 m/s. Another bullet of the same mass and size strikes the plank with a speed of 90 m/s. Its speed after ...
Course Review 2
... In a circus act Bimbo, The Human Cannonball, is fired from the muzzle of a cannon that is angled at 600 to the horizontal and sits 3.0 m from the floor. If Bimbo has a mass of 65 kg and leaves the muzzle of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time du ...
... In a circus act Bimbo, The Human Cannonball, is fired from the muzzle of a cannon that is angled at 600 to the horizontal and sits 3.0 m from the floor. If Bimbo has a mass of 65 kg and leaves the muzzle of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time du ...
Document
... c. the forces act at different times. d. All of the above ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. moving objects. b. objects that are not moving. c. objects that are accelerating. d. Both (a) and (b) _____ 8. To accelerate two objects at the same rate, the force used to push the object ...
... c. the forces act at different times. d. All of the above ______ 7. .Newton’s first law of motion applies to a. moving objects. b. objects that are not moving. c. objects that are accelerating. d. Both (a) and (b) _____ 8. To accelerate two objects at the same rate, the force used to push the object ...
HW8 - Bryn Mawr College
... A unif~rul stick of mass M and length I is. suspended horizontally with ~ndB on the edge of a table, and the other end A is held by hand.Point A. As; suddenly released. At the instant after release: (a) What is die. torque around B? (b) Whai is the 'angular acceleration around B? (c)'What is the ver ...
... A unif~rul stick of mass M and length I is. suspended horizontally with ~ndB on the edge of a table, and the other end A is held by hand.Point A. As; suddenly released. At the instant after release: (a) What is die. torque around B? (b) Whai is the 'angular acceleration around B? (c)'What is the ver ...
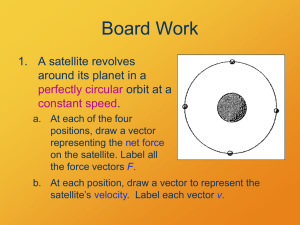
Satellite Motion
... This is the same for a freely falling object. Velocity does not change the force or acceleration. ...
... This is the same for a freely falling object. Velocity does not change the force or acceleration. ...
Physics 108
... Work Energy Theorem The amount of kinetic energy transferred to the object is equal to the work done. DKE = W Many of the problems can be worked from here ...
... Work Energy Theorem The amount of kinetic energy transferred to the object is equal to the work done. DKE = W Many of the problems can be worked from here ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
Newton`s Laws Notes
... An object at rest will remain at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. An object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. a. Also called the law of inertia b. Example: an object travelling through space will continue to move forever until a force (such as gravity ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force. An object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. a. Also called the law of inertia b. Example: an object travelling through space will continue to move forever until a force (such as gravity ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... K.E.= 1/2 . m . v2 Example : Find the kinetic energy of a 400-kg car moving with a speed of 10 m/s. Solution : K.E. = 1/2 . m . v2 = 1/2 . 400 . 100 = 20000j Work-Energy Theorem : Work is change I n kinetic energy. If work is done on an object its the amount of work. W = K.E. ...
... K.E.= 1/2 . m . v2 Example : Find the kinetic energy of a 400-kg car moving with a speed of 10 m/s. Solution : K.E. = 1/2 . m . v2 = 1/2 . 400 . 100 = 20000j Work-Energy Theorem : Work is change I n kinetic energy. If work is done on an object its the amount of work. W = K.E. ...
Work and Energy - mrweaverphysics
... •Predict changes in mechanical energy when positive or negative work is done on the center of mass •Analyze a system and categorize the internal energy as potential, kinetic, or some combination of potential and kinetic. •Solve problems involving work, power, and/or energy •Solve problems involving ...
... •Predict changes in mechanical energy when positive or negative work is done on the center of mass •Analyze a system and categorize the internal energy as potential, kinetic, or some combination of potential and kinetic. •Solve problems involving work, power, and/or energy •Solve problems involving ...