Important Equations in Physics (A2) Unit 1: Non-uniform
... unit newtons, N, always directed towards the centre of the circle of radius r unit m/s2 or rad/s2 direction always towards the centre of the circle Time taken for one complete oscillation. Unit seconds Number of oscillations per second. Unit oscillations per second or hertz or Hz The distance from t ...
... unit newtons, N, always directed towards the centre of the circle of radius r unit m/s2 or rad/s2 direction always towards the centre of the circle Time taken for one complete oscillation. Unit seconds Number of oscillations per second. Unit oscillations per second or hertz or Hz The distance from t ...
Chapter 1. The Birth of Modern Physics
... The statistical interpretation of thermodynamics, through Statistical Mechanics (or Statistical Physics), was establish in the second half of the nineteenth century by Maxwell, Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906), and the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs (1839-1903). This theory bring us closer t ...
... The statistical interpretation of thermodynamics, through Statistical Mechanics (or Statistical Physics), was establish in the second half of the nineteenth century by Maxwell, Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906), and the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs (1839-1903). This theory bring us closer t ...
SHM Dynamics WS (honors)
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
Chapter 6 – Force and Motion II
... - Appears when there is a relative velocity between a fluid and a body. - Opposes the relative motion of a body in a fluid. - Points in the direction in which the fluid flows. ...
... - Appears when there is a relative velocity between a fluid and a body. - Opposes the relative motion of a body in a fluid. - Points in the direction in which the fluid flows. ...
Project1: Automation using Light Sensors
... Isaac Newton, put forth three laws. The first of these laws, sometimes referred to as the law of inertia is that “an object at rest tends to stay at rest, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force”. This essentially means that an object that is still doesn’t want to move, so something else will have ...
... Isaac Newton, put forth three laws. The first of these laws, sometimes referred to as the law of inertia is that “an object at rest tends to stay at rest, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force”. This essentially means that an object that is still doesn’t want to move, so something else will have ...
to the Chapter 3 Instructor`s Manual
... resisting frictional force on the buggy is smaller since it is on wheels. 7. Suppose you have a choice of driving your speeding car head on into a massive concrete wall or hitting an identical car head on. Which would produce the greatest change in the momentum of your car? a. The identical car. b. ...
... resisting frictional force on the buggy is smaller since it is on wheels. 7. Suppose you have a choice of driving your speeding car head on into a massive concrete wall or hitting an identical car head on. Which would produce the greatest change in the momentum of your car? a. The identical car. b. ...
Name
... We all use devices every day that use energy - or more accurately, transfer energy from one form to another. Everything we use wastes energy - some of the energy transfers into forms that are not useful to us. For example when driving a car, energy from burning fuel is transferred into kinetic energ ...
... We all use devices every day that use energy - or more accurately, transfer energy from one form to another. Everything we use wastes energy - some of the energy transfers into forms that are not useful to us. For example when driving a car, energy from burning fuel is transferred into kinetic energ ...
Rotary
... -Angular velocity is the change in angular displacement per unit time. The symbol for angular velocity is ω and the units are typically rad s-1. Angular speed is the magnitude of angular velocity. -The instantaneous angular velocity is given by -Using the formula for angular position and letting ...
... -Angular velocity is the change in angular displacement per unit time. The symbol for angular velocity is ω and the units are typically rad s-1. Angular speed is the magnitude of angular velocity. -The instantaneous angular velocity is given by -Using the formula for angular position and letting ...
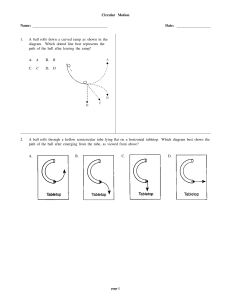
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... When a satellite is a distance R from the center of Earth, the force due to gravity on the satellite is F. What is the force due to gravity on the satellite when its distance from the center of Earth is 3R? A. ...
... When a satellite is a distance R from the center of Earth, the force due to gravity on the satellite is F. What is the force due to gravity on the satellite when its distance from the center of Earth is 3R? A. ...
Unit 1 exercises - Tick ( ) in front of true sentence, And Tick ( ) in
... a. The friction force affects in an opposite direction to the direction of motion. b. The friction force depends on the shape of the surface of two touching objects. c. Ball bearings are used to increase the friction force. d. The pushing of an object forward is opposed by a friction force at the sa ...
... a. The friction force affects in an opposite direction to the direction of motion. b. The friction force depends on the shape of the surface of two touching objects. c. Ball bearings are used to increase the friction force. d. The pushing of an object forward is opposed by a friction force at the sa ...
Physics Fall Midterm Review
... State the law of conservation of momentum Predict the final velocities of objects after collisions, given the initial velocities Identify different types of collisions Determine the changes in kinetic energy during perfectly inelastic collisions Compare conservation of momentum and conserv ...
... State the law of conservation of momentum Predict the final velocities of objects after collisions, given the initial velocities Identify different types of collisions Determine the changes in kinetic energy during perfectly inelastic collisions Compare conservation of momentum and conserv ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #120
... A battery having a potential difference of 180V is connected across a capacitor as shown here. The electric field in the evacuated region between the capacitor plates is uniform. The distance between the plates is 0.6cm and point P is 0.4cm from the lower plate. ...
... A battery having a potential difference of 180V is connected across a capacitor as shown here. The electric field in the evacuated region between the capacitor plates is uniform. The distance between the plates is 0.6cm and point P is 0.4cm from the lower plate. ...