4-2 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... m/s2 is the correct unit for acceleration. Does the sign make sense? The acceleration is in the positive direction because Anudja is pulling in the positive direction with a greater force than Sarah is pulling in the negative direction. Is the magnitude realistic? It is a reasonable acceleration for ...
... m/s2 is the correct unit for acceleration. Does the sign make sense? The acceleration is in the positive direction because Anudja is pulling in the positive direction with a greater force than Sarah is pulling in the negative direction. Is the magnitude realistic? It is a reasonable acceleration for ...
Chapter 8
... If we deal only with conservative forces and If we deal with an isolated system (no energy added or removed): The total mechanical energy of a system remains constant! ...
... If we deal only with conservative forces and If we deal with an isolated system (no energy added or removed): The total mechanical energy of a system remains constant! ...
Limitations on Newton`s 2nd Law
... The phenomenon of "weightlessness" occurs when there is no force of support on your body. When your body is effectively in "free fall", accelerating downward at the acceleration of gravity, then you are not being supported. The sensation of apparent weight comes from the support that you feel from t ...
... The phenomenon of "weightlessness" occurs when there is no force of support on your body. When your body is effectively in "free fall", accelerating downward at the acceleration of gravity, then you are not being supported. The sensation of apparent weight comes from the support that you feel from t ...
Chapter 15
... a spring and undergoes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. The total energy of the system is 2.00 J. ...
... a spring and undergoes simple harmonic motion with a period of 0.250 s. The total energy of the system is 2.00 J. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... The units of mass are kilograms. This is the third fundamental unit (along with meters and seconds) in the MKS system of units. Warning: this unit of kilograms has a prefix (kilo) in the basic unit! This can cause some computational problems, such as converting micrograms into MKS units. A microgram ...
... The units of mass are kilograms. This is the third fundamental unit (along with meters and seconds) in the MKS system of units. Warning: this unit of kilograms has a prefix (kilo) in the basic unit! This can cause some computational problems, such as converting micrograms into MKS units. A microgram ...
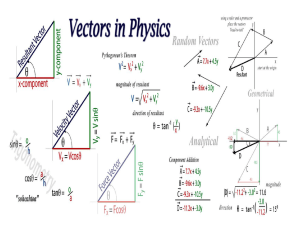
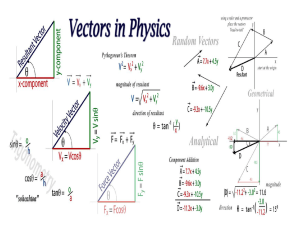
IB Physics Vector Presentation
... q (direction) • length proportional to amount • direction measured by angle ...
... q (direction) • length proportional to amount • direction measured by angle ...
Newton`s Second Law NTG (Hewitt) PPT
... Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. ...
... Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. ...
SIMPLE MACHINES
... simple machines One of six basic types of machines which are basis for all other forms of machines. have a rigid arm and a fulcrum. six types divided into two families. lever family: inclined plane family: simple lever ...
... simple machines One of six basic types of machines which are basis for all other forms of machines. have a rigid arm and a fulcrum. six types divided into two families. lever family: inclined plane family: simple lever ...
Purdue University PHYS221 EXAM I September 30,2003
... Each chamber in the figure below has unique magnetic field. A particles with charge +25 mC and mass of 10-10 kg enters the right chamber where B = 1.0 T directed into the page, with a velocity of 75 m/s. At what velocity does it leave the second chamber? The magnetic field in the second chamber is 0 ...
... Each chamber in the figure below has unique magnetic field. A particles with charge +25 mC and mass of 10-10 kg enters the right chamber where B = 1.0 T directed into the page, with a velocity of 75 m/s. At what velocity does it leave the second chamber? The magnetic field in the second chamber is 0 ...
Newtons Laws force mass and momentum 10710
... What does F = ma mean? Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ...
... What does F = ma mean? Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ...
Only external forces affect the motion of the center of mass
... a velocity of V0. It collides with a block of mass M, initially at rest. 1) What is the change in kinetic energy of the system of two balls: a) if the collision is perfectly elastic; b) if the collision is perfectly inelastic (balls stick together after collision). 2) For m = M = m0, find the veloci ...
... a velocity of V0. It collides with a block of mass M, initially at rest. 1) What is the change in kinetic energy of the system of two balls: a) if the collision is perfectly elastic; b) if the collision is perfectly inelastic (balls stick together after collision). 2) For m = M = m0, find the veloci ...
Lunar Base Supply Egg Drop - NSTA Learning Center
... The greater the force, the greater the acceleration The greater the mass, the greater the force needed for the same acceleration Calculated by: F = ma (F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration) ...
... The greater the force, the greater the acceleration The greater the mass, the greater the force needed for the same acceleration Calculated by: F = ma (F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration) ...