A note on the conservation of mechanical energy and the Galilean
... the system is isolated and also that the internal forces can be classified into two sets, namely the set of conservative forces and the set of forces whose total work is zero. Denoting by xi the position and by vi the velocity of particle of mass mi with respect to an arbitrarily chosen inertial ref ...
... the system is isolated and also that the internal forces can be classified into two sets, namely the set of conservative forces and the set of forces whose total work is zero. Denoting by xi the position and by vi the velocity of particle of mass mi with respect to an arbitrarily chosen inertial ref ...
Version A of Chapter 11 Quiz
... ____ 15. What is the speed of a bobsled whose distance-time graph indicates that it traveled 250 m in 25 s? a. 4 m/s c. 0.25 mph b. 250 m/s d. 10 m/s ____ 16. A distance-time graph indicates that an object moves 100 m in 4 s , remains at rest for 1 s, and then moves 150 m in 5 s. What is the average ...
... ____ 15. What is the speed of a bobsled whose distance-time graph indicates that it traveled 250 m in 25 s? a. 4 m/s c. 0.25 mph b. 250 m/s d. 10 m/s ____ 16. A distance-time graph indicates that an object moves 100 m in 4 s , remains at rest for 1 s, and then moves 150 m in 5 s. What is the average ...
Physics trivia
... All the energy comes from the work done to pull the train of cars up the lift hill. This is stored as potential energy. That energy is then converted into motion (kinetic energy) and is eventually consumed by the non-conservative forces acting on the cars -- mostly friction from the wheels, and air ...
... All the energy comes from the work done to pull the train of cars up the lift hill. This is stored as potential energy. That energy is then converted into motion (kinetic energy) and is eventually consumed by the non-conservative forces acting on the cars -- mostly friction from the wheels, and air ...
Gravitational Potential Energy
... Conservative and Nonconservative Forces • A conservative force allows conversion between kinetic and potential energy. Gravity and the spring force are conservative. • The work done between two points by any conservative force a) can be expressed in terms of a potential energy function. ...
... Conservative and Nonconservative Forces • A conservative force allows conversion between kinetic and potential energy. Gravity and the spring force are conservative. • The work done between two points by any conservative force a) can be expressed in terms of a potential energy function. ...
Universal Law of Gravitation Problems
... (a) The strength of the magnetic field is increased. (b) An electric field is added, in the same direction as the magnetic field. (c) The magnetic field is removed. 6. A straight wire 15 cm long, with a current of 12 A, lying at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, experiences a magnetic force ...
... (a) The strength of the magnetic field is increased. (b) An electric field is added, in the same direction as the magnetic field. (c) The magnetic field is removed. 6. A straight wire 15 cm long, with a current of 12 A, lying at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, experiences a magnetic force ...
iGCSE Physics Specification Questions Forces and Motion 1. What
... 12. Describe what happens to an object as it falls in terms of the forces acting on it and its motion. 13. What equation relates stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance? 14. What factors affect thinking distance? 15. What factors affect braking distance? 16. What is the relationshi ...
... 12. Describe what happens to an object as it falls in terms of the forces acting on it and its motion. 13. What equation relates stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance? 14. What factors affect thinking distance? 15. What factors affect braking distance? 16. What is the relationshi ...
Student Checklist - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 2. Explain how Aristotle and Galileo/Newton differed in their explanations of why objects stay moving and why objects stop moving. 3. Interpret how inertia helps to explain the motion of objects. 4. Explain the relationship between mass and inertia. 5. Explain what causes an object to change its mot ...
... 2. Explain how Aristotle and Galileo/Newton differed in their explanations of why objects stay moving and why objects stop moving. 3. Interpret how inertia helps to explain the motion of objects. 4. Explain the relationship between mass and inertia. 5. Explain what causes an object to change its mot ...
Edexcel Certificate/IGCSE Physics questions from the specification
... 12. Describe what happens to an object as it falls in terms of the forces acting on it and its motion. 13. What equation relates stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance? 14. What factors affect thinking distance? 15. What factors affect braking distance? 16. What is the relationshi ...
... 12. Describe what happens to an object as it falls in terms of the forces acting on it and its motion. 13. What equation relates stopping distance, thinking distance and braking distance? 14. What factors affect thinking distance? 15. What factors affect braking distance? 16. What is the relationshi ...
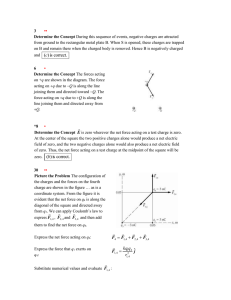
Solution - Jobworks Physics
... Now k is slightly different for situations in either air or a vacuum, but for us we will round this value off to be 9.0 x 109 Nm2/C2 Coulomb's Law is sometimes also written as: F = (1/4πεo)(q1q2/r2) The quantity εo is called the permittivity of free space. For a deeper explanation of what this is an ...
... Now k is slightly different for situations in either air or a vacuum, but for us we will round this value off to be 9.0 x 109 Nm2/C2 Coulomb's Law is sometimes also written as: F = (1/4πεo)(q1q2/r2) The quantity εo is called the permittivity of free space. For a deeper explanation of what this is an ...
Answer - whoawiki
... Because the mass of the Earth is greater than the mass of the moon it has a greater gravitational pull. If the mass (the amount of matter in an object) remains the same and the “ g “ increases so does the weight. ...
... Because the mass of the Earth is greater than the mass of the moon it has a greater gravitational pull. If the mass (the amount of matter in an object) remains the same and the “ g “ increases so does the weight. ...