Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Explain terminal speed and velocity. Use motion graphs and free-body diagrams to illustrate falling objects. Explain how acceleration rates change for falling objects as they approach terminal velocity. 10. Evaluate differences in how object fall through the atmosphere. 11. Explain the two component ...
... Explain terminal speed and velocity. Use motion graphs and free-body diagrams to illustrate falling objects. Explain how acceleration rates change for falling objects as they approach terminal velocity. 10. Evaluate differences in how object fall through the atmosphere. 11. Explain the two component ...
File - Science Stuff
... thermally, when a warmer object is in contact with a cooler one; 2) mechanically, when two objects push or pull on each other over a distance; 3) electrically, when an electrical source such as a battery or generator is connected in a complete circuit to an electrical device; or 4) by electromagneti ...
... thermally, when a warmer object is in contact with a cooler one; 2) mechanically, when two objects push or pull on each other over a distance; 3) electrically, when an electrical source such as a battery or generator is connected in a complete circuit to an electrical device; or 4) by electromagneti ...
1 Determining the Charge of an Electron: The Millikan Oil Drop
... divisions, you will be able to determine its actual speed in meters per second. 7) Pump the atomizer bulb 2 times to inject a cloud of particles into the electrode chamber. Allow the faster moving particles to clear, and then pick a particle that is slowly moving upward. Wait for it to cross a scale ...
... divisions, you will be able to determine its actual speed in meters per second. 7) Pump the atomizer bulb 2 times to inject a cloud of particles into the electrode chamber. Allow the faster moving particles to clear, and then pick a particle that is slowly moving upward. Wait for it to cross a scale ...
Please tear off this top page carefully (only the top page!!!). The
... The balls then roll down the ramp without slipping (neglect air resistance). The two balls reach the bottom of the ramp at the same time. a. True b. False 2. A wheel is spinning clockwise and slowing down. The wheel’s angular velocity and angular acceleration vectors point in opposite directions. a. ...
... The balls then roll down the ramp without slipping (neglect air resistance). The two balls reach the bottom of the ramp at the same time. a. True b. False 2. A wheel is spinning clockwise and slowing down. The wheel’s angular velocity and angular acceleration vectors point in opposite directions. a. ...
File
... The electric motor transforms electrical energy to kinetic energy. The kinetic energy is then transformed into useful ..................................................... energy. ...
... The electric motor transforms electrical energy to kinetic energy. The kinetic energy is then transformed into useful ..................................................... energy. ...
Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension
... When impulse and momentum were introduced, we used an example of a batted ball to discuss the impulse and momentum change that occurred with the ball. At the time, we did not consider what had happened to the bat. According to Newton’s third law, however, when the bat exerted a force on the ball, th ...
... When impulse and momentum were introduced, we used an example of a batted ball to discuss the impulse and momentum change that occurred with the ball. At the time, we did not consider what had happened to the bat. According to Newton’s third law, however, when the bat exerted a force on the ball, th ...
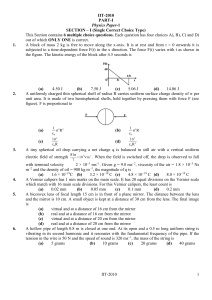
IIT Paper 2010 - auroraclasses.org
... This Section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Paragraphs for Question 50 To 52 When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in t ...
... This Section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct. Paragraphs for Question 50 To 52 When liquid medicine of density ρ is to be put in t ...
Linear Momentum and Collisions
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
... Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients o ...
Physics 12
... 4. Two equal charges contain a total of 3.5 J of potential energy when they are 5.6 m apart. What is the charge of one of the particles? 5. A 34 μC positive charge is initially placed 2.6 m away from a 78 μC positive charge. The 34 μC charge is then moved to a position of 1.2 m away from the 78 μC c ...
... 4. Two equal charges contain a total of 3.5 J of potential energy when they are 5.6 m apart. What is the charge of one of the particles? 5. A 34 μC positive charge is initially placed 2.6 m away from a 78 μC positive charge. The 34 μC charge is then moved to a position of 1.2 m away from the 78 μC c ...
particle level: forces and fields
... words, the point in space at which we set the potential energy to zero can be chosen at will. This implies that only differences in potential energies between different points in space have any physical significance. – The difference in potential energy between two points represents the net energy t ...
... words, the point in space at which we set the potential energy to zero can be chosen at will. This implies that only differences in potential energies between different points in space have any physical significance. – The difference in potential energy between two points represents the net energy t ...
Scaling laws in the macro-, micro- and nanoworlds
... When a body falls ‘vertically’ in a fluid, viscous friction is such that, after a certain time, it falls with constant velocity vlim . The transient time τ , is proportional to vlim . If the body is spherical, with radius r, the limiting velocity is given by vlim = 4ρgr 3 /18ηr, where η is the visco ...
... When a body falls ‘vertically’ in a fluid, viscous friction is such that, after a certain time, it falls with constant velocity vlim . The transient time τ , is proportional to vlim . If the body is spherical, with radius r, the limiting velocity is given by vlim = 4ρgr 3 /18ηr, where η is the visco ...
Rotational kinetic energy
... 1. Using the values for the maximum angular velocity (ωmax) of the smart pulley, calculate the angular velocity (ω) of the rotating disk, using the formula, ωD =ωmax (Rp/R). Record the values in Table I. 2. Using the calculated values for the angular velocity (ω) of the disk and the dimensions of th ...
... 1. Using the values for the maximum angular velocity (ωmax) of the smart pulley, calculate the angular velocity (ω) of the rotating disk, using the formula, ωD =ωmax (Rp/R). Record the values in Table I. 2. Using the calculated values for the angular velocity (ω) of the disk and the dimensions of th ...
Homework due 5-8
... A ferryboat of mass M1= 2.0 x 105 kilograms moves toward a docking bumper of mass M 2 that is attached to a shock absorber. Shown below is a speed v vs. time t graph of the ferryboat from the time it cuts off its engines to the time it first comes to rest after colliding with the bumper. At the inst ...
... A ferryboat of mass M1= 2.0 x 105 kilograms moves toward a docking bumper of mass M 2 that is attached to a shock absorber. Shown below is a speed v vs. time t graph of the ferryboat from the time it cuts off its engines to the time it first comes to rest after colliding with the bumper. At the inst ...
Newton`s Wagon - Newton`s Laws
... What happens when you kick a soccer ball? The ‘kick’ is the external force that Newton was talking about in his first law of motion. What happens to the ball after you kick it? The ball continues in a straight line as long as it can, until air drag, rolling resistance, and gravity, all of which ca ...
... What happens when you kick a soccer ball? The ‘kick’ is the external force that Newton was talking about in his first law of motion. What happens to the ball after you kick it? The ball continues in a straight line as long as it can, until air drag, rolling resistance, and gravity, all of which ca ...