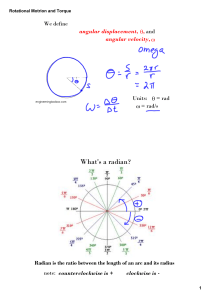
Name Date Per ______ Physics – Std 5e: Electrostatics and
... (a) magnitude of electric charges (b) separation distance between electric charges (c) both of these (d) none of these 6. Rub electrons from your hair with a comb and the comb becomes: (a) negatively charged (b) positively charged 7. Two protons attract each other gravitationally and repel each othe ...
... (a) magnitude of electric charges (b) separation distance between electric charges (c) both of these (d) none of these 6. Rub electrons from your hair with a comb and the comb becomes: (a) negatively charged (b) positively charged 7. Two protons attract each other gravitationally and repel each othe ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetic Forces
... D 3 - R T 2 8 : M O V I N G C H A R G E A L O N G A STRAIGHT C U R R E N T - C A R R Y I N G W I R E — A C C E L E R A T I O N ...
... D 3 - R T 2 8 : M O V I N G C H A R G E A L O N G A STRAIGHT C U R R E N T - C A R R Y I N G W I R E — A C C E L E R A T I O N ...
Exam: ETEN15 Accelerators, Particles and Fields, March 14
... Determine the position (x(t), y(t), z(t)) of the proton for t > 0. b) At what time T does the proton come back to the origin when E0 = 0? c) Assume that E0 > 0 and that the speed of the proton is non-relativistic. Determine the position (x(t), y(t), z(t)) of the proton for t > 0. d) Assume that E0 > ...
... Determine the position (x(t), y(t), z(t)) of the proton for t > 0. b) At what time T does the proton come back to the origin when E0 = 0? c) Assume that E0 > 0 and that the speed of the proton is non-relativistic. Determine the position (x(t), y(t), z(t)) of the proton for t > 0. d) Assume that E0 > ...
Ch. 19 Magnetism
... Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor We just saw how a magnetic field interacts with a single moving charge. Since a current carrying conductor (such as a wire) contains multiple moving charges, a magnetic field will exert a force on the ...
... Magnetic force on a current carrying conductor We just saw how a magnetic field interacts with a single moving charge. Since a current carrying conductor (such as a wire) contains multiple moving charges, a magnetic field will exert a force on the ...
Newton`s Second Law with Constant Mass
... while keeping the mass of the object constant. We shall keep in mind that the acceleration of the object is defined as the change of velocity with time i. e. it is the derivative of its velocity with respect to time. ...
... while keeping the mass of the object constant. We shall keep in mind that the acceleration of the object is defined as the change of velocity with time i. e. it is the derivative of its velocity with respect to time. ...
Scalar potential
... The electric field is a fundamental concept, with well-defined empirical content and meaning, which generalizes Coulomb’s law We will once again use the Helmholtz’ theorem to introduce ...
... The electric field is a fundamental concept, with well-defined empirical content and meaning, which generalizes Coulomb’s law We will once again use the Helmholtz’ theorem to introduce ...
Slide 1
... coil of wire It is a ______________________ that is attached to a paper cone. When current passes through the wire, the magnetic force makes the paper cone move. ...
... coil of wire It is a ______________________ that is attached to a paper cone. When current passes through the wire, the magnetic force makes the paper cone move. ...
FP-1st Sem Final Review-11
... calculated? What are its units? What is its symbol? Distance vs. displacement-How are they alike? How are they different? How is each defined? Average velocity-How is it defined in words and in symbols. What is the equation for it? What are its units? What is its symbol? How is it calculated? Avera ...
... calculated? What are its units? What is its symbol? Distance vs. displacement-How are they alike? How are they different? How is each defined? Average velocity-How is it defined in words and in symbols. What is the equation for it? What are its units? What is its symbol? How is it calculated? Avera ...
SECTION B ( 48 marks )
... volume of 0.02 m3 to a volume 0.03 m3. The increase in internal energy of the gas is A. 500 J B. 1000 J C. 1500 J D. 2500 J 35. A uniform wire is stretched under tension. The strain in the wire depends on (1) the cross-sectional area of the wire. (2) the Young modulus of the wire. (3) the unstretche ...
... volume of 0.02 m3 to a volume 0.03 m3. The increase in internal energy of the gas is A. 500 J B. 1000 J C. 1500 J D. 2500 J 35. A uniform wire is stretched under tension. The strain in the wire depends on (1) the cross-sectional area of the wire. (2) the Young modulus of the wire. (3) the unstretche ...
Document
... The following statements can be thought of as the definition of inertial reference frames. An IRF is a reference frame that is not accelerating (or rotating) with respect to the “fixed stars”. If one IRF exists, infinitely many exist since they are related by any arbitrary constant velocity vector ...
... The following statements can be thought of as the definition of inertial reference frames. An IRF is a reference frame that is not accelerating (or rotating) with respect to the “fixed stars”. If one IRF exists, infinitely many exist since they are related by any arbitrary constant velocity vector ...