Physics 1520, Spring 2013
... 1. Four lightweight balls A, B, C, and D are suspended by threads. Ball A has been touched by a charged rod (with unknown charge). When the balls are brought close together, without touching, the following observations are made: –Balls B, C, and D are attracted to ball A. –Balls B and D have no effe ...
... 1. Four lightweight balls A, B, C, and D are suspended by threads. Ball A has been touched by a charged rod (with unknown charge). When the balls are brought close together, without touching, the following observations are made: –Balls B, C, and D are attracted to ball A. –Balls B and D have no effe ...
Giancoli, PHYSICS,6/E
... causes it to undergo two displacements. The first has a magnitude of 150 cm and makes a angle of 1200 with the positive x-axis. The resultant displacement has a magnitude of 140 cm and is directed at an angle of 35.00 to the positive x axis. Find the magnitude and direction of the second displacemen ...
... causes it to undergo two displacements. The first has a magnitude of 150 cm and makes a angle of 1200 with the positive x-axis. The resultant displacement has a magnitude of 140 cm and is directed at an angle of 35.00 to the positive x axis. Find the magnitude and direction of the second displacemen ...
pages 251-300 - Light and Matter
... example 2 The motorcyclist in figure h is moving along an arc of a circle. It looks like he’s chosen to ride the slanted surface of the dirt at a place where it makes just the angle he wants, allowing him to get the force he needs on the tires as a normal force, without needing any frictional force. ...
... example 2 The motorcyclist in figure h is moving along an arc of a circle. It looks like he’s chosen to ride the slanted surface of the dirt at a place where it makes just the angle he wants, allowing him to get the force he needs on the tires as a normal force, without needing any frictional force. ...
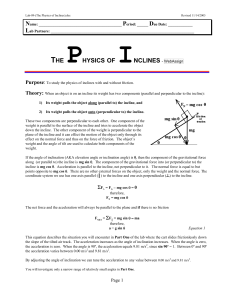
Lab-09-(The Physics of Inclines)
... along (or parallel to) the incline is mg sin θ. Τhe component of the gravitational force into (or perpendicular to) the incline is mg cos θ. Acceleration is parallel to the incline, not perpendicular to it. The normal force is equal to but points opposite to mg cos θ. There are no other external for ...
... along (or parallel to) the incline is mg sin θ. Τhe component of the gravitational force into (or perpendicular to) the incline is mg cos θ. Acceleration is parallel to the incline, not perpendicular to it. The normal force is equal to but points opposite to mg cos θ. There are no other external for ...
2015 Physics Guide
... If the initial vertical drop of the Boomerang takes 3.0 seconds and a speed of 25 meters per second is reached, what is its average rate of acceleration? How does this rate of acceleration compare to a body in free fall? ...
... If the initial vertical drop of the Boomerang takes 3.0 seconds and a speed of 25 meters per second is reached, what is its average rate of acceleration? How does this rate of acceleration compare to a body in free fall? ...
Monday, Nov. 11, 2002
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
... Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let’s consider a two particle system where the two exert forces on each other. ...
Chapter 4 DEFINITION OF QUANTITIES EVALUATED BY WAMIT
... The forces and other quantities evaluated by WAMIT are output in a standard nondimensional form, in terms of the appropriate combinations of the water density ρ, the acceleration of gravity g, the incident-wave amplitude A, frequency ω,and the length scale L defined by the input parameter ULEN in the ...
... The forces and other quantities evaluated by WAMIT are output in a standard nondimensional form, in terms of the appropriate combinations of the water density ρ, the acceleration of gravity g, the incident-wave amplitude A, frequency ω,and the length scale L defined by the input parameter ULEN in the ...
THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT
... 2. Why is the field view preferable to the action-at-a-distance view of forces? ____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
... 2. Why is the field view preferable to the action-at-a-distance view of forces? ____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ ...
AP1 Rotation - APlusPhysics
... in the system’s rotational inertia, and hence in its angular velocity and linear speed for a given angular momentum. SP: 1.4 The student can use representations and models to analyze situations or solve problems qualitatively and quantitatively. 3.3 The student can evaluate scientific questions. LO: ...
... in the system’s rotational inertia, and hence in its angular velocity and linear speed for a given angular momentum. SP: 1.4 The student can use representations and models to analyze situations or solve problems qualitatively and quantitatively. 3.3 The student can evaluate scientific questions. LO: ...
1986E1. Three point charges produce the electric equipotential lines
... ii. On the following diagram, show the direction of the force(s) acting on an electron after it enters the region between the plates. iii. On the diagram of the parallel plates above, show the trajectory of an electron that will exit through the small hole at position B. b. Determine the magnitude o ...
... ii. On the following diagram, show the direction of the force(s) acting on an electron after it enters the region between the plates. iii. On the diagram of the parallel plates above, show the trajectory of an electron that will exit through the small hole at position B. b. Determine the magnitude o ...
REVIEW: • ELECTRIC FORCE, ELECTRIC FIELD, • ELECTRIC
... • E vector at a point in space is tangent to the EFL through that point • “Density” of EFL is proportional to E (magnitude) in that region o Larger E → closer packing of lines • EFL start on positive charges and end on negative charges • Number of EFL starting/ending on charge is proportional to its ...
... • E vector at a point in space is tangent to the EFL through that point • “Density” of EFL is proportional to E (magnitude) in that region o Larger E → closer packing of lines • EFL start on positive charges and end on negative charges • Number of EFL starting/ending on charge is proportional to its ...