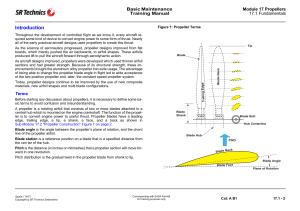
Year 11 2 Unit Physics Preliminary Exam 2007 General Instructions
... >C is required for total internal reflection. Intensity is proportional to 1/r2. F = qE and F = ma. Hence ma = qE or a = qE/m in the opposite direction of the field, as the particle is negatively charged. The voltage across the globe (and hence the power produced by the globe) is greatest in the ...
... >C is required for total internal reflection. Intensity is proportional to 1/r2. F = qE and F = ma. Hence ma = qE or a = qE/m in the opposite direction of the field, as the particle is negatively charged. The voltage across the globe (and hence the power produced by the globe) is greatest in the ...
Chapters 2, 3, and 4
... Fall 2005 Pflugerville ISD Cite: http://grove.ufl.edu/~bratt/Manatee%20and%20Researches/Fractals/rough%20surface%20of%20%20a%20glass.jpg ...
... Fall 2005 Pflugerville ISD Cite: http://grove.ufl.edu/~bratt/Manatee%20and%20Researches/Fractals/rough%20surface%20of%20%20a%20glass.jpg ...
8.07 Class Notes Fall 2010
... 13.6 The dilemma of the late 1800's physicist .......................................................... 95 13.7 The transformation of space and time ............................................................... 96 14 Transformation of Sources and Fields ........................................... ...
... 13.6 The dilemma of the late 1800's physicist .......................................................... 95 13.7 The transformation of space and time ............................................................... 96 14 Transformation of Sources and Fields ........................................... ...
Physics Mechanics
... nature of an object to stop once set in motion. This approach to motion was later formalized by Newton in a form that has come to be known as Newton’s first law of motion: “An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity, unless it experiences a ...
... nature of an object to stop once set in motion. This approach to motion was later formalized by Newton in a form that has come to be known as Newton’s first law of motion: “An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity, unless it experiences a ...
THE ORIGIN OF ELECTRICITY
... net charge, as part c of the picture shows. The process of giving one object a net electm charge without touching the object to a second charged object is called charging byin. duction. The process could also be used to give the sphere a negative net charge,if a posi. tively charged rod were used. T ...
... net charge, as part c of the picture shows. The process of giving one object a net electm charge without touching the object to a second charged object is called charging byin. duction. The process could also be used to give the sphere a negative net charge,if a posi. tively charged rod were used. T ...
Giancoli Ch 8.Word
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
CHAPTER 8
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
R - IBPhysics2016
... Potential and potential energy – gravitational Gravitational potential is derived from gravitational potential energy and is thus a scalar. There is no need to worry about vectors. EXAMPLE: Find the gravitational potential r at the midpoint of the 2750-m radius circle of 125-kg masses shown. SOLUTI ...
... Potential and potential energy – gravitational Gravitational potential is derived from gravitational potential energy and is thus a scalar. There is no need to worry about vectors. EXAMPLE: Find the gravitational potential r at the midpoint of the 2750-m radius circle of 125-kg masses shown. SOLUTI ...
GCE Physics A AS and A Level Specification
... phone when you need to speak to a person about an important issue. We will always try to resolve issues the first time you contact us but, should that not be possible, we will always come back to you (by telephone, email or letter) and keep working with you to find the solution. ...
... phone when you need to speak to a person about an important issue. We will always try to resolve issues the first time you contact us but, should that not be possible, we will always come back to you (by telephone, email or letter) and keep working with you to find the solution. ...
PM6-93
... coefficient of friction µ can vary with the load N. This can happen if the layers are such that they remain intact at low loads but break down at higher loads. The coefficient of friction then changes from that for surface layer sliding on surface layer to that of metal on metal or metal on surface ...
... coefficient of friction µ can vary with the load N. This can happen if the layers are such that they remain intact at low loads but break down at higher loads. The coefficient of friction then changes from that for surface layer sliding on surface layer to that of metal on metal or metal on surface ...
MOTIONS OF CELESTIAL BODIES: COMPUTER SIMULATIONS
... opportunity to perform interesting mini-research projects in physics and astronomy. Computer simulations in PLANETS AND SATELLITES enable students to see clearly how the systems that obey simple and precise physical laws behave, sometimes in unexpected and even irregular, chaotic ways. Although desi ...
... opportunity to perform interesting mini-research projects in physics and astronomy. Computer simulations in PLANETS AND SATELLITES enable students to see clearly how the systems that obey simple and precise physical laws behave, sometimes in unexpected and even irregular, chaotic ways. Although desi ...