Lx lecture on magnetic properties and microstructure
... directions (as discussed previously). • Can we estimate how much energy it takes to pull a domain away from its preferred direction? Answer: yes, easily. How? Integrate the area under the curve for an easy direction and compare that to the curve for a hard direction. • The area that we need is given ...
... directions (as discussed previously). • Can we estimate how much energy it takes to pull a domain away from its preferred direction? Answer: yes, easily. How? Integrate the area under the curve for an easy direction and compare that to the curve for a hard direction. • The area that we need is given ...
DISCOVERING AND ANALYZING MAGNETIC FIELDS
... decided to double the number of loops on the solenoid by putting another layer of wire on top of the previous layer without making the solenoid any longer, that student would find that the solenoid is stronger, as predicted by Equation 1. If the number of loops was doubled, then N would be twice as ...
... decided to double the number of loops on the solenoid by putting another layer of wire on top of the previous layer without making the solenoid any longer, that student would find that the solenoid is stronger, as predicted by Equation 1. If the number of loops was doubled, then N would be twice as ...
“The Language of the Permanent Magnet Industry”
... of magnets. Dipole ring magnets are cylindrically shaped, with magnets placed along the circumference of the cylinder cross sections. The segment magnets are pasted into place in such a way that the magnetic orientation direction is continuous. Direction of Magnetization – This refers to the "easy a ...
... of magnets. Dipole ring magnets are cylindrically shaped, with magnets placed along the circumference of the cylinder cross sections. The segment magnets are pasted into place in such a way that the magnetic orientation direction is continuous. Direction of Magnetization – This refers to the "easy a ...
An Experimental Study of Plasma Detachment
... A laboratory experiment set on adequately measuring and quantifying the physics involved in the final stages of plasma flowing through a magnetic nozzle, the separation of the magnetized plasma from the field lines that form the nozzle, should have to meet a number of specific required conditions1,1 ...
... A laboratory experiment set on adequately measuring and quantifying the physics involved in the final stages of plasma flowing through a magnetic nozzle, the separation of the magnetized plasma from the field lines that form the nozzle, should have to meet a number of specific required conditions1,1 ...
Muon spin rotation
... NMR and diffraction techniques. The NMR technique which is closest parallel to µSR is “pulsed NMR”, in which one observes time-dependent transverse nuclear polarization or a so-called “free induction decay” of the nuclear polarization. However, a key difference is the fact that in µSR one uses a spe ...
... NMR and diffraction techniques. The NMR technique which is closest parallel to µSR is “pulsed NMR”, in which one observes time-dependent transverse nuclear polarization or a so-called “free induction decay” of the nuclear polarization. However, a key difference is the fact that in µSR one uses a spe ...
Magnetic reconnection and relaxation phenomena in Spherical Tokamak
... (x, y) plane, which is formed in a driven reconnection process. This was a result we obtained numerically when we proposed the driven concept. The structure is created as a result of a nonlinear deformation driven by the external flow. It exhibits completely different figure from the structure of th ...
... (x, y) plane, which is formed in a driven reconnection process. This was a result we obtained numerically when we proposed the driven concept. The structure is created as a result of a nonlinear deformation driven by the external flow. It exhibits completely different figure from the structure of th ...
Chapter 8: Magnetism - Farmingdale State College
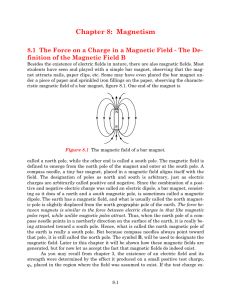
... dipole. The earth has a magnetic field, and what is usually called the north magnetic pole is slightly displaced from the north geographic pole of the earth. The force between magnets is similar to the force between electric charges in that like magnetic poles repel, while unlike magnetic poles attr ...
... dipole. The earth has a magnetic field, and what is usually called the north magnetic pole is slightly displaced from the north geographic pole of the earth. The force between magnets is similar to the force between electric charges in that like magnetic poles repel, while unlike magnetic poles attr ...
Electromagnetic Fields inside a Perfect Conductor
... In a broader vision of (quantum) electrodynamics, where “initial” conditions can include nonzero energy, the interior magnetic field of a perfect conductor can be nonzero, but timeindependent, in the rest frame of the conductor. A major challenge for “classical” electrodynamics is to provide a descr ...
... In a broader vision of (quantum) electrodynamics, where “initial” conditions can include nonzero energy, the interior magnetic field of a perfect conductor can be nonzero, but timeindependent, in the rest frame of the conductor. A major challenge for “classical” electrodynamics is to provide a descr ...
Neutron magnetic moment

The neutron magnetic moment is the intrinsic magnetic dipole moment of the neutron, symbol μn. Protons and neutrons, both nucleons, comprise the nucleus of atoms, and both nucleons behave as small magnets whose strengths are measured by their magnetic moments. The neutron interacts with normal matter primarily through the nuclear force and through its magnetic moment. The neutron's magnetic moment is exploited to probe the atomic structure of materials using scattering methods and to manipulate the properties of neutron beams in particle accelerators. The neutron was determined to have a magnetic moment by indirect methods in the mid 1930s. Luis Alvarez and Felix Bloch made the first accurate, direct measurement of the neutron's magnetic moment in 1940. The existence of the neutron's magnetic moment indicates the neutron is not an elementary particle. For an elementary particle to have an intrinsic magnetic moment, it must have both spin and electric charge. The neutron has spin 1/2 ħ, but it has no net charge. The existence of the neutron's magnetic moment was puzzling and defied a correct explanation until the quark model for particles was developed in the 1960s. The neutron is composed of three quarks, and the magnetic moments of these elementary particles combine to give the neutron its magnetic moment.