1. Object A has a charge of 2 nC, and object B has a charge of 6 nC
... 8. A test charge of 3 µC is at a point P where an external electric field is directed to the right and has a magnitude of 4 106 N/C. If the test charge is replaced with another test charge of - 3 µC, the external electric field at P . (a) is unaffected ...
... 8. A test charge of 3 µC is at a point P where an external electric field is directed to the right and has a magnitude of 4 106 N/C. If the test charge is replaced with another test charge of - 3 µC, the external electric field at P . (a) is unaffected ...
Homework Set 6
... directed toward the left along the axis of both coils. (a) As the current from the battery, and the leftward field it produces, increase in magnitude, the induced current in the leftmost coil opposes the increased leftward field by flowing right to left through R and producing a field directed towar ...
... directed toward the left along the axis of both coils. (a) As the current from the battery, and the leftward field it produces, increase in magnitude, the induced current in the leftmost coil opposes the increased leftward field by flowing right to left through R and producing a field directed towar ...
HW00 - Review Problems
... amps, the circuit breaker will trip, stopping the current). Estimate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance of 10 cm from a long straight wire carrying a current of 10 A. Compare ...
... amps, the circuit breaker will trip, stopping the current). Estimate the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance of 10 cm from a long straight wire carrying a current of 10 A. Compare ...
Modelling Protogalactic Collapse and Magnetic Field Evolution with FLASH Chris Orban
... where B is in units of gauss and ω is in units of hertz. The constant α is determined from the ratio of the extra terms that were brought in to generalize Eqs. (6) and (17) (and specifically from the proportionality between the electron number density ne and electron pressure Pe to the actual densit ...
... where B is in units of gauss and ω is in units of hertz. The constant α is determined from the ratio of the extra terms that were brought in to generalize Eqs. (6) and (17) (and specifically from the proportionality between the electron number density ne and electron pressure Pe to the actual densit ...
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 21 Giancoli Physics: Principles with
... from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials ...
... from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials ...
electromagnets arrangement for electromagnetic
... The objective of this paper is to analyse the superior electromagnet placement to apply strong forces on the corresponding magnets used as automotive windshield wipers with different configuration as a replacement to conventional motors. The electromagnetics are engaged to observe the solenoids attr ...
... The objective of this paper is to analyse the superior electromagnet placement to apply strong forces on the corresponding magnets used as automotive windshield wipers with different configuration as a replacement to conventional motors. The electromagnetics are engaged to observe the solenoids attr ...
Ch. 22: Magnetism (Dr. Andrei Galiautdinov, UGA)
... (b) Calculate the magnitude of the net magnetic field at points A and B. (a) According to the RHR, the magnetic field due to each current is out of the page at A, whereas at B, the field due to the 6.2 A current is into the page and the field due to the 4.5 A current is out of the page. So, since th ...
... (b) Calculate the magnitude of the net magnetic field at points A and B. (a) According to the RHR, the magnetic field due to each current is out of the page at A, whereas at B, the field due to the 6.2 A current is into the page and the field due to the 4.5 A current is out of the page. So, since th ...
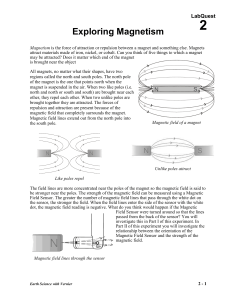
02 Expl Magnet LQ
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion between a magnet and something else. Magnets attract materials made of iron, nickel, or cobalt. Can you think of five things to which a magnet may be attracted? Does it matter which end of the magnet is brought near the object All magnets, no matter ...
... Magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion between a magnet and something else. Magnets attract materials made of iron, nickel, or cobalt. Can you think of five things to which a magnet may be attracted? Does it matter which end of the magnet is brought near the object All magnets, no matter ...
magnetism - davis.k12.ut.us
... Magnets are used constantly in today’s homes. All electric motors use electromagnets that run everything from refrigerators and washing machines to electric trains and robots. Audio and videotape players have electromagnets that record and read the tape. TV picture tubes use an electromagnet to help ...
... Magnets are used constantly in today’s homes. All electric motors use electromagnets that run everything from refrigerators and washing machines to electric trains and robots. Audio and videotape players have electromagnets that record and read the tape. TV picture tubes use an electromagnet to help ...
Chapter 16 Engineering Magnetism: Magnetic Field Calculations and Inductors 16.1 Homework # 140
... b.) Describe the direction of the electric field at all points a given distance, r, from the center, where r < R. c.) If the magnetic field strength is increasing at a rate of 0.250 T/s and R = 12.00 cm, what is E at 9.00 cm? d.) Write an equation that describes the magnitude of the electric field, ...
... b.) Describe the direction of the electric field at all points a given distance, r, from the center, where r < R. c.) If the magnetic field strength is increasing at a rate of 0.250 T/s and R = 12.00 cm, what is E at 9.00 cm? d.) Write an equation that describes the magnitude of the electric field, ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.