Magnets and Magnetic Field
... • One end of a magnet is referred to as its north pole and is labeled “N”. – The end of a bar magnet that points toward the north geographic pole of the Earth is the “northseeking” pole, or simply the north pole. ...
... • One end of a magnet is referred to as its north pole and is labeled “N”. – The end of a bar magnet that points toward the north geographic pole of the Earth is the “northseeking” pole, or simply the north pole. ...
Chapter 7 Magnetism: Electromagnets
... o Loudspeaker (344) – a device that changes electrical energy into sound o Microphone (345) – a device that uses a magnet to convert sound into electrical signals What is an electromagnet? Main Idea An electric current flowing through a wire produces a magnetic field around the wire. Supporting Deta ...
... o Loudspeaker (344) – a device that changes electrical energy into sound o Microphone (345) – a device that uses a magnet to convert sound into electrical signals What is an electromagnet? Main Idea An electric current flowing through a wire produces a magnetic field around the wire. Supporting Deta ...
The Earth`s magnetic field
... Geomagnetism • The magnetic field of the Earth has reversed its direction many times, typically every few hundred thousand years. • One knows that from the magnetization of iron-rich lava. It gets magnetized by the Earth’s magnetic field during cooling and keeps its magnetization after it solidifie ...
... Geomagnetism • The magnetic field of the Earth has reversed its direction many times, typically every few hundred thousand years. • One knows that from the magnetization of iron-rich lava. It gets magnetized by the Earth’s magnetic field during cooling and keeps its magnetization after it solidifie ...
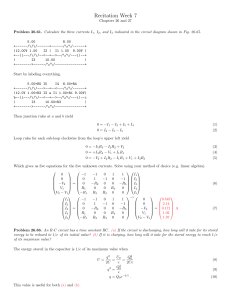
1
... A cloud of positive charge has a volume charge density of P = Po rlR where r is the distance from the center of a sphere of radius R and Po is a constant. Find the magnitude of the electric field E at a point inside the sphere at distance r < R. Ii'J ::::'f:l t\V\ ~ l\ ~M ~. ...
... A cloud of positive charge has a volume charge density of P = Po rlR where r is the distance from the center of a sphere of radius R and Po is a constant. Find the magnitude of the electric field E at a point inside the sphere at distance r < R. Ii'J ::::'f:l t\V\ ~ l\ ~M ~. ...
Magnetic Fields
... 5. Relocate the compass so that the tail of the compass needle now points where the point you previously made is for the tip (see Diagram #1 below). Place another point where the tip is. 6. Repeat this process until a magnetic field line can be drawn continuously from the North pole of the magnet(s) ...
... 5. Relocate the compass so that the tail of the compass needle now points where the point you previously made is for the tip (see Diagram #1 below). Place another point where the tip is. 6. Repeat this process until a magnetic field line can be drawn continuously from the North pole of the magnet(s) ...
Week 12
... Is this the exact vector potential for a flat ring of current with m=Ia, or is it approximate? ...
... Is this the exact vector potential for a flat ring of current with m=Ia, or is it approximate? ...
Magnetism - Kania´s Science Page
... magnetic field produced by a current flowing in a straight wire or in a coil. (Ch 36) Students know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby ...
... magnetic field produced by a current flowing in a straight wire or in a coil. (Ch 36) Students know changing magnetic fields produce electric fields, thereby inducing currents in nearby ...
Integrated Science Chapter 20 and 21 PRETEST
... 2. If the two charges represented in Figure 20-1 were brought near each other, they would a. attract each other. c. cause static discharge. b. repel each other. d. have no effect on each other. 3. What do electric forces between charges depend on? a. the quantity of charge involved c. both a. and b. ...
... 2. If the two charges represented in Figure 20-1 were brought near each other, they would a. attract each other. c. cause static discharge. b. repel each other. d. have no effect on each other. 3. What do electric forces between charges depend on? a. the quantity of charge involved c. both a. and b. ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.