Dipole - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some (usually small) distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an ...
... negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some (usually small) distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an ...
Magnetism - Deakin University Blogs
... often expect magnets to attract any metal object rather than only iron and steel. Magnets have no effect on aluminium, brass, silver or copper. Students will often not know what metal common objects are made of, and, in fact, some substances that look like metal are coated plastic, and some plastic- ...
... often expect magnets to attract any metal object rather than only iron and steel. Magnets have no effect on aluminium, brass, silver or copper. Students will often not know what metal common objects are made of, and, in fact, some substances that look like metal are coated plastic, and some plastic- ...
DISCOVERING AND ANALYZING MAGNETIC FIELDS
... calculations were not exact because the current output was different depending on the age of the battery; however, they provided a good approximation. With the nail inside, the solenoid became an iron core solenoid and the permeability constant changed to the permeability of iron given in Equation 3 ...
... calculations were not exact because the current output was different depending on the age of the battery; however, they provided a good approximation. With the nail inside, the solenoid became an iron core solenoid and the permeability constant changed to the permeability of iron given in Equation 3 ...
Nonlinear waves and shocks in relativistic two-fluid hydrodynamics
... has two parts: an unimpeded motion along the direction of the magnetic field, and a gyration around (i.e., transverse to) it. In the case of a parallel shock, the field lines pass through the shock, and a particle’s motion along the field will carry the particle through (and away from) the shock re ...
... has two parts: an unimpeded motion along the direction of the magnetic field, and a gyration around (i.e., transverse to) it. In the case of a parallel shock, the field lines pass through the shock, and a particle’s motion along the field will carry the particle through (and away from) the shock re ...
SC related electric and magnetic field phenomena observed by the... satellite inside the plasmasphere
... Electric and magnetic field variations inside the plasmasphere associated with SCs identified on the ground are analyzed based on the Akebono satellite observations which have been carried out more than 13 years since March 1989. 126 electric field observation data corresponding to SCs show abrupt c ...
... Electric and magnetic field variations inside the plasmasphere associated with SCs identified on the ground are analyzed based on the Akebono satellite observations which have been carried out more than 13 years since March 1989. 126 electric field observation data corresponding to SCs show abrupt c ...
Module 4 UNDERSTANDING ELECTRICITY AND
... What is electricity? In today’s world we grow up in an environment where electrical power is everywhere around us and we sometimes accept this unquestioningly ... we take it for granted. 6 a.m. Another weekday. The clock-radio blares, but you lie in bed a few minutes longer, listening to the news an ...
... What is electricity? In today’s world we grow up in an environment where electrical power is everywhere around us and we sometimes accept this unquestioningly ... we take it for granted. 6 a.m. Another weekday. The clock-radio blares, but you lie in bed a few minutes longer, listening to the news an ...
Spin Hall Magnetoresistance Induced by a Nonequilibrium Proximity Effect
... responsible for a nonequilibrium spin accumulation near the surface [Fig. 1(f)] and subsequent spin diffusion [27,28] as described below. Finally, the ISHE in Pt induces an electric current from the reflected spin current [see Fig. 1(c)], causing an electromotive force along the film plane. This add ...
... responsible for a nonequilibrium spin accumulation near the surface [Fig. 1(f)] and subsequent spin diffusion [27,28] as described below. Finally, the ISHE in Pt induces an electric current from the reflected spin current [see Fig. 1(c)], causing an electromotive force along the film plane. This add ...
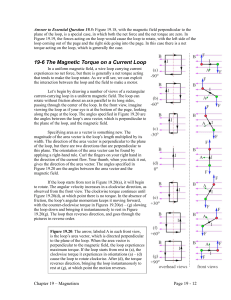
19-6 The Magnetic Torque on a Current Loop
... distance along and the line of the force is 90°. A factor of 2 accounts for the two identical torques, which are both clockwise. The magnitude of the net torque on the loop in this orientation is: , where A = HW is the area of the loop. As the loop rotates, the torque is reduced as the angle between ...
... distance along and the line of the force is 90°. A factor of 2 accounts for the two identical torques, which are both clockwise. The magnitude of the net torque on the loop in this orientation is: , where A = HW is the area of the loop. As the loop rotates, the torque is reduced as the angle between ...
... 4*10-7mbar. The V[TCNE]2 thin film prepared in this vacuum, oxidized completely by the presence of oxygen during the film growth. Organic magnetoresistance (OMAR) devices which are simple organic diode structures were fabricated and characterized, as they are compatible with high vacuum conditions. ...
Chapter 22
... There are more than one way to generate induced emf/current. An emf can be induced by changing the area of a coil in a constant magnetic field as shown in magnetic field as shown in the figure on the right. ...
... There are more than one way to generate induced emf/current. An emf can be induced by changing the area of a coil in a constant magnetic field as shown in magnetic field as shown in the figure on the right. ...
magnetic fields and forces
... We can disregard the forces created by current within the top and bottom sides of the square, since they both run perpendicular to the straight wire, and are equal distance from the wire. The forces from the top and bottom sides conveniently cancel each other out. However, the forces from the two si ...
... We can disregard the forces created by current within the top and bottom sides of the square, since they both run perpendicular to the straight wire, and are equal distance from the wire. The forces from the top and bottom sides conveniently cancel each other out. However, the forces from the two si ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.