The first results of the cilindric Vlasov
... (Lancellotti and Dorning, 1998) Lancellotti and Dorning showed that there exist “critical initial states” that mark the transition between the Landau regime (in which the wave is definitively damped to zero) ant the O’Neil regime (in which the electric field goes on oscillating around an approximate ...
... (Lancellotti and Dorning, 1998) Lancellotti and Dorning showed that there exist “critical initial states” that mark the transition between the Landau regime (in which the wave is definitively damped to zero) ant the O’Neil regime (in which the electric field goes on oscillating around an approximate ...
lec27
... It is not obvious where they are, because we are so focused on details when we learn this material for the first time. One of the big ideas arises from the observation that magnetic poles always come in pairs, unlike + and – charged particles. In the next lecture, I’ll introduce the idea of magnetic ...
... It is not obvious where they are, because we are so focused on details when we learn this material for the first time. One of the big ideas arises from the observation that magnetic poles always come in pairs, unlike + and – charged particles. In the next lecture, I’ll introduce the idea of magnetic ...
magnetic field
... When electric charges are in motion they exert forces on each other that can’t be explained by Coulomb’s law. If two parallel current carrying conductors are near each other they attract each other when the currents are in the same direction and repel each other when the currents are in opposite dir ...
... When electric charges are in motion they exert forces on each other that can’t be explained by Coulomb’s law. If two parallel current carrying conductors are near each other they attract each other when the currents are in the same direction and repel each other when the currents are in opposite dir ...
Exam - UCSD Physics
... A nonuniform electric field is directed along the x-axis at all points in space. This magnitude of the field varies with x, but not with respect to y or z. The axis of a cylindrical surface, 0.80 m long and 0.20 m in diameter, is aligned parallel to the x-axis. The electric fields E1 and E2, at the ...
... A nonuniform electric field is directed along the x-axis at all points in space. This magnitude of the field varies with x, but not with respect to y or z. The axis of a cylindrical surface, 0.80 m long and 0.20 m in diameter, is aligned parallel to the x-axis. The electric fields E1 and E2, at the ...
投影片 1
... • The turning of a coil in a magnetic field produces motional emfs in both sides of the coil which add. • Since the component of the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field changes sinusoidally with the rotation, the generated voltage is sinusoidal or AC. • This process can be described in term ...
... • The turning of a coil in a magnetic field produces motional emfs in both sides of the coil which add. • Since the component of the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field changes sinusoidally with the rotation, the generated voltage is sinusoidal or AC. • This process can be described in term ...
PPT
... • A square loop of wire of side L is rotated at a uniform frequency f in the presence of a uniform magnetic field B as shown. • Describe the EMF induced in the loop. ...
... • A square loop of wire of side L is rotated at a uniform frequency f in the presence of a uniform magnetic field B as shown. • Describe the EMF induced in the loop. ...
Magnetic field
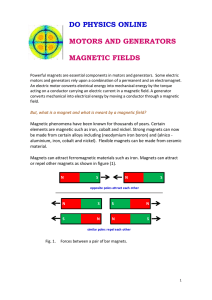
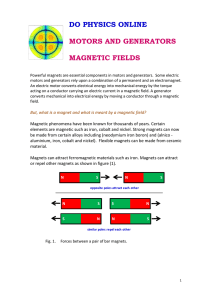
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.