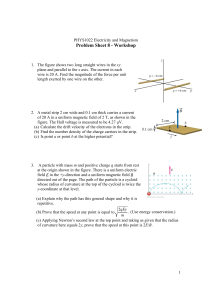
☺ PLAN 1. Ampere’s law 2. Applications
... 2. Applications Require a high symmetry. ♣ Magnetic field due to i in a long straight wire — again. (Faster. No need to assume that the wire diameter is zero.) ♣ Magnetic field inside the wire. ♣ Solenoid. ♣ Toroid. ...
... 2. Applications Require a high symmetry. ♣ Magnetic field due to i in a long straight wire — again. (Faster. No need to assume that the wire diameter is zero.) ♣ Magnetic field inside the wire. ♣ Solenoid. ♣ Toroid. ...
ch 20 21 22
... Electrically charged objects obey the following rules: 1. Law of conservation of charge - charge may be transferred from object to object, but it cannot be created or destroyed 2. Opposite charges attract, and like charges repel 3. Charges can act on each other even at a distance, because any charge ...
... Electrically charged objects obey the following rules: 1. Law of conservation of charge - charge may be transferred from object to object, but it cannot be created or destroyed 2. Opposite charges attract, and like charges repel 3. Charges can act on each other even at a distance, because any charge ...
Electrostatics II
... demonstrated by sustaining currents in superconducting lead rings for many years with no measurable reduction. An induced current in an ordinary metal ring would decay rapidly from the dissipation of ordinary resistance, but superconducting rings had exhibited a decay constant of over a billion year ...
... demonstrated by sustaining currents in superconducting lead rings for many years with no measurable reduction. An induced current in an ordinary metal ring would decay rapidly from the dissipation of ordinary resistance, but superconducting rings had exhibited a decay constant of over a billion year ...
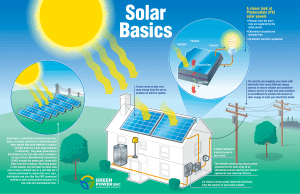
What is energy
... Which energy source provides the U.S. with its second largest amount of electricity? Electric companies use what unit of measure to bill their customers for energy use? Light bulbs and other home appliances are measured in what electrical power unit? How is electricity used, measured and sold? In wh ...
... Which energy source provides the U.S. with its second largest amount of electricity? Electric companies use what unit of measure to bill their customers for energy use? Light bulbs and other home appliances are measured in what electrical power unit? How is electricity used, measured and sold? In wh ...
ELECTRICITY NOTES
... • ELECTRICITY: form of energy that occurs when electrons move from place to place • Electricity can form whenever (e-) electrons are gained or lost ...
... • ELECTRICITY: form of energy that occurs when electrons move from place to place • Electricity can form whenever (e-) electrons are gained or lost ...
the strength of an electromagnet depends on the current
... 11. Explain briefly how this relay works. ...
... 11. Explain briefly how this relay works. ...
Transmission of Electricity
... wrong with one or more of the power stations, it is possible to get electricity from another source. ...
... wrong with one or more of the power stations, it is possible to get electricity from another source. ...
Chapter 6 - Topic 11 - Electromagnetic induction – AHL.
... Chapter 6 - Topic 11 - Electromagnetic induction – AHL. Essential idea: The majority of electricity generated throughout the world is generated by machines that were designed to operate using the principles of electromagnetic induction. 11.1 – Electromagnetic induction Nature of science 1.8 Experime ...
... Chapter 6 - Topic 11 - Electromagnetic induction – AHL. Essential idea: The majority of electricity generated throughout the world is generated by machines that were designed to operate using the principles of electromagnetic induction. 11.1 – Electromagnetic induction Nature of science 1.8 Experime ...
Fatih C. Mercan PHYS 670 – AU 2003 Lesson Plan Title:
... As you know there have been great discoveries about electricity in the last few years. Perhaps the most important one is Volta’s discovery of a battery that allowed us to have electric current. Using Volta’s battery now we can do more experiments on electric current and learn more about the nature o ...
... As you know there have been great discoveries about electricity in the last few years. Perhaps the most important one is Volta’s discovery of a battery that allowed us to have electric current. Using Volta’s battery now we can do more experiments on electric current and learn more about the nature o ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... A. A magnetic field moving around a coil of wire causes an electric current, and an electric current in a coil of wire causes a magnetic field. B. The flow of electrons through either a series or parallel circuit is known as an electric current. C. Motors, telephones, and computers are all devices t ...
... A. A magnetic field moving around a coil of wire causes an electric current, and an electric current in a coil of wire causes a magnetic field. B. The flow of electrons through either a series or parallel circuit is known as an electric current. C. Motors, telephones, and computers are all devices t ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.