Presentations
... north pole of a bar magnet as shown. The loop is now allowed to fall toward the magnet. “I'm not sure I comprehend the drawing correctly, but I think the reaction would gravitate upward in reaction to the north pole of the magnet.” “since the loop is not moving there is no energy produced.” ...
... north pole of a bar magnet as shown. The loop is now allowed to fall toward the magnet. “I'm not sure I comprehend the drawing correctly, but I think the reaction would gravitate upward in reaction to the north pole of the magnet.” “since the loop is not moving there is no energy produced.” ...
09. Electricity Notes
... • An electric battery is a device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections provided to power electrical devices such as flashlights, smartphones, and electric cars. ...
... • An electric battery is a device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections provided to power electrical devices such as flashlights, smartphones, and electric cars. ...
The Control of Electricity in Circuits
... • Unlike primary cells, a secondary cell can be discharged and recharged many hundreds of times. • Secondary cells are often referred to rechargeable batteries. • Secondary cells are so named since there are two chemical processes involved: – one to discharge the cell – one to charge the cell ...
... • Unlike primary cells, a secondary cell can be discharged and recharged many hundreds of times. • Secondary cells are often referred to rechargeable batteries. • Secondary cells are so named since there are two chemical processes involved: – one to discharge the cell – one to charge the cell ...
AP PHYSICS C: PROBLEM SET 9A ELECTRICAL AWESOMELAND
... a. On the diagram, indicate with an arrow the direction of the net electric field at point P. ...
... a. On the diagram, indicate with an arrow the direction of the net electric field at point P. ...
electric circuit
... Light bulbs, resistors, motors, and heaters usually have much greater resistance than wires and batteries. ...
... Light bulbs, resistors, motors, and heaters usually have much greater resistance than wires and batteries. ...
Student Objective Students will be able to…
... What part of an atom spins to produce a magnetic field? ______________________ ...
... What part of an atom spins to produce a magnetic field? ______________________ ...
Chap 2.3 notes
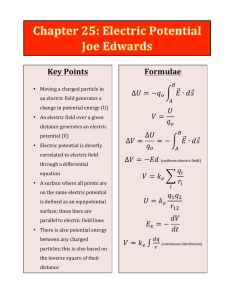
... • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
... • The fundamental charge on an electron is 1.6 X 10-19 C. • 1 C = 1/ 1.6 X 10-19 = 6.25 X 1018 electrons or 6,250,000,000,000,000,000 electrons. ...
2005 C Mechanics 1. (a) ____ increases
... The acceleration is greater on the way up because the forces due to gravity and air resistance are in the same direction, thus, making a greater net force on the ball than on the way down where these two forces act in opposite directions. The distance it rises is the same distance it falls. Therefor ...
... The acceleration is greater on the way up because the forces due to gravity and air resistance are in the same direction, thus, making a greater net force on the ball than on the way down where these two forces act in opposite directions. The distance it rises is the same distance it falls. Therefor ...
induces
... A) Because you’re farther from Earth’s core than a common magnet. B) Because the Earth’s magnetic field is spread over a whole planet. C) The materials in a refrigerator magnet can generate magnetism more efficiently than those in the center of the Earth. D) All of the above E) None of the above ...
... A) Because you’re farther from Earth’s core than a common magnet. B) Because the Earth’s magnetic field is spread over a whole planet. C) The materials in a refrigerator magnet can generate magnetism more efficiently than those in the center of the Earth. D) All of the above E) None of the above ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.