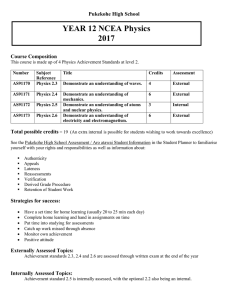
This course is made up of 4 Physics
... Students will be expected to carry out on-going study throughout the year, learning for topic assessments which relate to the units. Each major topic will be assessed with a knowledge test using the NCEA system of Achieve, Merit and Excellence. The school exam late in term three will give students p ...
... Students will be expected to carry out on-going study throughout the year, learning for topic assessments which relate to the units. Each major topic will be assessed with a knowledge test using the NCEA system of Achieve, Merit and Excellence. The school exam late in term three will give students p ...
AQA GCSE Physics Sample Pages
... Some metals, for example iron, steel, cobalt and nickel, are magnetic. A magnet will attract them. If you drop some steel pins on the floor you can pick them up using a magnet. A magnetic force is an example of a non-contact force, which acts over a distance. In Figure 5.4, you can see a bar magnet ...
... Some metals, for example iron, steel, cobalt and nickel, are magnetic. A magnet will attract them. If you drop some steel pins on the floor you can pick them up using a magnet. A magnetic force is an example of a non-contact force, which acts over a distance. In Figure 5.4, you can see a bar magnet ...
ELECTRIC INDUCTION FURNACE
... Induction furnaces offer certain advantages over other furnace systems. They include: Higher Yield. The absence of combustion sources reduces oxidation losses that can be significant in production economics. Faster Startup. Full power from the power supply is available, instantaneously, thus reducin ...
... Induction furnaces offer certain advantages over other furnace systems. They include: Higher Yield. The absence of combustion sources reduces oxidation losses that can be significant in production economics. Faster Startup. Full power from the power supply is available, instantaneously, thus reducin ...
Chapter 11 Inductance and Magnetic Energy
... clockwise as seen from above. The force on the charges due to this electric field is thus opposite the direction the external agents are trying to spin the rings up (counterclockwise), and thus the agents have to do additional work to spin up the charges because of their charge. This is the source o ...
... clockwise as seen from above. The force on the charges due to this electric field is thus opposite the direction the external agents are trying to spin the rings up (counterclockwise), and thus the agents have to do additional work to spin up the charges because of their charge. This is the source o ...
Analysis of Contact Force in Eddy-current System Using the
... The magnetic force is an important design factor for the mechanical structural design of electric power apparatus. Large magnetic force on a part of the system can cause mechanical problems such as deformation, vibration, noise, and even fracture, either in the part, or in neighboring parts. To avoi ...
... The magnetic force is an important design factor for the mechanical structural design of electric power apparatus. Large magnetic force on a part of the system can cause mechanical problems such as deformation, vibration, noise, and even fracture, either in the part, or in neighboring parts. To avoi ...
f. Physics notes 2 (DOC).
... fields are superposable, it follows from Eq. (90) that electric potentials must also be superposable. Thus, the electric potential generated by a set of charges distributed in space is just the scalar sum of the potentials generated by each charge taken in isolation. Clearly, it is far easier to det ...
... fields are superposable, it follows from Eq. (90) that electric potentials must also be superposable. Thus, the electric potential generated by a set of charges distributed in space is just the scalar sum of the potentials generated by each charge taken in isolation. Clearly, it is far easier to det ...
Cost 286 Hamburg, `Numerical Simulation of a Dipole Antenna
... The thin-wire formulation technique employed here to simulate this problem is based on a quasi-static solution for the field around the wire. This is a symmetrical solution and therefore can only be used to place the wire centrally in the a computational cell. In cases where an offset wire descript ...
... The thin-wire formulation technique employed here to simulate this problem is based on a quasi-static solution for the field around the wire. This is a symmetrical solution and therefore can only be used to place the wire centrally in the a computational cell. In cases where an offset wire descript ...
7. Static Electricity and Capacitance
... tall building. The upper end of the strip terminates in one or more sharp spikes above the highest point of the building. The lower end is connected to a metal plate buried in moist earth. The lightning conductor protects a building from being damaged by lightning in a number of ways. During a thund ...
... tall building. The upper end of the strip terminates in one or more sharp spikes above the highest point of the building. The lower end is connected to a metal plate buried in moist earth. The lightning conductor protects a building from being damaged by lightning in a number of ways. During a thund ...
Lab 17 - College of San Mateo
... 1. Check to see that all three buttons of the galvanometer are up. If any appears to be in the depressed position, rotate it to release it. 2. Test the galvanometer as follows: Connect the positive (red) terminal of the power supply to the left terminal of the galvanometer. (Left is defined as you l ...
... 1. Check to see that all three buttons of the galvanometer are up. If any appears to be in the depressed position, rotate it to release it. 2. Test the galvanometer as follows: Connect the positive (red) terminal of the power supply to the left terminal of the galvanometer. (Left is defined as you l ...
Teacher Guide
... video, explaining text, suggested activities and a glossary to make parts of the physics curriculum in upper secondary schools more engaging and accessible. This teacher guide and a comprehensive teacher seminar support and explain how to use the e-modules in teaching. The teacher seminar goes into ...
... video, explaining text, suggested activities and a glossary to make parts of the physics curriculum in upper secondary schools more engaging and accessible. This teacher guide and a comprehensive teacher seminar support and explain how to use the e-modules in teaching. The teacher seminar goes into ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.