phy.104.outline.s2010 - Student Learning Outcomes (SLO
... Course Description: This is a continuation of PHY 103 with an emphasis on electrostatics, direct current and alternating current circuits, electromagnetism, magnetic properties of matter, and electromagnetic oscillations. The laboratory is based upon electrical measurements using modern electronic t ...
... Course Description: This is a continuation of PHY 103 with an emphasis on electrostatics, direct current and alternating current circuits, electromagnetism, magnetic properties of matter, and electromagnetic oscillations. The laboratory is based upon electrical measurements using modern electronic t ...
Sample Test (Word Doc)
... kq/R2 iii. kq/r2 iv. kq/(4πR2) (c) Two negative point charges are separated by a distance d. The electric field is strongest: i. directly between the two charges ii. everywhere along the line that separates the two charges (perpendicular to the line that connects them) iii. along the line that conne ...
... kq/R2 iii. kq/r2 iv. kq/(4πR2) (c) Two negative point charges are separated by a distance d. The electric field is strongest: i. directly between the two charges ii. everywhere along the line that separates the two charges (perpendicular to the line that connects them) iii. along the line that conne ...
Electric Field
... • Electric Force (F) - the actual force felt by a charge at some location. • Electric Field (E) - found for a location only – tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there: ...
... • Electric Force (F) - the actual force felt by a charge at some location. • Electric Field (E) - found for a location only – tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there: ...
Maxwell`s electromagnetic theory and special relativity
... him. He also gave a more complete list of which materials would be attracted by his electrics. In the process of these experiments, Gilbert invented what was, in a sense, the first electroscope (called, by Gilbert, the versorium); a fine needle of metal (or certain other substances) delicately balance ...
... him. He also gave a more complete list of which materials would be attracted by his electrics. In the process of these experiments, Gilbert invented what was, in a sense, the first electroscope (called, by Gilbert, the versorium); a fine needle of metal (or certain other substances) delicately balance ...
Problem Set 02
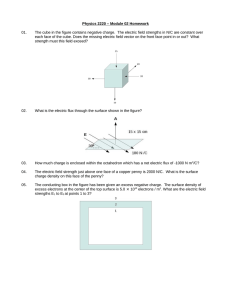
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
484221Kerneis
... expression is a simplification that can be easily deduced by studying the electric field between two infinite plates in cylindrical coordinates. Other methods have been developed to estimate the parameters of capacitors, possibly in different configurations: energetic models [Al Jaber, 2000], fictit ...
... expression is a simplification that can be easily deduced by studying the electric field between two infinite plates in cylindrical coordinates. Other methods have been developed to estimate the parameters of capacitors, possibly in different configurations: energetic models [Al Jaber, 2000], fictit ...
Measuring electricity
... 7. A circuit in your home can handle more than one appliance at a time. When more than one appliance is being used on a circuit, the total current is the sum of the currents being drawn by each appliance. a. Are the appliances wired in series or in parallel in the circuit? b. Suppose that the toast ...
... 7. A circuit in your home can handle more than one appliance at a time. When more than one appliance is being used on a circuit, the total current is the sum of the currents being drawn by each appliance. a. Are the appliances wired in series or in parallel in the circuit? b. Suppose that the toast ...
SNC1D7: Static and Current Electricity Test
... a) Electrons have a choice of paths in a series circuit, and no path choice in a parallel circuit b) Electrons have a choice of paths in a parallel circuit, and no path choice in a series circuit c) Series connections have lower resistances than parallel connections d) Series connections have higher ...
... a) Electrons have a choice of paths in a series circuit, and no path choice in a parallel circuit b) Electrons have a choice of paths in a parallel circuit, and no path choice in a series circuit c) Series connections have lower resistances than parallel connections d) Series connections have higher ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.





![LectureOutline-Circuits [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008795108_1-518ef7d981aabafef7ae5b5f16796a62-300x300.png)