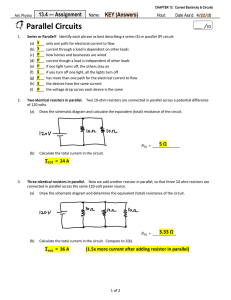
PSAA Curriculum
... moving electromagnetic coil. The voltmeter is calibrated to show the amount of voltage which would cause an amount of current to flow through the carefully selected resistance of the voltmeter. The voltmeter is current sensitive. The extent of the movement of the meter pointer is directly proportion ...
... moving electromagnetic coil. The voltmeter is calibrated to show the amount of voltage which would cause an amount of current to flow through the carefully selected resistance of the voltmeter. The voltmeter is current sensitive. The extent of the movement of the meter pointer is directly proportion ...
Unit 2 Section 3 - Belfast Royal Academy
... There are two types of Transformers: 1. STEP-UP TRANSFORMERS (Ns>Np) are used to increase the voltage at the POWER STATION. This is done to reduce power loss through the generation of heat. 2. STEP-DOWN TRANSFORMERS (Ns
... There are two types of Transformers: 1. STEP-UP TRANSFORMERS (Ns>Np) are used to increase the voltage at the POWER STATION. This is done to reduce power loss through the generation of heat. 2. STEP-DOWN TRANSFORMERS (Ns
Series DC Motors
... DC machine Construction • Stator: Stationary part of the machine. The stator carries a field winding that is used to produce the required magnetic field by DC excitation. Often know as the field. • Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the machine. The rotor carries a distributed winding, and is ...
... DC machine Construction • Stator: Stationary part of the machine. The stator carries a field winding that is used to produce the required magnetic field by DC excitation. Often know as the field. • Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the machine. The rotor carries a distributed winding, and is ...
key to full question paper on electrostatics
... and Z? What is the work done in moving a change of 20 m c from point X to Y? (b) Can we have non-zero electric potential in the space, where electric field strength is zero? ...
... and Z? What is the work done in moving a change of 20 m c from point X to Y? (b) Can we have non-zero electric potential in the space, where electric field strength is zero? ...
zahn
... magnetometry sensors for measurement of dielectric permittivity, electrical conductivity, magnetic permeability, and volume charge in flowing liquids, with applications to nondestructive testing and evaluation measurements and for the identification of metal, low-metal content, and dielectric landmi ...
... magnetometry sensors for measurement of dielectric permittivity, electrical conductivity, magnetic permeability, and volume charge in flowing liquids, with applications to nondestructive testing and evaluation measurements and for the identification of metal, low-metal content, and dielectric landmi ...
Mutual / Self-Induction * Learning Outcomes
... a coil of wire (circuit 1), while the other consists of a d.c. power supply, open switch, and coil of wire (circuit 2). 2. Move the coils next to each other. 3. Close the switch in circuit 2 and note an instantaneous deflection in the galvanometer needle in circuit 1. 4. Leave the switch closed, not ...
... a coil of wire (circuit 1), while the other consists of a d.c. power supply, open switch, and coil of wire (circuit 2). 2. Move the coils next to each other. 3. Close the switch in circuit 2 and note an instantaneous deflection in the galvanometer needle in circuit 1. 4. Leave the switch closed, not ...
Chapter 22
... Ch 22-2 Electric Field Field: Region of space characterized by a physical property Scalar physical property- scalar field; vector physical property- vector field The Electric Field characteristics: Exerts force on a positive test charge Electric field is due to a charge and surrounds it D ...
... Ch 22-2 Electric Field Field: Region of space characterized by a physical property Scalar physical property- scalar field; vector physical property- vector field The Electric Field characteristics: Exerts force on a positive test charge Electric field is due to a charge and surrounds it D ...
EE3321 ELECTROMAGENTIC FIELD THEORY
... 600 BC - 1599 – Humans discover the magnetic lodestone as well as the attracting properties of amber. Advanced societies, in particular the Chinese and the Europeans, exploit the properties of magnets in compasses, a tool that makes possible exploration of the seas, “new worlds” and the nature of Ea ...
... 600 BC - 1599 – Humans discover the magnetic lodestone as well as the attracting properties of amber. Advanced societies, in particular the Chinese and the Europeans, exploit the properties of magnets in compasses, a tool that makes possible exploration of the seas, “new worlds” and the nature of Ea ...
MAGNETISM MAGNETISM
... attracted to a wire that carries a current. When the current is OFF, the needle points North, to the earth’s magnetic pole. ...
... attracted to a wire that carries a current. When the current is OFF, the needle points North, to the earth’s magnetic pole. ...
File - MIT Section X
... Inductor is a passive electric device that stores energy in its magnetic field when a current flows through it A coil of wire wound on a core ...
... Inductor is a passive electric device that stores energy in its magnetic field when a current flows through it A coil of wire wound on a core ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.