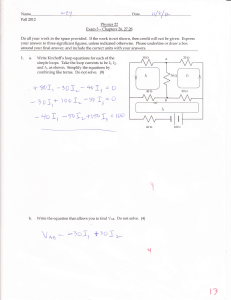
exam2
... component of the Earth's magnetic field is 6.0 × 10-5 T. Find the magnitude of the induced emf between the tips of the wings when the speed of the plane is 225 m/s. A) B) C) D) E) ...
... component of the Earth's magnetic field is 6.0 × 10-5 T. Find the magnitude of the induced emf between the tips of the wings when the speed of the plane is 225 m/s. A) B) C) D) E) ...
11. Sources of Magnetic Fields
... moment: they are little permanent magnets. At high temperatures (above the Curie temperature, which is 1043 K for iron ) these are oriented in random directions so the net magnetism is zero. But if they are cooled below the Curie temperature, most of them (not all) line up the same direction. That i ...
... moment: they are little permanent magnets. At high temperatures (above the Curie temperature, which is 1043 K for iron ) these are oriented in random directions so the net magnetism is zero. But if they are cooled below the Curie temperature, most of them (not all) line up the same direction. That i ...
Capacitors - Physics Champion
... Hard magnets, such as steel, are magnetised, but afterwards take a lot of work to de-magnetise. They're good for making permanent magnets, for example. Soft magnets are the opposite. With an example being iron, they are magnetised, but easily lost their magnetism, be it through vibration or any othe ...
... Hard magnets, such as steel, are magnetised, but afterwards take a lot of work to de-magnetise. They're good for making permanent magnets, for example. Soft magnets are the opposite. With an example being iron, they are magnetised, but easily lost their magnetism, be it through vibration or any othe ...
Electromagnets
... around a magnet and sending a current through the wire. You already knew that magnets attract (pull) or repel (push) other magnets and magnetic objects. But did you know that magnets con also exert their force on other materials in a way that makes these materials magnetic? When a current of electri ...
... around a magnet and sending a current through the wire. You already knew that magnets attract (pull) or repel (push) other magnets and magnetic objects. But did you know that magnets con also exert their force on other materials in a way that makes these materials magnetic? When a current of electri ...
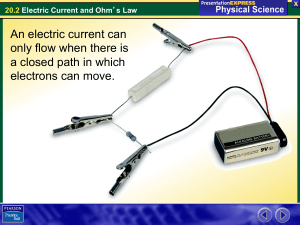
20.2 Electric Current and Ohm
... Conductors and Insulators A metal is made up of ions in a lattice. The ions are not free to move. • Each ion has one or more electrons that are not tightly bound to it. • These free electrons can conduct charge. • Most materials do not easily conduct charge because they don’t have free electrons. ...
... Conductors and Insulators A metal is made up of ions in a lattice. The ions are not free to move. • Each ion has one or more electrons that are not tightly bound to it. • These free electrons can conduct charge. • Most materials do not easily conduct charge because they don’t have free electrons. ...
magnetic
... Einstein showed that magnetism is simply electrical force as seen from a “different perspective.” It’s existence is a CONSEQUENCE of the way the spacetime fabric of the universe is woven! ...
... Einstein showed that magnetism is simply electrical force as seen from a “different perspective.” It’s existence is a CONSEQUENCE of the way the spacetime fabric of the universe is woven! ...
charge
... 1. the lamps are brighter than when connected in series 2. the lamps can be controlled individually with switches 3. one lamp will continue working even if the other does not ...
... 1. the lamps are brighter than when connected in series 2. the lamps can be controlled individually with switches 3. one lamp will continue working even if the other does not ...
Induced voltages and Inductance Faraday`s Law
... Look at straight conductor of length (L) moving with constant velocity through a uniform B-field pointing into the page. In this example the velocity is normal to B-field. Force on the electrons (-) is FB = qvB downward ...
... Look at straight conductor of length (L) moving with constant velocity through a uniform B-field pointing into the page. In this example the velocity is normal to B-field. Force on the electrons (-) is FB = qvB downward ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.