Illustrated Guide to PHYSICS
... first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or, if it is moving it will continue to move at a constant speed in the same direction, unless it is acted on by an external force. This might be a single force or the resultant of two or more unbalanced forces. ...
... first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or, if it is moving it will continue to move at a constant speed in the same direction, unless it is acted on by an external force. This might be a single force or the resultant of two or more unbalanced forces. ...
(electric field of a point charge).
... interactions are governed by a simple relationship known as Coulomb's law and are most conveniently described by using the concept of electric field. We'll explore all these concepts in this chapter and expand on them in the three chapters that follow. In later chapters we'll expand our discussion t ...
... interactions are governed by a simple relationship known as Coulomb's law and are most conveniently described by using the concept of electric field. We'll explore all these concepts in this chapter and expand on them in the three chapters that follow. In later chapters we'll expand our discussion t ...
23 electromagnetic induction, ac circuits, and electrical technologies
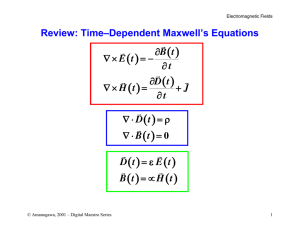
... caused by a magnetic force. That voltage could drive a current. Historically, it was very shortly after Oersted discovered currents cause magnetic fields that other scientists asked the following question: Can magnetic fields cause currents? The answer was soon found by experiment to be yes. In 1831 ...
... caused by a magnetic force. That voltage could drive a current. Historically, it was very shortly after Oersted discovered currents cause magnetic fields that other scientists asked the following question: Can magnetic fields cause currents? The answer was soon found by experiment to be yes. In 1831 ...
1. Sources, Exposure and Exposure Assessment
... from natural sources by several orders of magnitude. The existence of the geomagnetic field has been known since ancient times. The geomagnetic field is primarily dipolar in nature. The total field intensity diminishes from its maxima of about 60 μT at the magnetic poles, to a minimum of about 30 μT ...
... from natural sources by several orders of magnitude. The existence of the geomagnetic field has been known since ancient times. The geomagnetic field is primarily dipolar in nature. The total field intensity diminishes from its maxima of about 60 μT at the magnetic poles, to a minimum of about 30 μT ...
Electromagnetic models of the lightning return stroke
... loading has been also suggested. The artificial dielectric medium is used only for finding the distribution of current along the lightning channel, after which the channel is allowed to radiate in air. Resistive loading is used to control current attenuation with height. In contrast with distributed ...
... loading has been also suggested. The artificial dielectric medium is used only for finding the distribution of current along the lightning channel, after which the channel is allowed to radiate in air. Resistive loading is used to control current attenuation with height. In contrast with distributed ...
Notes on (calculus based) Physics
... The list of overtones (frequencies of vibrations) of a drum is completely determined by the shape of the drumhead. Is the converse true? That is, what physical quantities regarding the shape of a drum can one infer, if the complete list of overtones is given. This is popularly stated as ‘Can one hea ...
... The list of overtones (frequencies of vibrations) of a drum is completely determined by the shape of the drumhead. Is the converse true? That is, what physical quantities regarding the shape of a drum can one infer, if the complete list of overtones is given. This is popularly stated as ‘Can one hea ...
Document
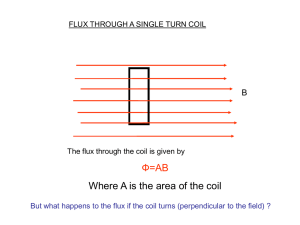
... rotating in the same direction. The new north pole of the coil is repelled by the north end and attracted to the south end of the permanent magnets. The new south pole of the coil is repelled by the south and attracted to the north ends of the permanent magnets. ...
... rotating in the same direction. The new north pole of the coil is repelled by the north end and attracted to the south end of the permanent magnets. The new south pole of the coil is repelled by the south and attracted to the north ends of the permanent magnets. ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Durg
... 1. Electrostatics (Static Electricity or Frictional Electricity): The branch of Physics, which deals with the study of electric charges at rest, the forces between the static charges, fields and potentials due to these charges is called Electrostatics or Static Electricity or Frictional Electricity. ...
... 1. Electrostatics (Static Electricity or Frictional Electricity): The branch of Physics, which deals with the study of electric charges at rest, the forces between the static charges, fields and potentials due to these charges is called Electrostatics or Static Electricity or Frictional Electricity. ...
OpenStax Physics Text for 2B - Chapter 6
... create a current. The Hall effect is a voltage caused by a magnetic force. That voltage could drive a current. Historically, it was very shortly after Oersted discovered currents cause magnetic fields that other scientists asked the following question: Can magnetic fields cause currents? The answer ...
... create a current. The Hall effect is a voltage caused by a magnetic force. That voltage could drive a current. Historically, it was very shortly after Oersted discovered currents cause magnetic fields that other scientists asked the following question: Can magnetic fields cause currents? The answer ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.