Protons for Breakfast
... ‘how the world works’. One can’t make sense of things matter and fields as without appreciating this fundamental ‘duality’. two different kinds ‘Action at a Distance’ was the phrase used to summarise – of ”entity” that indeed mock – the concept of a ‘field’. At the start of the exist in “space|”. ...
... ‘how the world works’. One can’t make sense of things matter and fields as without appreciating this fundamental ‘duality’. two different kinds ‘Action at a Distance’ was the phrase used to summarise – of ”entity” that indeed mock – the concept of a ‘field’. At the start of the exist in “space|”. ...
AP Clicker Forces
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
ppt - Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators CASA
... Relativistic Electromagnetism Classical electromagnetic potentials can be shown to combine to a four-potential (with c = 1): ...
... Relativistic Electromagnetism Classical electromagnetic potentials can be shown to combine to a four-potential (with c = 1): ...
F - Uplift North Hills Prep
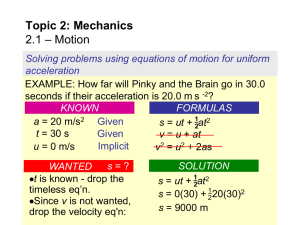
... Solving problems involving forces and resultant force PRACTICE: A 25-kg mass is hanging via three cords as shown. Find the tension in each of the three cords, in Newtons. SOLUTION: Since all of the angles are the same use the formulas we just derived: T3 = mg = 25(10) = 250 n T1 = mg / 1.366 = 25 ...
... Solving problems involving forces and resultant force PRACTICE: A 25-kg mass is hanging via three cords as shown. Find the tension in each of the three cords, in Newtons. SOLUTION: Since all of the angles are the same use the formulas we just derived: T3 = mg = 25(10) = 250 n T1 = mg / 1.366 = 25 ...
Green`s functions for Maxwell`s equations: application to
... der Waals forces originating from the vacuum ¯uctuations, or zero-point ¯uctuations, in the quantized electromagnetic ®eld [10]. Dispersion forces are relevant in calculating, for example, the force between the tip of an atomic force microscope and the surface of a material when the distance is suc ...
... der Waals forces originating from the vacuum ¯uctuations, or zero-point ¯uctuations, in the quantized electromagnetic ®eld [10]. Dispersion forces are relevant in calculating, for example, the force between the tip of an atomic force microscope and the surface of a material when the distance is suc ...
3D Visualization and Visual Data Mining
... 5 Magnetic reconnection in timedependent changes in magnetic flux ropes The changes in magnetic field topology estimated in Section 4.2 are verified by visualizing the magnetic field lines. PHANToM— an input interface in 3D space—has been used to interactively specify the starting points for drawing ...
... 5 Magnetic reconnection in timedependent changes in magnetic flux ropes The changes in magnetic field topology estimated in Section 4.2 are verified by visualizing the magnetic field lines. PHANToM— an input interface in 3D space—has been used to interactively specify the starting points for drawing ...
Electric Fields
... You have learned in class that electric charges produce electric fields, and that an electric field exerts a force on another charge (in the same direction as the field if the charge is +; opposite to the field if the charge is −). So, how can we measure the presence of an electric field? Well, you ...
... You have learned in class that electric charges produce electric fields, and that an electric field exerts a force on another charge (in the same direction as the field if the charge is +; opposite to the field if the charge is −). So, how can we measure the presence of an electric field? Well, you ...
Is the electrostatic force between a point charge
... metallic object always arrange themselves to minimize the total electrostatic energy of the system.2 A corollary of this theorem is that the electrostatic energy of a system composed of a metallic object and a charge is always lower than the energy of the charge in vacuum. We let UðzÞ denote the ele ...
... metallic object always arrange themselves to minimize the total electrostatic energy of the system.2 A corollary of this theorem is that the electrostatic energy of a system composed of a metallic object and a charge is always lower than the energy of the charge in vacuum. We let UðzÞ denote the ele ...
AXIEM™ White Paper
... This type of simulation also gets the transmission line properties per unit length. The FEM meshes the cross section in triangles and solves for the electric field on each of the meshes. The advantage of this technique is that can account for the loss and internal inductance in the transmission line ...
... This type of simulation also gets the transmission line properties per unit length. The FEM meshes the cross section in triangles and solves for the electric field on each of the meshes. The advantage of this technique is that can account for the loss and internal inductance in the transmission line ...
Observation of universal conductance-fluctuation crossovers in mesoscopic Li wires *
... the remarkable features of UCF is that their amplitude depends on the physical symmetries of the system under study, such as time-reversal symmetry or spin symmetry. Hence the UCF amplitude changes when the magnetic field exceeds certain values, and also varies in the presence or absence of magnetic ...
... the remarkable features of UCF is that their amplitude depends on the physical symmetries of the system under study, such as time-reversal symmetry or spin symmetry. Hence the UCF amplitude changes when the magnetic field exceeds certain values, and also varies in the presence or absence of magnetic ...
Abdel-Salam Hafez Abdel-Salam Hamza_2-Abdo
... of normally erected towers. It is noticed that higher magnetic field values are found underneath the staggered line conductors (line 2) located at mid span in this case. When compared to the case of normally erected line towers, the impact on the magnetic field levels underneath the first line (line ...
... of normally erected towers. It is noticed that higher magnetic field values are found underneath the staggered line conductors (line 2) located at mid span in this case. When compared to the case of normally erected line towers, the impact on the magnetic field levels underneath the first line (line ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.