the vlasov–poisson system with strong magnetic field
... the problem being posed for (x, v) ∈ T3 × R3 and t > 0. A detailed mathematical study of (1.7a–c) can be found in [10,11] mostly in the case of a constant magnetic field. Two cases of nonconstant magnetic fields will be considered in the present paper; they may give rise to some nontrivial geometric ...
... the problem being posed for (x, v) ∈ T3 × R3 and t > 0. A detailed mathematical study of (1.7a–c) can be found in [10,11] mostly in the case of a constant magnetic field. Two cases of nonconstant magnetic fields will be considered in the present paper; they may give rise to some nontrivial geometric ...
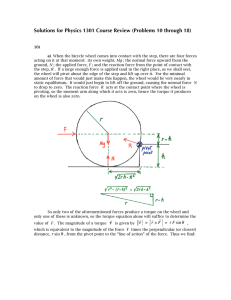
Is the electrostatic force between a point charge and a neutral
... A classic problem in electrostatics is to compute the force between a point charge and a perfectly conducting, neutral metallic sphere [Fig. 1(a)]. The problem can be easily solved using the method of images. One finds that the force on the point charge can be computed by summing the forces exerted ...
... A classic problem in electrostatics is to compute the force between a point charge and a perfectly conducting, neutral metallic sphere [Fig. 1(a)]. The problem can be easily solved using the method of images. One finds that the force on the point charge can be computed by summing the forces exerted ...
Global Magnetospheric Plasma Convection Stefan Eriksson
... This thesis deals with the global aspects of plasma convection in the magnetosphere as measured by the low-altitude polar orbiting Astrid-2 and FAST satellites. The major focus is on the electric field measurements, but they are also complemented by magnetic field, ion and electron particle data, wh ...
... This thesis deals with the global aspects of plasma convection in the magnetosphere as measured by the low-altitude polar orbiting Astrid-2 and FAST satellites. The major focus is on the electric field measurements, but they are also complemented by magnetic field, ion and electron particle data, wh ...
Generation of parallel electric fields in the Jupiter–Io torus wake region
... is seen at the left with the brightest emissions at the base of the Io flux tube. An emission trail extends eastward. (bottom) The coordinate system used in this article. momentum exchange between Jupiter and the subcorotating plasma is regulated by the ionospheric conductivity [Hill, 1979; Pontius ...
... is seen at the left with the brightest emissions at the base of the Io flux tube. An emission trail extends eastward. (bottom) The coordinate system used in this article. momentum exchange between Jupiter and the subcorotating plasma is regulated by the ionospheric conductivity [Hill, 1979; Pontius ...
Lecture Notes 09: Electrostatic Fields In Matter, Dielectric Materials and Their Properties
... 0.667 1030 m3 which is 4.5 → 6 larger than that predicted by either theory!!! ...
... 0.667 1030 m3 which is 4.5 → 6 larger than that predicted by either theory!!! ...
Electric Potential
... of 1 V. The potential difference also has units of electric field times distance. From this, it follows that the SI unit of electric field (N/C) can also be expressed in volts per meter: ...
... of 1 V. The potential difference also has units of electric field times distance. From this, it follows that the SI unit of electric field (N/C) can also be expressed in volts per meter: ...
Undergraduate Physics Courses - Ohio University Physics and
... equations, Conservation of energy and Poynting vector, conservation of momentum and Maxwell’s stress tensor, conservation of charge and equation of continuity, plane electromagnetic waves in vacuum and matter, wave guides, scalar and vector potentials, gauge transformations, retardation and LienardW ...
... equations, Conservation of energy and Poynting vector, conservation of momentum and Maxwell’s stress tensor, conservation of charge and equation of continuity, plane electromagnetic waves in vacuum and matter, wave guides, scalar and vector potentials, gauge transformations, retardation and LienardW ...
The Electric Field
... • If they charges are both positive, they will repel one another. Moving two charges that repel each other closer together requires mechanical work. This work will be stored as electric potential energy, as is shown in the figure below. If the charges are released, they fly apart from one another, c ...
... • If they charges are both positive, they will repel one another. Moving two charges that repel each other closer together requires mechanical work. This work will be stored as electric potential energy, as is shown in the figure below. If the charges are released, they fly apart from one another, c ...
Spin-Polarizing Sodium Atoms
... is called Bose-Einstein condensation. In 1995 a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) was observed for the first time [1, 2, 3]. The first sodium BEC of this university’s group was observed in August 2004 [4]. The achievement of a BEC is an important step towards the study of atoms in optical lattices. For ...
... is called Bose-Einstein condensation. In 1995 a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) was observed for the first time [1, 2, 3]. The first sodium BEC of this university’s group was observed in August 2004 [4]. The achievement of a BEC is an important step towards the study of atoms in optical lattices. For ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.