Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field 29.1 The Magnetic Field
... Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field By analogy with electrostatics, why don’t we study magnetostatics first? Due to complicated mathematics (lack of magnetic monopole). In 1820, Oersted established the link between electricity and magnetism. He found that a compass needle fluctuates during a thunderstorm, ...
... Chapter 29 The Magnetic Field By analogy with electrostatics, why don’t we study magnetostatics first? Due to complicated mathematics (lack of magnetic monopole). In 1820, Oersted established the link between electricity and magnetism. He found that a compass needle fluctuates during a thunderstorm, ...
WiTricity - Wireless Electricity
... If one ensures to operate in that regime in a given system, the energy transfer can be very efficient. While these considerations are universal, applying to all kinds of resonances (e.g., acoustic, mechanical, electromagnetic, etc.), the MIT team focused on one particular type: magnetically coup ...
... If one ensures to operate in that regime in a given system, the energy transfer can be very efficient. While these considerations are universal, applying to all kinds of resonances (e.g., acoustic, mechanical, electromagnetic, etc.), the MIT team focused on one particular type: magnetically coup ...
Solenoid worksheet
... 8. On each diagram in your answer booklet, draw the magnetic lines of force that are present and indicate the magnetic poles when a current flows through the two solenoids. ...
... 8. On each diagram in your answer booklet, draw the magnetic lines of force that are present and indicate the magnetic poles when a current flows through the two solenoids. ...
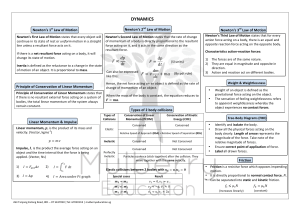
dynamics - Mulberry Education Centre
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section IX Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser
... showed that light (or any E/M radiation) can self-propagate, it took another 50 years before Einstein demonstrated this with the Special Theory of Relativity in 1905. Prior to this, light was assumed to propagate on a medium in space called the Ether. f ) In the late-1800s, Michelson and Morley trie ...
... showed that light (or any E/M radiation) can self-propagate, it took another 50 years before Einstein demonstrated this with the Special Theory of Relativity in 1905. Prior to this, light was assumed to propagate on a medium in space called the Ether. f ) In the late-1800s, Michelson and Morley trie ...
15 HW 5.1 Magnetism.pub
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
Ch 21 Sec 3 Guided Reading
... 16. If there are more loops in the secondary coil of a transformer than in the primary coil, will the voltage in the secondary coil be higher or lower than in the primary coil? 17. Why is a transformer necessary so that electrical energy can be brought into a home? ...
... 16. If there are more loops in the secondary coil of a transformer than in the primary coil, will the voltage in the secondary coil be higher or lower than in the primary coil? 17. Why is a transformer necessary so that electrical energy can be brought into a home? ...
Câmara de bolhas - high school teachers at CERN
... energy to the medium. Hence, it does not cause the initiation of boiling along its path, therefore you get no bubbles. What other particles would not leave a track in a bubble chamber ? • A charged particle travelling through the same medium interacts with it trough Coulomb’s Force. In this way it t ...
... energy to the medium. Hence, it does not cause the initiation of boiling along its path, therefore you get no bubbles. What other particles would not leave a track in a bubble chamber ? • A charged particle travelling through the same medium interacts with it trough Coulomb’s Force. In this way it t ...
1102 Calculus II 11.12 Application of Taylor Series
... 1102 Calculus II 11.12 Application of Taylor Series Taylor series can be used to show that theories reduce to other theories under certain values of parameters. There is a beautiful example in the text relating special relativity to classical mechanics under the assumption that the speed of light is ...
... 1102 Calculus II 11.12 Application of Taylor Series Taylor series can be used to show that theories reduce to other theories under certain values of parameters. There is a beautiful example in the text relating special relativity to classical mechanics under the assumption that the speed of light is ...
Ferrofluids - SRJC | Santa Rosa Junior College
... Charles Wolfe, Newell Jensen, Jonathan Hogander and Seth McDonough ...
... Charles Wolfe, Newell Jensen, Jonathan Hogander and Seth McDonough ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.