The Influence of Surface Inhomogeneities On Deep Electromagnetic
... a common nature both for exploration with use of electromagnetic fields of natural originf' and for exploration with fields excited by controlled sources of current. To overcome such difficulties, use should be made of electromagnetic field modelling. Still, it should be noted that despite a high le ...
... a common nature both for exploration with use of electromagnetic fields of natural originf' and for exploration with fields excited by controlled sources of current. To overcome such difficulties, use should be made of electromagnetic field modelling. Still, it should be noted that despite a high le ...
Flow Control and Propulsion in Poor Conductors
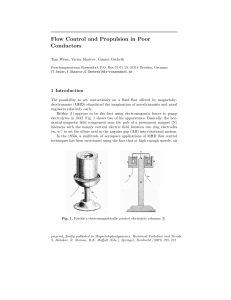
... problems. Resler and Sears [2] and Busemann [3] proposed, among others, to use magnetic fields to control heat transfer, decelerate or accelerate vehicles and to prevent flow separation. Although enthusiasm for the practical application of these ideas waned later on, the topic is now again under inv ...
... problems. Resler and Sears [2] and Busemann [3] proposed, among others, to use magnetic fields to control heat transfer, decelerate or accelerate vehicles and to prevent flow separation. Although enthusiasm for the practical application of these ideas waned later on, the topic is now again under inv ...
GAUSS` LAW
... Two uniformly charged planes with surface charge densities of 3.00×10−9 C m−2 and −1.00× 10−9 C m−2 lie parallel to each other a distance 8.00 cm apart in a vacuum. Draw the field lines between the plates and behind each plate and find E everywhere. (Hint: use superposition.) ...
... Two uniformly charged planes with surface charge densities of 3.00×10−9 C m−2 and −1.00× 10−9 C m−2 lie parallel to each other a distance 8.00 cm apart in a vacuum. Draw the field lines between the plates and behind each plate and find E everywhere. (Hint: use superposition.) ...
PowerPoint
... 1135 text uses the right hand rule shown in the figure, so we’ll use the same rule in Physics 2135. There are a number of variations of this rule. Unfortunately, most of the Youtube videos I find say to use your palm for A , your thumb for B , and your outstretched fingers for A B . This includes ...
... 1135 text uses the right hand rule shown in the figure, so we’ll use the same rule in Physics 2135. There are a number of variations of this rule. Unfortunately, most of the Youtube videos I find say to use your palm for A , your thumb for B , and your outstretched fingers for A B . This includes ...
Chap 1.3 notes
... • The origin of electric charge is found in the atom. • The nucleus of the atom contains positively charged protons (p+) and neutral neutrons (n0). • The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons (e-). ...
... • The origin of electric charge is found in the atom. • The nucleus of the atom contains positively charged protons (p+) and neutral neutrons (n0). • The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons (e-). ...
1. (a) Explain the meanings of Newton`s second and third Laws of
... 1. (a) Explain the meanings of Newton’s second and third Laws of Motion. (3 marks) (b) Apply these laws to the rapid impact between two bodies, which were initially moving with unequal velocities along the same direction, and show that linear momentum is conserved. Explain whether the total kinetic ...
... 1. (a) Explain the meanings of Newton’s second and third Laws of Motion. (3 marks) (b) Apply these laws to the rapid impact between two bodies, which were initially moving with unequal velocities along the same direction, and show that linear momentum is conserved. Explain whether the total kinetic ...
Unit 5 Force and Motion Vocabulary
... Force-‐ a push or pull Mass-‐the amount of matter in an object Motion-a change in an object’s position over time Position- an object’s location relative to a reference point. Friction- a force that tends to oppose motion between objects that interact with each ...
... Force-‐ a push or pull Mass-‐the amount of matter in an object Motion-a change in an object’s position over time Position- an object’s location relative to a reference point. Friction- a force that tends to oppose motion between objects that interact with each ...
Observation of Locally Negative Velocity of the Electromagnetic
... zero angular momentum is considered. There, however, the negative initial propagation of the average radial position for a ring-shaped wave packet is specific to the twodimensional case, and is related to the violation of the Huygens principle in the space of even dimensions [15]. The present effect ...
... zero angular momentum is considered. There, however, the negative initial propagation of the average radial position for a ring-shaped wave packet is specific to the twodimensional case, and is related to the violation of the Huygens principle in the space of even dimensions [15]. The present effect ...
Pinball-Example
... making a bulb light up Where’s the science? I learned a lot about making a light bulb light up, I learned that you can use metal things to complete a circuit a the reason it is science is that you can learn how to use a switch and you can use loads. A load is something that can have electricity in ...
... making a bulb light up Where’s the science? I learned a lot about making a light bulb light up, I learned that you can use metal things to complete a circuit a the reason it is science is that you can learn how to use a switch and you can use loads. A load is something that can have electricity in ...
The Electric Field
... electric field E is tangent to this line. No two field lines can cross! 2. The line must begin at positive charge and terminate on the negative one unless go to ...
... electric field E is tangent to this line. No two field lines can cross! 2. The line must begin at positive charge and terminate on the negative one unless go to ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.