Unit 3 EMR 2015
... Quantum (Particle) Theory: Light travels as a tiny bundle of energy in the vacuum of space. •Newton used particle theory to explain refraction. He thought light consisted of particles with _______. mass As the particles travelled from one medium to another they experienced a different force from th ...
... Quantum (Particle) Theory: Light travels as a tiny bundle of energy in the vacuum of space. •Newton used particle theory to explain refraction. He thought light consisted of particles with _______. mass As the particles travelled from one medium to another they experienced a different force from th ...
The Study of the Force Generated from a Changing Magnetic Field
... magnetic field was set up that exerted a braking force on the falling magnets to slow them down. Thus, due to magnetic repulsion, the magnets fall much slower than a non-magnetic reference weight. Then Newtons Second Law (F = ma) was used to measure the magnetic braking force by connecting the NIB m ...
... magnetic field was set up that exerted a braking force on the falling magnets to slow them down. Thus, due to magnetic repulsion, the magnets fall much slower than a non-magnetic reference weight. Then Newtons Second Law (F = ma) was used to measure the magnetic braking force by connecting the NIB m ...
Ch 21 PowerPoint Notes
... • The arrows on the field lines indicate what direction a compass needle would point at each point in space. • Where lines are close together, the field is strong. • Where lines are more spread out, the field is weak. ...
... • The arrows on the field lines indicate what direction a compass needle would point at each point in space. • Where lines are close together, the field is strong. • Where lines are more spread out, the field is weak. ...
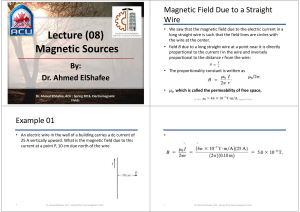
view file - Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
... compared to the field inside. Thus the first term in this sum will be zero. • B is perpendicular to the segments be and da inside the solenoid, and is nearly zero between and outside the coils, ...
... compared to the field inside. Thus the first term in this sum will be zero. • B is perpendicular to the segments be and da inside the solenoid, and is nearly zero between and outside the coils, ...
Work done (J) - MrSimonPorter
... Ft = mv – mu The quantity Ft is called the impulse, and of course mv – mu is the change in ...
... Ft = mv – mu The quantity Ft is called the impulse, and of course mv – mu is the change in ...
Here is the PowerPoint slide that I presented to the Science 10 class
... energy would change from one form to another. In our discussion today, we have seen electrical energy turn into mechanical energy and also from mechanical to electrical. Motors would help us to utilize the electrical energy that we have to do work through the form of mechanical energy. Generator doe ...
... energy would change from one form to another. In our discussion today, we have seen electrical energy turn into mechanical energy and also from mechanical to electrical. Motors would help us to utilize the electrical energy that we have to do work through the form of mechanical energy. Generator doe ...
practice exam
... 11. A spherical drop of water carrying a charge of 30 pC has a potential of 500 V at its surface (with V=0 at infinity). (a) (3 points) What is the radius of the drop? ...
... 11. A spherical drop of water carrying a charge of 30 pC has a potential of 500 V at its surface (with V=0 at infinity). (a) (3 points) What is the radius of the drop? ...
Newton`s Law
... Earth as an inertial frame of reference will be completely satisfactory for most purposes. Once we know one inertial reference frame, we can find many other ones. Based on experimental observations, we assume that the space is isotropic, i.e., if frame A is inertial and frame B differs from A only b ...
... Earth as an inertial frame of reference will be completely satisfactory for most purposes. Once we know one inertial reference frame, we can find many other ones. Based on experimental observations, we assume that the space is isotropic, i.e., if frame A is inertial and frame B differs from A only b ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.