MAGNETISM1
... By placing two bar magnets (magnetic iron) end to end they either attract or repel one another. A bar magnet is referred to as a permanent magnet because it retains its magnetic properties. Around each magnet there exists a magnetic flux which when brought into the range of a similar field will caus ...
... By placing two bar magnets (magnetic iron) end to end they either attract or repel one another. A bar magnet is referred to as a permanent magnet because it retains its magnetic properties. Around each magnet there exists a magnetic flux which when brought into the range of a similar field will caus ...
Phy107Fall06Lect29
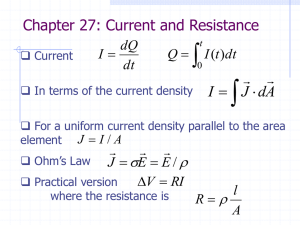
... • For larger currents, the voltage is no longer zero, and power is dissipated. ...
... • For larger currents, the voltage is no longer zero, and power is dissipated. ...
Buletin Stiintific - UPB - Seria A - numar 2 - 2008
... ELECTRIC FIELD AND INTENSE LASER RADIATION EFFECTS ON THE INTERBAND TRANSITIONS IN QUANTUM WELLS Ecaterina NICULESCU, Anca IORGA, Adrian RADU ...
... ELECTRIC FIELD AND INTENSE LASER RADIATION EFFECTS ON THE INTERBAND TRANSITIONS IN QUANTUM WELLS Ecaterina NICULESCU, Anca IORGA, Adrian RADU ...
PHY481 - Lecture 17: Magnets field lines, North and South. Lorentz
... In the past couple of years there have been exciting research developments in magnetostatics with the discovery of solid state magnetic materials where unbound magnetic monopoles have been found and magnetic currents have ~ ·B ~ 6= 0!. If these materials can be developed further it will be been gene ...
... In the past couple of years there have been exciting research developments in magnetostatics with the discovery of solid state magnetic materials where unbound magnetic monopoles have been found and magnetic currents have ~ ·B ~ 6= 0!. If these materials can be developed further it will be been gene ...
Review Sheet – Electrostatics
... b) one charge is doubled? c) both charges are doubled? d) the distance between them is halved? 21. Draw the electric field lines around: a) a single positive charge b) a single negative charge c) two like charges d) two unlike charges e) two parallel plates 22. Be able to draw electric force vectors ...
... b) one charge is doubled? c) both charges are doubled? d) the distance between them is halved? 21. Draw the electric field lines around: a) a single positive charge b) a single negative charge c) two like charges d) two unlike charges e) two parallel plates 22. Be able to draw electric force vectors ...
Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion
... drift speed (~10-4 m/s) The drift speed of electrical conduction can be understood through the Drude model which applies classical mechanics ...
... drift speed (~10-4 m/s) The drift speed of electrical conduction can be understood through the Drude model which applies classical mechanics ...
Electric Fields
... A fly accumulates 3.0 x 10-10 C of positive charge as it flies through the air. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a location of 2.0 cm away from the fly? ...
... A fly accumulates 3.0 x 10-10 C of positive charge as it flies through the air. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a location of 2.0 cm away from the fly? ...
Changing approach to teaching electromagnetism in a conceptually
... is not acceptable, especially in a conceptually oriented physics course. To ignore this problem would mean reducing physics to a cluster of disconnected units of knowledge, contrary to the aims usually proclaimed by physics educators. It may be just those good students who had internalized the const ...
... is not acceptable, especially in a conceptually oriented physics course. To ignore this problem would mean reducing physics to a cluster of disconnected units of knowledge, contrary to the aims usually proclaimed by physics educators. It may be just those good students who had internalized the const ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.