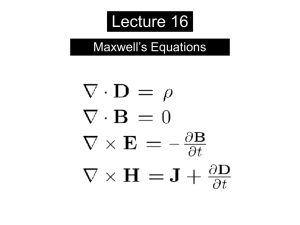Draft_EN50499 - Docbox
... the work place must first be characterised. This requires the employer to establish what electrical equipment that exists in the work place and is emitting electromagnetic fields into the work place. The first decision box of Figure 1 relates to compliant equipment. Most work places will contain onl ...
... the work place must first be characterised. This requires the employer to establish what electrical equipment that exists in the work place and is emitting electromagnetic fields into the work place. The first decision box of Figure 1 relates to compliant equipment. Most work places will contain onl ...
mass action and conservation of current
... where we use the vector identity that the divergence of a curl is always zero. B is the magnetic vector field; µ0 is the magnetic constant, the magnetic ‘permeability’ of a vacuum; and ε0 is the corresponding ‘electrostatic constant’, the permittivity of free space. Note that µ0 ε0 = c-2, where c is ...
... where we use the vector identity that the divergence of a curl is always zero. B is the magnetic vector field; µ0 is the magnetic constant, the magnetic ‘permeability’ of a vacuum; and ε0 is the corresponding ‘electrostatic constant’, the permittivity of free space. Note that µ0 ε0 = c-2, where c is ...
Lecture 16 - The Local Group
... When the experiment we’ve been thinking about with the charging capacitor is actually performed, the predicted magnetic field between the plates is, in fact, observed. - Maxwell’s theoretical hunch was right! To summarize what it means: •a changing magnetic field creates an induced electric field (F ...
... When the experiment we’ve been thinking about with the charging capacitor is actually performed, the predicted magnetic field between the plates is, in fact, observed. - Maxwell’s theoretical hunch was right! To summarize what it means: •a changing magnetic field creates an induced electric field (F ...
Electric Potential
... This lecture introduces electric potential energy and something called “electric potential.” Electric potential energy is “just like” gravitational potential energy. Except that all matter exerts an attractive gravitational force, but charged particles exert either attractive or repulsive electrica ...
... This lecture introduces electric potential energy and something called “electric potential.” Electric potential energy is “just like” gravitational potential energy. Except that all matter exerts an attractive gravitational force, but charged particles exert either attractive or repulsive electrica ...
Microscopic and macroscopic polarization within a combined quantum
... the second hyperpolarizability. The numerical coefficients K(⫺ s ; a ,...) are the same as for the macroscopic polarization and again this ensures that all 共hyper兲polarizabilities of the same order have the same static limit. The subscripts ␣ ,  , ␥ ,... denote molecule-fixed axes and again the ...
... the second hyperpolarizability. The numerical coefficients K(⫺ s ; a ,...) are the same as for the macroscopic polarization and again this ensures that all 共hyper兲polarizabilities of the same order have the same static limit. The subscripts ␣ ,  , ␥ ,... denote molecule-fixed axes and again the ...
Effect of an external electric field on the dissociation energy and the
... The effect of a homogeneous external electric field parallel to the hydrogen bond in the FH¯ FH dimer has been studied by theoretical methods. The quantum theory of atoms in molecules methodology has been used for analyzing the electron distribution of the dimer, calculated with different hydrogen b ...
... The effect of a homogeneous external electric field parallel to the hydrogen bond in the FH¯ FH dimer has been studied by theoretical methods. The quantum theory of atoms in molecules methodology has been used for analyzing the electron distribution of the dimer, calculated with different hydrogen b ...
The Photon consists of a Positive and a Negative Charge
... proposed that the positive charge propagates in the radial direction and at the same time it rotates clockwise perpendicular to the radial direction resulting in a helix shaped motion. The negative charge rotates counter clockwise resulting that the two charges propagate along a double helix with th ...
... proposed that the positive charge propagates in the radial direction and at the same time it rotates clockwise perpendicular to the radial direction resulting in a helix shaped motion. The negative charge rotates counter clockwise resulting that the two charges propagate along a double helix with th ...
lab 5 Magnetic Fields and Forces
... allows us to explore the structure of the Universe, the atomic structure of materials, and the quark structure of elementary particles. The magnetic interaction can best be described using the concept of a field. For this reason, your experiences exploring the electric field concept are also applica ...
... allows us to explore the structure of the Universe, the atomic structure of materials, and the quark structure of elementary particles. The magnetic interaction can best be described using the concept of a field. For this reason, your experiences exploring the electric field concept are also applica ...
Physical Science Physics - Department of Basic Education
... Break up your learning sections into manageable parts. Trying to learn too much at one time will only result in a tired, unfocused and anxious brain. ...
... Break up your learning sections into manageable parts. Trying to learn too much at one time will only result in a tired, unfocused and anxious brain. ...
Multipole Expansion of the Electrostatic Potential
... The potential of a localized charge distribution at large distance can be expanded as a series of multipole terms.1 The terms of the series depend on the charge spatial distribution in the system and have different dependence from the distance. In this chapter we will first examine the electric dipo ...
... The potential of a localized charge distribution at large distance can be expanded as a series of multipole terms.1 The terms of the series depend on the charge spatial distribution in the system and have different dependence from the distance. In this chapter we will first examine the electric dipo ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.