ISNS4371_011807_bw
... For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surface to provide such an opposing force - no sensation of weight (no apparent weight). - free-fall - experience ...
... For a body supported in a stationary position, normal force exactly balances earth's gravitational force - apparent weight has the same magnitude as actual weight. If no contact with any surface to provide such an opposing force - no sensation of weight (no apparent weight). - free-fall - experience ...
Basic Biomechanics, (5th edition) by Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
... resistance produced which tends to spring back the molecules to their original position and this internal resistance per unit area is know as Stress. Pressure is nothing but force acting on a unit ...
... resistance produced which tends to spring back the molecules to their original position and this internal resistance per unit area is know as Stress. Pressure is nothing but force acting on a unit ...
Q1. The diagram shows the forces acting on a skydiver. Draw a ring
... Use the equation in the box to calculate the maximum weight this passenger seems to have during the ride. weight = mass × gravitational field strength Show clearly how you work out your answer. ...
... Use the equation in the box to calculate the maximum weight this passenger seems to have during the ride. weight = mass × gravitational field strength Show clearly how you work out your answer. ...
Document
... N & S always together as dipole (NO “magnetic charge”) Opposite poles attract, like poles repel N ...
... N & S always together as dipole (NO “magnetic charge”) Opposite poles attract, like poles repel N ...
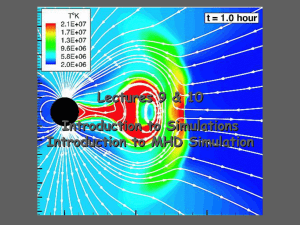
Introduction to simulations
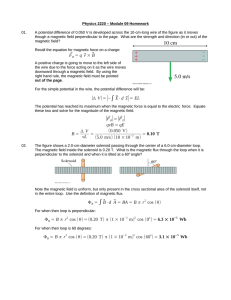
... – As long as frozen in flux holds plasmas can mix along flux tubes but not across them. When two plasma regimes interact a thin boundary will separate the plasma The magnetic field on either side of the boundary will be tangential to the boundary (e.g. a current sheet forms). ...
... – As long as frozen in flux holds plasmas can mix along flux tubes but not across them. When two plasma regimes interact a thin boundary will separate the plasma The magnetic field on either side of the boundary will be tangential to the boundary (e.g. a current sheet forms). ...
9th lecture Kirchhoff`s laws and Electromotance
... groups ionize the hydrogen ions can leave the neighborhood of the surface. This process stops, however, when the appearing electric field gets strong enough to withhold the remaining hydrogen ions. The order of magnitude of this voltage is 1 V. This small voltage in itself would not be enough to cau ...
... groups ionize the hydrogen ions can leave the neighborhood of the surface. This process stops, however, when the appearing electric field gets strong enough to withhold the remaining hydrogen ions. The order of magnitude of this voltage is 1 V. This small voltage in itself would not be enough to cau ...
Force - TeacherWeb
... GRAVITY- Force of attraction between all objects in the universe. NEWTON- SI unit of force. WEIGHT- Measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. ...
... GRAVITY- Force of attraction between all objects in the universe. NEWTON- SI unit of force. WEIGHT- Measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. ...
dynamics - moorsscience
... 2. Electromagnetic force: The force that exists between charged particles (repulsion or attraction). This force is transmitted by electric fields. Magnetic fields are linked to electric fields (as are electricity and magnetism) so it is called the electromagnetic force. 3. Gravitation or gravity is ...
... 2. Electromagnetic force: The force that exists between charged particles (repulsion or attraction). This force is transmitted by electric fields. Magnetic fields are linked to electric fields (as are electricity and magnetism) so it is called the electromagnetic force. 3. Gravitation or gravity is ...
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
... electric currents. There are also two kinds of electric currents: direct (DC) and alternating (AC). Electricity and magnetism are closely related. Flowing electrons produce a magnetic field, and spinning magnets cause an electric current to flow. Electromagnetism is the interaction of these two impo ...
... electric currents. There are also two kinds of electric currents: direct (DC) and alternating (AC). Electricity and magnetism are closely related. Flowing electrons produce a magnetic field, and spinning magnets cause an electric current to flow. Electromagnetism is the interaction of these two impo ...
Slide 1
... An electric field exists in a region if space if a charge placed in that region experiences an electric force. ...
... An electric field exists in a region if space if a charge placed in that region experiences an electric force. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... scientific fields, subordinating all of them to philosophy, considered as the apex of knowledge. In the subsequent centuries, this discipline was in turn subdivided, following a hierarchical order, into ethics, physics and logic/rhetoric. Later, after higher instruction was re-evaluated in the Middl ...
... scientific fields, subordinating all of them to philosophy, considered as the apex of knowledge. In the subsequent centuries, this discipline was in turn subdivided, following a hierarchical order, into ethics, physics and logic/rhetoric. Later, after higher instruction was re-evaluated in the Middl ...
Week 2 - UniMAP Portal
... resistance produced which tends to spring back the molecules to their original position and this internal resistance per unit area is know as Stress. Pressure is nothing but force acting on a unit ...
... resistance produced which tends to spring back the molecules to their original position and this internal resistance per unit area is know as Stress. Pressure is nothing but force acting on a unit ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.