S. Savin
... The plasma jets, accelerated sunward, often are regarded as proof for a macroreconnection; while every jet, accelerated in MSH should be reflected by a magnetic barrier for ...
... The plasma jets, accelerated sunward, often are regarded as proof for a macroreconnection; while every jet, accelerated in MSH should be reflected by a magnetic barrier for ...
physics b
... motion on Earth. They are taken to Planet X, which has the same diameter as Earth but twice the mass. Which of the following statements is true about the periods of the two objects on Planet X compared to their periods on earth? (A) Both are shorter. (B) Both are the same. (C) Both are longer. (D) T ...
... motion on Earth. They are taken to Planet X, which has the same diameter as Earth but twice the mass. Which of the following statements is true about the periods of the two objects on Planet X compared to their periods on earth? (A) Both are shorter. (B) Both are the same. (C) Both are longer. (D) T ...
Space Plasma Physics
... • Suitable boundary conditions are derived from measurements of the photospheric field vector. - Bn and Jn for positive or negative polarity on boundary (Grad-Rubin) - Magnetic field vector Bx By Bz on boundary (Magnetofrictional, Optimization) ...
... • Suitable boundary conditions are derived from measurements of the photospheric field vector. - Bn and Jn for positive or negative polarity on boundary (Grad-Rubin) - Magnetic field vector Bx By Bz on boundary (Magnetofrictional, Optimization) ...
Force and Motion Force Classifying Forces
... proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass 3) If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. ...
... proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass 3) If two objects interact, the force exerted on object 1 by object 2 is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the force exerted on object 2 by object 1. ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
What state and other requrements
... superconductors are nearly limitless, but most of them have to be operated at very cold temperatures which presents problems. There are two types of superconductors-Type I and Type II as they were so aptly named. Type I superconductors generally need to be cooled with liquid helium and have critical ...
... superconductors are nearly limitless, but most of them have to be operated at very cold temperatures which presents problems. There are two types of superconductors-Type I and Type II as they were so aptly named. Type I superconductors generally need to be cooled with liquid helium and have critical ...
chapter28.3 - Colorado Mesa University
... The Electric Potential Energy of a charge q in the uniform Efield of a parallel-plate capacitor is… ...
... The Electric Potential Energy of a charge q in the uniform Efield of a parallel-plate capacitor is… ...
Monday, Oct. 7, 2002
... it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
... it experiences a resistive force proportional to its speed. The ball reaches a terminal speed of 5.00 cm/s. Determine the time constant t and the time it takes the ball to reach 90% of its terminal speed. ...
workshop on ME - Kendriya Vidyalaya SAC, Vastrapur, Ahmedabad
... does not affect the current. Therefore to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a low resistance, called shunt, is connected in parallel with the galvanometer coil. ...
... does not affect the current. Therefore to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a low resistance, called shunt, is connected in parallel with the galvanometer coil. ...
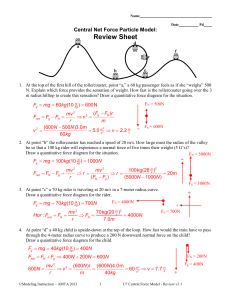
Central Net Force Particle Model:
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.