Science Essentials 7 for NSW, Stage 4, Australian Curriculum
... ● use the term ‘field’ when describing forces acting at a distance (PW2a) ● describe ways in which objects become electrically charged, and investigate everyday situations where the effects of electrostatic forces can be observed (PW2b/d) ● describe the behaviour of magnetic poles and electric ch ...
... ● use the term ‘field’ when describing forces acting at a distance (PW2a) ● describe ways in which objects become electrically charged, and investigate everyday situations where the effects of electrostatic forces can be observed (PW2b/d) ● describe the behaviour of magnetic poles and electric ch ...
Snímek 1
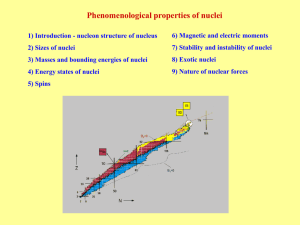
... Nuclear forces are attractive (bond nucleus together), for very short distances (~0.4 fm) they are repulsive (nucleus does not collapse). More accurate form of nuclear force potential can be obtained by scattering of nucleons on nucleons or nuclei. ...
... Nuclear forces are attractive (bond nucleus together), for very short distances (~0.4 fm) they are repulsive (nucleus does not collapse). More accurate form of nuclear force potential can be obtained by scattering of nucleons on nucleons or nuclei. ...
17 - Northern Highlands
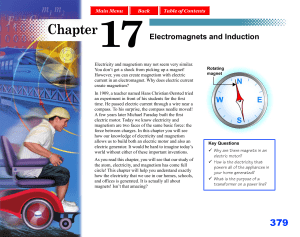
... For a long time, people believed electricity and magnetism were unrelated. As scientists began to understand electricity better, they searched for relationships between electricity and magnetism. In 1819, Hans Christian Øersted, a Danish physicist and chemist, placed a compass needle near a wire in ...
... For a long time, people believed electricity and magnetism were unrelated. As scientists began to understand electricity better, they searched for relationships between electricity and magnetism. In 1819, Hans Christian Øersted, a Danish physicist and chemist, placed a compass needle near a wire in ...
Tangential force
... figure a tangential force F is applied at a distance r from the axis of rotation. If the minimum torque required to open the door is 3.1 N·m, what force must be applied if r is (a) 0.94 m, or (b) 0.35 m? Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1151G Department of Physics ...
... figure a tangential force F is applied at a distance r from the axis of rotation. If the minimum torque required to open the door is 3.1 N·m, what force must be applied if r is (a) 0.94 m, or (b) 0.35 m? Dr. Jie Zou PHY 1151G Department of Physics ...
Magnetic quenching of time-reversed light in photorefractive diluted magnetic semiconductors
... Phase conjugation is a nonlinear optical effect1 involving coherent light beams that interact in a nonlinear optical material to generate a beam that exactly retraces the path and reconstructs the wave front of one of the incident waves, called the probe. This property suggests possible applications ...
... Phase conjugation is a nonlinear optical effect1 involving coherent light beams that interact in a nonlinear optical material to generate a beam that exactly retraces the path and reconstructs the wave front of one of the incident waves, called the probe. This property suggests possible applications ...
Dimensionless Physical Constant Mysteries
... (6) α1/2 may be obtained using a certain combination of π, e, 2 and 5 (e.g., the golden ratio Φ = φ1 = 2 cos( π5 )). (7) There are many π and e combinations which are not unique solutions to this important unique physical number.4 (8) The α math formula must be useful for solving physical mysteries, ...
... (6) α1/2 may be obtained using a certain combination of π, e, 2 and 5 (e.g., the golden ratio Φ = φ1 = 2 cos( π5 )). (7) There are many π and e combinations which are not unique solutions to this important unique physical number.4 (8) The α math formula must be useful for solving physical mysteries, ...
A Robust Multi-Scale Field-Only Formulation of Electromagnetic
... Sec. V. As expected, scattering by dielectric bodies considered in Sec. VI is more complex in technical details but the basic framework is the same. The key result in this case is a generalised Fresnel condition and Snell’s law at a curved dielectric boundary that reduces naturally to the familiar r ...
... Sec. V. As expected, scattering by dielectric bodies considered in Sec. VI is more complex in technical details but the basic framework is the same. The key result in this case is a generalised Fresnel condition and Snell’s law at a curved dielectric boundary that reduces naturally to the familiar r ...
Magnetic Devices for a Beam Energy Recovery THz Free Electron
... the original equipment. The initial magnetic field generated in the undulator does not depend on the distance of the gap but wavelength (equation 5) and thus it is possible to make a comparison between the simulation and the experiment. The materials used were a NdFeB magnetic material is (33SH) and ...
... the original equipment. The initial magnetic field generated in the undulator does not depend on the distance of the gap but wavelength (equation 5) and thus it is possible to make a comparison between the simulation and the experiment. The materials used were a NdFeB magnetic material is (33SH) and ...
berezinskii-kosterlitz-thouless transition and the haldane conjecture
... There are classes of systems, which may look quite different, In the limit ξ → ∞, the spacing between the lattice points but which share the same critical behavior, so we say that they becomes insignificant (it is negligible compared to ξ), so this belong to the same universality class. This means i ...
... There are classes of systems, which may look quite different, In the limit ξ → ∞, the spacing between the lattice points but which share the same critical behavior, so we say that they becomes insignificant (it is negligible compared to ξ), so this belong to the same universality class. This means i ...
Electric Potential around Point Charges
... contact as long as the object is in the Earth’s gravitational field. Gravity is a “force field” Force field – a region in space in which an object can be placed and forces will be exerted on the object without contact Electrical charges can move other electrical charges without making contact; there ...
... contact as long as the object is in the Earth’s gravitational field. Gravity is a “force field” Force field – a region in space in which an object can be placed and forces will be exerted on the object without contact Electrical charges can move other electrical charges without making contact; there ...
Physics 1002 – Magnetic Fields (Read objectives on screen
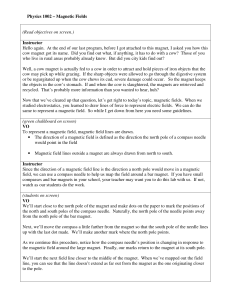
... Inside the magnet, the field lines continue to form closed loops, like this. However, you won’t need to draw these because we’ll concentrate on the field surrounding the magnet. Instructor Mapping magnetic fields using the compass method would take a long, long time. But there’s an easier way. Remem ...
... Inside the magnet, the field lines continue to form closed loops, like this. However, you won’t need to draw these because we’ll concentrate on the field surrounding the magnet. Instructor Mapping magnetic fields using the compass method would take a long, long time. But there’s an easier way. Remem ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science Maglev Module
... objects attract, while objects with like charge repel. The strength of the electric force between two charged objects is proportional to the magnitudes of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (Coulomb’s Law). Predict how the electric force between charged ...
... objects attract, while objects with like charge repel. The strength of the electric force between two charged objects is proportional to the magnitudes of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (Coulomb’s Law). Predict how the electric force between charged ...
Date: Thu, 4 Aug 2005 - ASU Modeling Instruction
... I needed to chime in on the current discussion of which force/property terms tend to cause confusion, and might therefore be avoided. I find that my students tend to confuse the terms normal force (Fn) and net force. Unless I'm very careful (and sometimes even then) some will start thinking off bot ...
... I needed to chime in on the current discussion of which force/property terms tend to cause confusion, and might therefore be avoided. I find that my students tend to confuse the terms normal force (Fn) and net force. Unless I'm very careful (and sometimes even then) some will start thinking off bot ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.