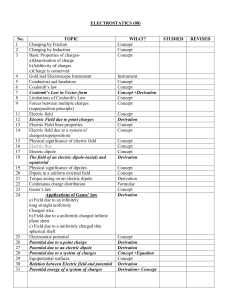
electrostatics (08)
... Comparison between Coulombs law in electrostatics and Biot-Savarts Law Magnetic field on the axis of a circular current carrying loop Circular current loop as a magnetic dipole Ampere s circuital law Application of Ampere s circuital law Magnetic field due to a solenoid Application of Ampere s circu ...
... Comparison between Coulombs law in electrostatics and Biot-Savarts Law Magnetic field on the axis of a circular current carrying loop Circular current loop as a magnetic dipole Ampere s circuital law Application of Ampere s circuital law Magnetic field due to a solenoid Application of Ampere s circu ...
as a PDF
... 1.3.3 A detailed model for the exotic Cooper pair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.3.4 Speculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.4 Exotic atoms, wormhole super conductivity and wormhole magnetic fields . . 1.4.1 Exotic atoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 1.3.3 A detailed model for the exotic Cooper pair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.3.4 Speculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.4 Exotic atoms, wormhole super conductivity and wormhole magnetic fields . . 1.4.1 Exotic atoms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Simulation of the formation of antihydrogen in a nested Penning trap:
... study antihydrogen formation in the equilibrium situation. ...
... study antihydrogen formation in the equilibrium situation. ...
I - CBSE Guess
... 23) Solid air-fresheners are complex chemical compounds. What kind of chemical bonding would these compounds have and why? [Ans: Air-fresheners will have covalent bonding. It is because, they are soft solids which slowly change into gaseous state at room temperature, which are the characteristics of ...
... 23) Solid air-fresheners are complex chemical compounds. What kind of chemical bonding would these compounds have and why? [Ans: Air-fresheners will have covalent bonding. It is because, they are soft solids which slowly change into gaseous state at room temperature, which are the characteristics of ...
TGD AND EEG
... 3.1.4 Fractal hierarchy of EEGs and ZEGs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167 3.1.5 The effects of ELF em fields on brain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167 3.1.6 TGD assigns 10 Hz biorhythm to electron as an intrinsic frequency scale . . . . 168 3.1.7 DNA and topologic ...
... 3.1.4 Fractal hierarchy of EEGs and ZEGs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167 3.1.5 The effects of ELF em fields on brain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167 3.1.6 TGD assigns 10 Hz biorhythm to electron as an intrinsic frequency scale . . . . 168 3.1.7 DNA and topologic ...
Bioelectromagnetism
... the fundamentals of many contemporary methods were actually developed years ago. Our scope in the later chapters is necessarily limited, and thus readers will find only an overview of the topics (applications). Despite their brevity, these applications should help clarify and strengthen the reader's ...
... the fundamentals of many contemporary methods were actually developed years ago. Our scope in the later chapters is necessarily limited, and thus readers will find only an overview of the topics (applications). Despite their brevity, these applications should help clarify and strengthen the reader's ...
mechanics of material forces
... appearing in the theory of fluid mixtures (Ray Bowen, M. Grinfeld) and with its jump at discontinuity surfaces. It would be dangerous to pursue this historical disquisition further. If we did, we would enter a period where most active contributors to the field are still active at the time of this wr ...
... appearing in the theory of fluid mixtures (Ray Bowen, M. Grinfeld) and with its jump at discontinuity surfaces. It would be dangerous to pursue this historical disquisition further. If we did, we would enter a period where most active contributors to the field are still active at the time of this wr ...
Magneto optical trapping of potassium-39 in a ring cavity
... an optical ring cavity. Firstly we load a potassium-39 magneto optical trap (MOT) inside the ring cavity. To achieve this a laser system, rectangular magnetic coils system and vacuum system are designed and constructed. To stabilise the laser system, a detailed study of various potassium spectroscop ...
... an optical ring cavity. Firstly we load a potassium-39 magneto optical trap (MOT) inside the ring cavity. To achieve this a laser system, rectangular magnetic coils system and vacuum system are designed and constructed. To stabilise the laser system, a detailed study of various potassium spectroscop ...
THE SCIENCE OF JET
... electrons and forms a positive ion. For any species of atom there will be a plasma temperature above which all the atoms have lost an electron, and the gas is then said to be fully ionised. In the case of the hydrogen isotopes, hydrogen, deuterium and tritium, the atom has only one electron, and con ...
... electrons and forms a positive ion. For any species of atom there will be a plasma temperature above which all the atoms have lost an electron, and the gas is then said to be fully ionised. In the case of the hydrogen isotopes, hydrogen, deuterium and tritium, the atom has only one electron, and con ...
RASHBA SPIN-ORBIT INTERACTION IN MESOSCOPIC SYSTEMS Frank Erik Meijer
... ripe for me to become rich; I first had to continue increasing my knowledge and understanding of the physical world around me in the form of a PhD. The present thesis describes the electron transport and spin dynamics in solid-state systems, and is the result of four years of research in Delft and i ...
... ripe for me to become rich; I first had to continue increasing my knowledge and understanding of the physical world around me in the form of a PhD. The present thesis describes the electron transport and spin dynamics in solid-state systems, and is the result of four years of research in Delft and i ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.