Magnetic field pattern around a flat coil
... Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule We can easily deduce the direction of the force on the current-carrying wire when it is placed in a magnetic field using Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule. It helps us to predict the direction of motion or force. ...
... Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule We can easily deduce the direction of the force on the current-carrying wire when it is placed in a magnetic field using Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule. It helps us to predict the direction of motion or force. ...
PH2200 Practice Final Exam Spring 2004
... is entirely in the plus and minus z directions in space as described in an xyz coordinate system. Select the incorrect statement about this wave. (A) The magnetic field of this wave must be entirely in the x-y plane. (B) If the magnetic field of this wave is entirely in the plus and minus x directio ...
... is entirely in the plus and minus z directions in space as described in an xyz coordinate system. Select the incorrect statement about this wave. (A) The magnetic field of this wave must be entirely in the x-y plane. (B) If the magnetic field of this wave is entirely in the plus and minus x directio ...
File
... Different materials influence the strength of the electromagnet. Different metals can be used for the core: iron, steel, nickel or cobalt. Iron is most commonly used because when you turn off the electricity it demagnetizes. Metals like steel remain magnetized thus creating a permanent magnet. ...
... Different materials influence the strength of the electromagnet. Different metals can be used for the core: iron, steel, nickel or cobalt. Iron is most commonly used because when you turn off the electricity it demagnetizes. Metals like steel remain magnetized thus creating a permanent magnet. ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
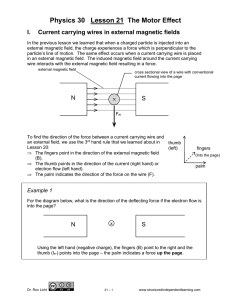
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
Magnetic Materials Background: 7. Hysteresis
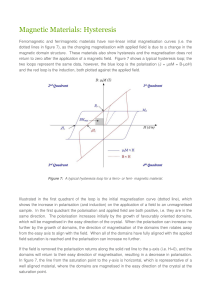
... The hysteresis loop is a means of characterising magnetic materials, and various parameters can be determined from it. From the first quadrant the saturation polarisation, JS and hence the saturation magnetisation, MS can be measured. Most of the useful information, however, can be derived from the ...
... The hysteresis loop is a means of characterising magnetic materials, and various parameters can be determined from it. From the first quadrant the saturation polarisation, JS and hence the saturation magnetisation, MS can be measured. Most of the useful information, however, can be derived from the ...
Syllabus - Tennessee State University
... for further study in the natural or health sciences. Learning Objective: Students will be able to apply the principles of physics in medical or biological contexts. Course Audience: This course is primarily for students majoring in biology, chemistry, and allied health. Attendance: Attendance is req ...
... for further study in the natural or health sciences. Learning Objective: Students will be able to apply the principles of physics in medical or biological contexts. Course Audience: This course is primarily for students majoring in biology, chemistry, and allied health. Attendance: Attendance is req ...
2. Electromagnetism
... Occurs when a changing magnetic field is used to induce current flow – The induced current flow will oppose the action that induced it – This is known as self-induction – This law establishes magnetic polarity Application in Radiology – This principle is applied to rotating anodes ...
... Occurs when a changing magnetic field is used to induce current flow – The induced current flow will oppose the action that induced it – This is known as self-induction – This law establishes magnetic polarity Application in Radiology – This principle is applied to rotating anodes ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.