PowerPoint Presentation - Slide 1 - plutonium
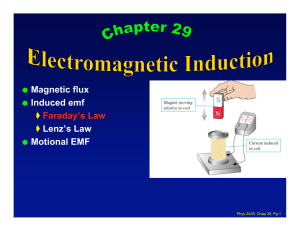
... An induced emf gives rise to a current whose magnetic filed opposes the original change in flux (in a closed circuit) It is also valid for an open circuit: An induced emf is always in the direction that opposes the original change in flux that caused it . ...
... An induced emf gives rise to a current whose magnetic filed opposes the original change in flux (in a closed circuit) It is also valid for an open circuit: An induced emf is always in the direction that opposes the original change in flux that caused it . ...
What is a magnetic field? by David Sligar
... may leave behind a neutron star, or a black hole, depending on the mass available. Certain magnetic rapidly rotating neutron stars, known as Magnetars, are believed to produce the strongest magnetic fields in the universe. A black hole is an object of such dense mass that it creates a gravitational ...
... may leave behind a neutron star, or a black hole, depending on the mass available. Certain magnetic rapidly rotating neutron stars, known as Magnetars, are believed to produce the strongest magnetic fields in the universe. A black hole is an object of such dense mass that it creates a gravitational ...
Errors and Limitations of the Magnetic Compass
... "magnetosphere"). Of the many time variations due to the external field, only two are of importance here: the diurnal variation and magnetic storms. Every day the magnetic field undergoes a regular variation. The declination (in the southern hemisphere) moves to the west of its mean value in the mor ...
... "magnetosphere"). Of the many time variations due to the external field, only two are of importance here: the diurnal variation and magnetic storms. Every day the magnetic field undergoes a regular variation. The declination (in the southern hemisphere) moves to the west of its mean value in the mor ...
Chapter 20 Concept Tests - University of Colorado Boulder
... A) Yes, the electrons go straight through B) No, the electrons are bent Answers: Yes, the forces can cancel so the particle can move straight through. Yes, the electrons also go straight through. ...
... A) Yes, the electrons go straight through B) No, the electrons are bent Answers: Yes, the forces can cancel so the particle can move straight through. Yes, the electrons also go straight through. ...
Welcome to the Vanderbilt Center for Radiation Oncology
... Motors and Back emf As the motor rotates, the magnetic flux through the loop changes with time This induces a back emf that tends to reduce the current applied to the motor from the external source When a motor is first turned on, the current is very large because there is no back emf initial ...
... Motors and Back emf As the motor rotates, the magnetic flux through the loop changes with time This induces a back emf that tends to reduce the current applied to the motor from the external source When a motor is first turned on, the current is very large because there is no back emf initial ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.