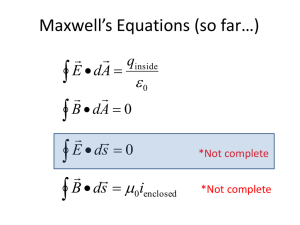HW #8 Solutions
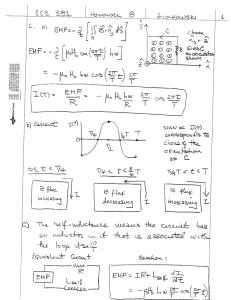
... Problem 6.5 A circular-loop TV antenna with 0.02-m2 area is in the presence of a uniform-amplitude 300-MHz signal. When oriented for maximum response, the loop develops an emf with a peak value of 30 (mV). What is the peak magnitude of B of the incident wave? Solution: TV loop antennas have one tur ...
... Problem 6.5 A circular-loop TV antenna with 0.02-m2 area is in the presence of a uniform-amplitude 300-MHz signal. When oriented for maximum response, the loop develops an emf with a peak value of 30 (mV). What is the peak magnitude of B of the incident wave? Solution: TV loop antennas have one tur ...
Sheath properties and related phenomena of the plasma wall
... 510-6 Torr. On the tube axis, at one end is mounted the multi-channel analyzer while at the other end is mounted an electron gun. The electron gun is used as source of electrons, the latter ones being accelerated up to 100 eV. For an analyzer having the channel diameters in the range of 0.3-0.9 mm, ...
... 510-6 Torr. On the tube axis, at one end is mounted the multi-channel analyzer while at the other end is mounted an electron gun. The electron gun is used as source of electrons, the latter ones being accelerated up to 100 eV. For an analyzer having the channel diameters in the range of 0.3-0.9 mm, ...
CT31-1
... F-11. Two loop of wires labeled A and B are placed near each other as shown. A large current I in loop A is suddenly turned on. This causes an induced current in loop B which causes A) A net replusive force - the two loops repel B) A net attractive force - the two loops attract C) whether the force ...
... F-11. Two loop of wires labeled A and B are placed near each other as shown. A large current I in loop A is suddenly turned on. This causes an induced current in loop B which causes A) A net replusive force - the two loops repel B) A net attractive force - the two loops attract C) whether the force ...
holiday homework (physics)-2017
... 7. Define the term electric flux .Write its S.I.unit. 8. An electric dipole of dipole moment 20x10-6 C m and is enclosed by closed surface. What is the net flux coming out of the surface? 9. Why does electric field inside a dielectric decrease when it is placed in an external electric field? 10.An e ...
... 7. Define the term electric flux .Write its S.I.unit. 8. An electric dipole of dipole moment 20x10-6 C m and is enclosed by closed surface. What is the net flux coming out of the surface? 9. Why does electric field inside a dielectric decrease when it is placed in an external electric field? 10.An e ...
physics - Career Point Kota
... Characteristic properties of photons : (i) Energy of photon is directly proportional to the frequency (or inversely proportional to the wavelength). (ii) In photon-electron collision, total energy and momentum of the system of two constituents remains constant. (iii) In the interaction of photons wi ...
... Characteristic properties of photons : (i) Energy of photon is directly proportional to the frequency (or inversely proportional to the wavelength). (ii) In photon-electron collision, total energy and momentum of the system of two constituents remains constant. (iii) In the interaction of photons wi ...
Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance and expulsion of magnetic fields occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature. It was discovered by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 in Leiden. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state. The occurrence of the Meissner effect indicates that superconductivity cannot be understood simply as the idealization of perfect conductivity in classical physics.The electrical resistivity of a metallic conductor decreases gradually as temperature is lowered. In ordinary conductors, such as copper or silver, this decrease is limited by impurities and other defects. Even near absolute zero, a real sample of a normal conductor shows some resistance. In a superconductor, the resistance drops abruptly to zero when the material is cooled below its critical temperature. An electric current flowing through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source.In 1986, it was discovered that some cuprate-perovskite ceramic materials have a critical temperature above 90 K (−183 °C). Such a high transition temperature is theoretically impossible for a conventional superconductor, leading the materials to be termed high-temperature superconductors. Liquid nitrogen boils at 77 K, and superconduction at higher temperatures than this facilitates many experiments and applications that are less practical at lower temperatures.