Heart Anatomy Glossary The heart is a fist
... The heart is a fist-sized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body. Oxygenpoor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava). The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary artery to the lung ...
... The heart is a fist-sized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body. Oxygenpoor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava). The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary artery to the lung ...
Biochemistry - U
... in rupture of the ventricular free wall (most common), intraventricular septum (left to right shunt produced), and papillary muscle rupture (least common) usually the posteriormedial muscle resulting in acute mitral valve regurgitation. Generally occurs in first week with 1-5% incidence. d) Ventricu ...
... in rupture of the ventricular free wall (most common), intraventricular septum (left to right shunt produced), and papillary muscle rupture (least common) usually the posteriormedial muscle resulting in acute mitral valve regurgitation. Generally occurs in first week with 1-5% incidence. d) Ventricu ...
VITAL SIGNS
... Rate: the number of beats per minute Volume: refers to the force or strength of the pulse: normal, bounding, weak, thready (barely perceivable) ...
... Rate: the number of beats per minute Volume: refers to the force or strength of the pulse: normal, bounding, weak, thready (barely perceivable) ...
Document
... Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) • Collection of venous blood (reservoir) • Adds oxygen (oxygenator) • Returns blood to a large artery (heat exchanger) • Level of fluid in reservoir is critical (type of pumps) • Activation of stress hormones ...
... Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) • Collection of venous blood (reservoir) • Adds oxygen (oxygenator) • Returns blood to a large artery (heat exchanger) • Level of fluid in reservoir is critical (type of pumps) • Activation of stress hormones ...
heart and blood vessels
... lower parts of the body, legs and abdomens) • Coronary sinus: drains blood from most of the vessels that supply the walls of the heart with blood. ...
... lower parts of the body, legs and abdomens) • Coronary sinus: drains blood from most of the vessels that supply the walls of the heart with blood. ...
ePapyrus PDF Document
... Department of Pediatrics,Grown-up Congenital Heart Clinic, Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 50 Irwon-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 135-710, Korea ...
... Department of Pediatrics,Grown-up Congenital Heart Clinic, Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 50 Irwon-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 135-710, Korea ...
Cardiology Board Exam - Palestine Medical Council
... 31. On treating ischaemic heart disease: …..A: patient’s education about risk factors is of paramount importance. …..B: beta- blockers should be considered for all patients. …..C: beta- blockers reduce oxygen demand but may cause coronary spasm. …..D: beta-blockers are safe in patients with stable o ...
... 31. On treating ischaemic heart disease: …..A: patient’s education about risk factors is of paramount importance. …..B: beta- blockers should be considered for all patients. …..C: beta- blockers reduce oxygen demand but may cause coronary spasm. …..D: beta-blockers are safe in patients with stable o ...
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart Heart Location
... – left side of heart pumps blood through body – left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into aorta – aorta branches into many arteries that travel to organs – arteries branch into many arterioles in tissue – arterioles branch into thin-walled capillaries for exchange of gases and nutrients – deoxygena ...
... – left side of heart pumps blood through body – left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into aorta – aorta branches into many arteries that travel to organs – arteries branch into many arterioles in tissue – arterioles branch into thin-walled capillaries for exchange of gases and nutrients – deoxygena ...
Circulation and Gas Exchange
... the right AV valve into the right ventricle. • Right ventricle contracts and blood is pumped into the pulmonary arteries through the semi-lunar valve • In the lungs the blood loses its carbon dioxide and gains fresh oxygen before entering the pulmonary veins. ...
... the right AV valve into the right ventricle. • Right ventricle contracts and blood is pumped into the pulmonary arteries through the semi-lunar valve • In the lungs the blood loses its carbon dioxide and gains fresh oxygen before entering the pulmonary veins. ...
File
... Character of the pain • Dull, constricting, choking or 'heavy', and is usually described as squeezing, crushing, burning or aching but not sharp, stabbing, pricking or knife-like. • The sensation can be described as breathlessness. • Patients often emphasise that it is a discomfort rather than a pa ...
... Character of the pain • Dull, constricting, choking or 'heavy', and is usually described as squeezing, crushing, burning or aching but not sharp, stabbing, pricking or knife-like. • The sensation can be described as breathlessness. • Patients often emphasise that it is a discomfort rather than a pa ...
Cardiovascular - Cloudfront.net
... "drops off" oxygen and nutrients and "picks up" waste products that were produced after osmosis.(toxins and carbon dioxide). After the exchange, blood returns to your heart. ...
... "drops off" oxygen and nutrients and "picks up" waste products that were produced after osmosis.(toxins and carbon dioxide). After the exchange, blood returns to your heart. ...
New notes
... intertia of blood and the collapse of the atria during contraction minimizes backflow into these vessels. F. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart (p. 668; Figs. 18.9–18.10) 1. The right side of the heart pumps blood into the pulmonary circuit; the left side of the heart pumps blood into the systemic c ...
... intertia of blood and the collapse of the atria during contraction minimizes backflow into these vessels. F. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart (p. 668; Figs. 18.9–18.10) 1. The right side of the heart pumps blood into the pulmonary circuit; the left side of the heart pumps blood into the systemic c ...
sudden loss of consciousness (syncope)
... death of a young athlete during a sports competition is the most obvious and reported example, but death during noncompetitive physical activity, during emotional upsets, or even during sleep are being recognized with progressively greater frequency. These events are usually due to a disturbance of ...
... death of a young athlete during a sports competition is the most obvious and reported example, but death during noncompetitive physical activity, during emotional upsets, or even during sleep are being recognized with progressively greater frequency. These events are usually due to a disturbance of ...
click
... Sick sinus syndrome The sinus node is a special group of cells in the heart, also known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The sinus node sends out regular electrical impulses that travel through an ‘electrical pathway’ in the heart, causing the chambers of the heart to contract and pump the blood th ...
... Sick sinus syndrome The sinus node is a special group of cells in the heart, also known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The sinus node sends out regular electrical impulses that travel through an ‘electrical pathway’ in the heart, causing the chambers of the heart to contract and pump the blood th ...
cardiovascular system (cvs) - Pharos University in Alexandria
... pressure pump and a group of blood vessels which comprise arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins. All such components of the circulatory system contain liquid blood which is ever circulating throughout life. The Heart is made up of two halves right and left, each half is made up of an ...
... pressure pump and a group of blood vessels which comprise arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins. All such components of the circulatory system contain liquid blood which is ever circulating throughout life. The Heart is made up of two halves right and left, each half is made up of an ...
Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation: What is the
... Yaariv Khaykin Heart Rhythm Program, Southlake Regional Health Center, Newmarket, Ontario, Canada. ...
... Yaariv Khaykin Heart Rhythm Program, Southlake Regional Health Center, Newmarket, Ontario, Canada. ...
Respiratory System - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The heart is a fist-sized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body. Oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava). The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary artery to the lun ...
... The heart is a fist-sized, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body. Oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium of the heart (via veins called the inferior vena cava and the superior vena cava). The blood is then pumped into the right ventricle and then through the pulmonary artery to the lun ...
A and P lesson 7 - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... increase blood flow. The arteries dilate during exercise so that more blood is delivered to active areas, increasing their oxygen supply. ...
... increase blood flow. The arteries dilate during exercise so that more blood is delivered to active areas, increasing their oxygen supply. ...
coronary artery disease
... Plaque may grow slowly Plaque may be stable or unstable Stable plaque causes stable angina Unstable plaque may rupture and forms thrombosis and obstruction Unstable plaque causes ACS (UA, NSTEMI, ...
... Plaque may grow slowly Plaque may be stable or unstable Stable plaque causes stable angina Unstable plaque may rupture and forms thrombosis and obstruction Unstable plaque causes ACS (UA, NSTEMI, ...
Cardiac Physiology
... Carbon dioxide is taken away from this blood. This blood flows through pulmonary veins to the left atrium of the heart. This high-oxygen is pumped from the left ventricle through the aorta, a large artery. Therefore, the left side of the heart receives blood from the pulmonary circulation. It pumps ...
... Carbon dioxide is taken away from this blood. This blood flows through pulmonary veins to the left atrium of the heart. This high-oxygen is pumped from the left ventricle through the aorta, a large artery. Therefore, the left side of the heart receives blood from the pulmonary circulation. It pumps ...
February 2006
... helps blood vessels open up when there is a need for increased blood flow, and has been shown to reduce dangerous plaque buildup in the arteries. Antioxidants have been shown to help the body regenerate tissue and prevent aging. There is now available a product that can give you the dosage to make a ...
... helps blood vessels open up when there is a need for increased blood flow, and has been shown to reduce dangerous plaque buildup in the arteries. Antioxidants have been shown to help the body regenerate tissue and prevent aging. There is now available a product that can give you the dosage to make a ...
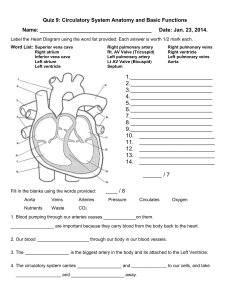
Quiz 9: Circulatory System Anatomy and Basic Functions
... _________________ are important because they carry blood from the body back to the heart. 2. Our blood __________________ through our body in our blood vessels. 3. The _______________ is the biggest artery in the body and its attached to the Left Ventricle. 4. The circulatory system carries ________ ...
... _________________ are important because they carry blood from the body back to the heart. 2. Our blood __________________ through our body in our blood vessels. 3. The _______________ is the biggest artery in the body and its attached to the Left Ventricle. 4. The circulatory system carries ________ ...
Cardiac surgery

Cardiovascular (heart) surgery is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. Frequently, it is done to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting), correct congenital heart disease, or treat valvular heart disease from various causes including endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease and atherosclerosis. It also includes heart transplantation.